What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2022-09-08 08:39:42 | Lazarus and the tale of three RATs (lien direct) |  By Jung soo An, Asheer Malhotra and Vitor Ventura.Cisco Talos has been tracking a new campaign operated by the Lazarus APT group, attributed to North Korea by the United States government. This campaign involved the exploitation of vulnerabilities in VMWare Horizon to gain an initial foothold into targeted organizations.Targeted organizations include energy providers from around the world, including those headquartered in the United States, Canada and Japan. The campaign is meant to infiltrate organizations around the world for establishing long term access and subsequently exfiltrating data of interest to the adversary's nation-state.Talos has discovered the use of two known families of malware in these intrusions - VSingle and YamaBot.Talos has also discovered the use of a recently disclosed implant we're calling "MagicRAT" in this campaign. IntroductionCisco Talos observed North Korean state-sponsored APT Lazarus Group conducting malicious activity between February and July 2022. Lazarus has been previously attributed to the North Korean government by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). The entry vectors involve the successful exploitation of vulnerabilities in VMWare products to establish initial footholds into enterprise networks, followed by the deployment of the group's custom malware implants, VSingle and YamaBot. In addition to these known malware families, we have also discovered the use of a previously unknown malware implant we're calling "MagicRAT."This campaign was previously partially disclosed by other security firms, but our findings reveal more details about the adversary's modus operandi. We have also observed an overlap of command and control (C2) and payload-hosting infrastructure between our findings and the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's (CISA) June advisory that detailed continued attempts from threat actors to compromise vulnerable VMWare Horizon servers.In this research, we illustrate Lazarus Group's post-exploitation tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) to establish a foothold, perform initial reconnaissance, deploy bespoke malware and move laterally across infected enterprises. We also provide details about the activities performed by the attackers when the VSingle backdoor is instrumented on the infected endpoints.In this campaign, Lazarus was primarily targeting energy companies in Canada, the U.S. and Japan. The main goal of these attacks was likely to establish long-term access into victim networks to conduct espionage operations in support of North Korean govern By Jung soo An, Asheer Malhotra and Vitor Ventura.Cisco Talos has been tracking a new campaign operated by the Lazarus APT group, attributed to North Korea by the United States government. This campaign involved the exploitation of vulnerabilities in VMWare Horizon to gain an initial foothold into targeted organizations.Targeted organizations include energy providers from around the world, including those headquartered in the United States, Canada and Japan. The campaign is meant to infiltrate organizations around the world for establishing long term access and subsequently exfiltrating data of interest to the adversary's nation-state.Talos has discovered the use of two known families of malware in these intrusions - VSingle and YamaBot.Talos has also discovered the use of a recently disclosed implant we're calling "MagicRAT" in this campaign. IntroductionCisco Talos observed North Korean state-sponsored APT Lazarus Group conducting malicious activity between February and July 2022. Lazarus has been previously attributed to the North Korean government by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). The entry vectors involve the successful exploitation of vulnerabilities in VMWare products to establish initial footholds into enterprise networks, followed by the deployment of the group's custom malware implants, VSingle and YamaBot. In addition to these known malware families, we have also discovered the use of a previously unknown malware implant we're calling "MagicRAT."This campaign was previously partially disclosed by other security firms, but our findings reveal more details about the adversary's modus operandi. We have also observed an overlap of command and control (C2) and payload-hosting infrastructure between our findings and the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's (CISA) June advisory that detailed continued attempts from threat actors to compromise vulnerable VMWare Horizon servers.In this research, we illustrate Lazarus Group's post-exploitation tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) to establish a foothold, perform initial reconnaissance, deploy bespoke malware and move laterally across infected enterprises. We also provide details about the activities performed by the attackers when the VSingle backdoor is instrumented on the infected endpoints.In this campaign, Lazarus was primarily targeting energy companies in Canada, the U.S. and Japan. The main goal of these attacks was likely to establish long-term access into victim networks to conduct espionage operations in support of North Korean govern |
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Medical | APT 38 | ||
| 2022-09-07 22:15:08 | CVE-2022-36082 (lien direct) | mangadex-downloader is a command-line tool to download manga from MangaDex. When using `file:` command and `` is a web URL location (http, https), mangadex-downloader between versions 1.3.0 and 1.7.2 will try to open and read a file in local disk for each line of website contents. Version 1.7.2 contains a patch for this issue. | Tool | ★★★★★ | ||
| 2022-09-07 21:15:08 | CVE-2022-36049 (lien direct) | Flux2 is a tool for keeping Kubernetes clusters in sync with sources of configuration, and Flux's helm-controller is a Kubernetes operator that allows one to declaratively manage Helm chart releases. Helm controller is tightly integrated with the Helm SDK. A vulnerability found in the Helm SDK that affects flux2 v0.0.17 until v0.32.0 and helm-controller v0.0.4 until v0.23.0 allows for specific data inputs to cause high memory consumption. In some platforms, this could cause the controller to panic and stop processing reconciliations. In a shared cluster multi-tenancy environment, a tenant could create a HelmRelease that makes the controller panic, denying all other tenants from their Helm releases being reconciled. Patches are available in flux2 v0.32.0 and helm-controller v0.23.0. | Tool Vulnerability | Uber | ||
| 2022-09-07 15:53:37 | Next-Gen Linux Malware Takes Over Devices With Unique Tool Set (lien direct) | The Shikitega malware takes over IoT and endpoint devices, exploits vulnerabilities, uses advanced encoding, abuses cloud services for C2, installs a cryptominer, and allows full remote control. | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-09-07 15:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: EvilProxy Defeats Second Factor, Ragnar Locker Ransomware Hits Critical Infrastructure, Montenegro Blames Russia for Massive Cyberattack, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Critical infrastructure, Crypto mining, Delayed execution, Phishing, Ransomware, Reverse proxy, Russia, and Steganography. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
EvilProxy Phishing-As-A-Service With MFA Bypass Emerged In Dark Web
(published: September 5, 2022)
Resecurity researchers analyzed EvilProxy, a phishing kit that uses reverse proxy and cookie injection methods to bypass two-factor authentication (2FA). EvilProxy uses extensive virtual machine checks and browser fingerprinting. If the victim passes the checks, Evilproxy acts as a proxy between the victim and the legitimate site that asks for credentials. EvilProxy is being sold as a service on the dark web. Since early May 2022, Evilproxy enables phishing attacks against customer accounts of major brands such as Apple, Facebook, GoDaddy, GitHub, Google, Dropbox, Instagram, Microsoft, Twitter, Yahoo, Yandex, and others.
Analyst Comment: EvilProxy is a dangerous automation tool that enables more phishing attacks. Additionally, EvilProxy targeting GitHub and npmjs accounts increases risks of follow-up supply-chain attacks. Anomali platform has historic EvilProxy network indicators that can help when investigating incidents affecting 2FA. With 2FA bypass, users need to be aware of phishing risks and pay even more attention to domains that ask for their credentials and 2FA codes.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Proxy - T1090 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195
Tags: EvilProxy, Phishing, Phishing-as-s-service, Reverse proxy, Cookie injection, 2FA, MFA, Supply chain
Ragnar Locker Ransomware Targeting the Energy Sector
(published: September 1, 2022)
Cybereason researchers investigated the Ragnar Locker ransomware that was involved in cyberattack on DESFA, a Greek pipeline company. On August 19, 2022, the Ragnar Locker group listed DESFA on its data leak site. The group has been active since 2019 and it is not the first time it targets critical infrastructure companies with the double-extortion scheme. Their Ragnar Locker ransomware shows the typical abilities of modern ransomware including system information and location collection, deleting shadow copies, identifying processes (antiviruses, backup solutions, IT remote management solutions, and virtual-based software), and encrypting the system with the exception list in mind.
Analyst Comment: Ragnar Locker appears to be an aggressive ransomware group that is not shy attacking critical infrastructure as far as they are not in the Commonwealth of Independent States (Russia and associated countries). Always be on high alert while reading emails, in particular those with attachments, URL redirection, false sense of urgency or poor grammar. Use anti-spam and antivirus protection, and avoid opening email from untrusted or unverified senders. Additionally, it is important to have a comprehensive and teste
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
EvilProxy Phishing-As-A-Service With MFA Bypass Emerged In Dark Web
(published: September 5, 2022)
Resecurity researchers analyzed EvilProxy, a phishing kit that uses reverse proxy and cookie injection methods to bypass two-factor authentication (2FA). EvilProxy uses extensive virtual machine checks and browser fingerprinting. If the victim passes the checks, Evilproxy acts as a proxy between the victim and the legitimate site that asks for credentials. EvilProxy is being sold as a service on the dark web. Since early May 2022, Evilproxy enables phishing attacks against customer accounts of major brands such as Apple, Facebook, GoDaddy, GitHub, Google, Dropbox, Instagram, Microsoft, Twitter, Yahoo, Yandex, and others.
Analyst Comment: EvilProxy is a dangerous automation tool that enables more phishing attacks. Additionally, EvilProxy targeting GitHub and npmjs accounts increases risks of follow-up supply-chain attacks. Anomali platform has historic EvilProxy network indicators that can help when investigating incidents affecting 2FA. With 2FA bypass, users need to be aware of phishing risks and pay even more attention to domains that ask for their credentials and 2FA codes.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Proxy - T1090 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195
Tags: EvilProxy, Phishing, Phishing-as-s-service, Reverse proxy, Cookie injection, 2FA, MFA, Supply chain
Ragnar Locker Ransomware Targeting the Energy Sector
(published: September 1, 2022)
Cybereason researchers investigated the Ragnar Locker ransomware that was involved in cyberattack on DESFA, a Greek pipeline company. On August 19, 2022, the Ragnar Locker group listed DESFA on its data leak site. The group has been active since 2019 and it is not the first time it targets critical infrastructure companies with the double-extortion scheme. Their Ragnar Locker ransomware shows the typical abilities of modern ransomware including system information and location collection, deleting shadow copies, identifying processes (antiviruses, backup solutions, IT remote management solutions, and virtual-based software), and encrypting the system with the exception list in mind.
Analyst Comment: Ragnar Locker appears to be an aggressive ransomware group that is not shy attacking critical infrastructure as far as they are not in the Commonwealth of Independent States (Russia and associated countries). Always be on high alert while reading emails, in particular those with attachments, URL redirection, false sense of urgency or poor grammar. Use anti-spam and antivirus protection, and avoid opening email from untrusted or unverified senders. Additionally, it is important to have a comprehensive and teste |
Ransomware Malware Tool Threat Patching Guideline | Yahoo | ||
| 2022-09-06 11:02:07 | Attacks on Sysmon Revisited - SysmonEnte (lien direct) | In this blogpost we demonstrate an attack on the integrity of Sysmon which generates a minimal amount of observable events making this attack difficult to detect in environments where no additional security products are installed.tl;dr:Suspend all threads of Sysmon.Create a limited handle to Sysmon and elevate it by duplication.Clone the pseudo handle of Sysmon to itself in order to bypass SACL as proposed by James Forshaw.Inject a hook manipulating all events (in particular ProcessAccess events on Sysmon).Resume all threads.We also release a POC called SysmonEnte.BackgroundAt Code White we are used to performing complex attacks against hardened and strictly monitored environments. A reasonable approach to stay under the radar of the blue team is to blend in with false positives by adapting normal process- and user behavior, carefully choosing host processes for injected tools and targeting specific user accounts.However, clients with whom we have been working for a while have reached a high level of maturity. Their security teams strictly follow all the hardening advice we give them and invest a lot of time in collecting and base-lining security related logs while constantly developing and adapting detection rules.We often see clients making heavy use of Sysmon, along with the Windows Event Logs and a traditional AV solution. For them, Sysmon is the root of trust for their security monitoring and its integrity must be ensured. However, an attacker who has successfully and covertly attacked, compromised the integrity of Sysmon and effectively breaks the security model of these clients.In order to undermine the aforementioned security-setup, we aimed at attacking Sysmon to tamper with events in a manner which is difficult to detect using Sysmon itself or the Windows Event Logs.Attacks on Sysmon and DetectionHaving done some Googling on how to blind Sysmon, we realized that all publicly documented ways are detectable via Sysmon itself or the Windows Event Logs (at least those we found) :Unloading Sysmon Driver - Detectable via Sysmon event id 255, Windows Security Event ID 4672.Attacks Via Custom Driver - Detectable via Sysmon event id 6, Driver loaded.Kill the Sysmon Service - Sysmon Event ID 10 (Process Access with at least PROCESS_TERMINATE flag set; The last event forwarded by Sysmon).Manipulating the Rules Registry Key - Event ID 16.Patching Sysmon in Memory - Event ID 10.While we were confident that we can kill Sysmon before throwing Event ID 5 (Process terminated) we thought that a host not sending any events would be suspicious and could be observed in a client's SIEM. Also, loading a signed, whitelisted and exploitable driver to attack from Kernel land was out of scope to maintain stability.Since all of these documented attack vectors are somehow detectable via Sysmon itself, the Windows Event Logs or can cause stability issues we needed a new attack vector with the following capabilities:Not detectable via Sysmon itselfNot detectable via Windows Event LogSysmon must stay aliveAttack from usermodeInjecting and manipulating the control flow of Sysmon seemed the most promising.Attack DescriptionSimilarly to SysmonQuiet or EvtMute, the idea is to inject code into Sysmon which redirects the | Tool | |||
| 2022-09-06 09:23:00 | Dispelling 5 Myths and Misconceptions Surrounding File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) (lien direct) | >File integrity monitoring (FIM) started back in 1997 when Gene Kim launched Tripwire and its “Change Audit” solution. Just a few years later, Change Audit became FIM; this rebranded tool worked with the 12 security controls identified in Visa's Cardholder Information Security Program (CISP). CISP became PCI DSS 1.0, and things continued to evolve after that. Which brings us to […]… Read More | Tool | |||
| 2022-09-05 15:00:00 | EvilProxy Phishing Toolkit Spotted on Dark Web Forums (lien direct) | The tool highlights the growth in attacks against online services and MFA authorization mechanisms | Tool | |||
| 2022-09-02 16:00:00 | US Police Deployed Obscure Smartphone Tracking Tool With No Warrants (lien direct) | It would allow police to search billions of mobile device-based records, including GPS data | Tool | |||
| 2022-09-01 16:50:00 | Security Operations are More Difficult Now More Than Ever. Buy Why? (lien direct) | According to recent research by ESG, 52% of respondents believe security operations are more difficult today than they were two years ago. Responses stated this was due to multiple factors, such as the increasingly dangerous threat landscape, a growing attack surface, the volume and complexity of security alerts, and public cloud proliferation. Today’s threats are more sophisticated than ever, making them more challenging to defend against. Security teams must constantly do more with less, protecting more data, endpoints, and applications. And, as the threat landscape evolves, so will they, but chances are they must do so with fewer resources. The growing list of challenges is never-ending. So what tops the list? An Ever-Growing Attack Surface Organizations are collecting and storing more data than ever, driven by more cloud-based applications and services. This new on-prem/off-prem environment has created more potential entry points for attackers. Additionally, many organizations lose track of their assets, failing to update policies and their security infrastructure, leaving them vulnerable to attacks that exploit known vulnerabilities. Another reason security teams face more challenges today is the increasing number of mobile devices and cloud apps used by employees. These devices and apps can provide a convenient way for employees to access company data, but they can also be a security risk if they are not adequately secured. The Evolving Threat Landscape As the attack surface grows, so does the number of potential threats. Security teams must now contend with a broader range of threats, including sophisticated malware, zero-day exploits, and ransomware. Additionally, attackers are becoming more brazen and are targeting high-profile organizations with well-funded security operations. In addition, the rise of social media has created new opportunities for hackers to launch cyber attacks. Social media platforms can spread malware or gather information about people’s online habits, used to launch targeted attacks and infiltrate enterprise organizations. Increasing Compliance Requirements Organizations must comply with an ever-growing number of regulations, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), that require security teams to put in place additional controls and processes, which can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, compliance failures can result in heavy fines and strain an already tight budget. Limited Resources According to (ISC)²'s 2021 Cyber Workforce Report, the global cybersecurity workforce needs to grow 65 percent to defend organizations’ critical assets effectively. While the number of professionals required to fill the gap has decreased, the number of qualified cyber professionals will fall even further due to the growing demand for highly skilled individuals. Complex Tech Stack Enterprises frequently deploy new security tools and services to address changing needs and increased threats. As previously mentioned, a typical enterprise SOC may use a combination of twenty or more technologies, making it difficult to customize each solution for its environment. The interoperability issues caused by the possibility of using multiple vendors make it very challenging to get a complete picture of your overall security environment. The Need to Adapt Despite these challenges, security teams must find ways to adapt to protect their organizations effectively against ever-evolving threats. So what c | Malware Tool Threat Guideline | |||
| 2022-09-01 13:20:32 | CrowdStrike Introduces Sandbox Scryer: A Free Threat-Hunting Tool for Generating MITRE ATT&CK and Navigator Data (lien direct) | Sandbox Scryer is an open-source tool for producing threat hunting and intelligence data from public sandbox detonation output The tool leverages the MITRE ATT&CK Framework to organize and prioritize findings, assisting in assembling indicators of compromise (IOCs), understanding attack movement and hunting threats By allowing researchers to send thousands of samples to a sandbox for […] | Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2022-09-01 13:15:08 | CVE-2022-36055 (lien direct) | Helm is a tool for managing Charts. Charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources. Fuzz testing, provided by the CNCF, identified input to functions in the _strvals_ package that can cause an out of memory panic. The _strvals_ package contains a parser that turns strings in to Go structures. The _strvals_ package converts these strings into structures Go can work with. Some string inputs can cause array data structures to be created causing an out of memory panic. Applications that use the _strvals_ package in the Helm SDK to parse user supplied input can suffer a Denial of Service when that input causes a panic that cannot be recovered from. The Helm Client will panic with input to `--set`, `--set-string`, and other value setting flags that causes an out of memory panic. Helm is not a long running service so the panic will not affect future uses of the Helm client. This issue has been resolved in 3.9.4. SDK users can validate strings supplied by users won't create large arrays causing significant memory usage before passing them to the _strvals_ functions. | Tool | Uber | ||
| 2022-08-31 23:26:41 | RAT Tool Disguised as Solution File (*.sln) Being Distributed on Github (lien direct) | The ASEC analysis team has recently discovered the distribution of a RAT Tool disguised as a solution file (*.sln) on GitHub. As shown in Figure 1, the malware distributor is sharing a source code on GitHub titled “Jpg Png Exploit Downloader Fud Cryter Malware Builder Cve 2022”. The file composition looks normal, but the solution file (*.sln) is actually a RAT tool. It is through methods like this that the malware distributor lures users to run the RAT tool by... | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-08-31 20:15:08 | CVE-2022-36048 (lien direct) | Zulip is an open-source team collaboration tool with topic-based threading that combines email and chat. When displaying messages with embedded remote images, Zulip normally loads the image preview via a go-camo proxy server. However, an attacker who can send messages could include a crafted URL that tricks the server into embedding a remote image reference directly. This could allow the attacker to infer the viewer’s IP address and browser fingerprinting information. This vulnerability is fixed in Zulip Server 5.6. Zulip organizations with image and link previews [disabled](https://zulip.com/help/allow-image-link-previews) are not affected. | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-08-31 15:15:08 | CVE-2022-36035 (lien direct) | Flux is a tool for keeping Kubernetes clusters in sync with sources of configuration (like Git repositories), and automating updates to configuration when there is new code to deploy. Flux CLI allows users to deploy Flux components into a Kubernetes cluster via command-line. The vulnerability allows other applications to replace the Flux deployment information with arbitrary content which is deployed into the target Kubernetes cluster instead. The vulnerability is due to the improper handling of user-supplied input, which results in a path traversal that can be controlled by the attacker. Users sharing the same shell between other applications and the Flux CLI commands could be affected by this vulnerability. In some scenarios no errors may be presented, which may cause end users not to realize that something is amiss. A safe workaround is to execute Flux CLI in ephemeral and isolated shell environments, which can ensure no persistent values exist from previous processes. However, upgrading to the latest version of the CLI is still the recommended mitigation strategy. | Tool Vulnerability | Uber | ||
| 2022-08-31 10:00:00 | Examiner les journaux unifiés macOS Reviewing macOS Unified Logs (lien direct) |
En commençant par MacOS 10.12 (Sierra), Apple a introduit un changement de clé dans la façon dont la journalisation a été effectuée sur leurs systèmes.Ce nouveau système de journalisation a remplacé les journaux UNIX communs par des journaux unifiés macOS.Ces journaux peuvent fournir aux enquêteurs de la crisence un artefact précieux pour aider à étudier les systèmes MacOS ou d'autres appareils Apple.
Dans cet article de blog, nous couvrirons un aperçu des journaux unifiés et des défis présentés pour les utiliser lors d'une enquête.Avec ce billet de blog, nous avons également publié un outil intitulé « macOS-UnifiedLogs " pour aider à surmonter certains des défis dans l'analyse des données de journal, et à
Beginning with macOS 10.12 (Sierra), Apple introduced a key change to how logging was done on their systems. This new logging system replaced common Unix logs with macOS Unified Logs. These logs can provide forensic investigators a valuable artifact to aid in investigating macOS systems or other Apple devices. In this blog post, we will cover an overview of the Unified Logs and the challenges presented in using them during an investigation. Along with this blog post, we also released a tool called “macos-unifiedlogs" to help overcome some of the challenges in parsing log data, and to |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-08-30 22:21:30 | New ODGen Tool Unearths 180 Zero-Days in Node.js Libraries (lien direct) | New graph-based tool offers a better alternative to current approaches for finding vulnerabilities in JavaScript code, they note. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-30 15:01:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: First Real-Life Video-Spoofing Attack, MagicWeb Backdoors via Non-Standard Key Identifier, LockBit Ransomware Blames Victim for DDoSing Back, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Authentication, DDoS, Fingerprinting, Iran, North Korea, Ransomware, and Russia. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
LastPass Hackers Stole Source Code
(published: August 26, 2022)
In August 2022, an unidentified threat actor gained access to portions of the password management giant LastPass development environment. LastPass informed that it happened through a single compromised developer account and the attacker took portions of source code and some proprietary LastPass technical information. The company claims that this incident did not affect customer data or encrypted password vaults.
Analyst Comment: This incident doesn’t seem to have an immediate impact on LastPass users. Still, organizations relying on LastPass should raise the concern in their risk assessment since “white-box hacking” (when source code of the attacking system is known) is easier for threat actors. Organizations providing public-facing software should take maximum measures to block threat actors from their development environment and establish robust and transparent security protocols and practices with all third parties involved in their code development.
Tags: LastPass, Password manager, Data breach, Source code
Mercury Leveraging Log4j 2 Vulnerabilities in Unpatched Systems to Target Israeli
(published: August 25, 2022)
Starting in July 2022, a new campaign by Iran-sponsored group Static Kitten (Mercury, MuddyWater) was detected targeting Israeli organizations. Microsoft researchers detected that this campaign was leveraging exploitation of Log4j 2 vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-45046 and CVE-2021-44228) in SysAid applications (IT management tools). For persistence Static Kitten was dropping webshells, creating local administrator accounts, stealing credentials, and adding their tools in the startup folders and autostart extensibility point (ASEP) registry keys. Overall the group was heavily using various open-source and built-in operating system tools: eHorus remote management software, Ligolo reverse tunneling tool, Mimikatz credential theft tool, PowerShell programs, RemCom remote service, Venom proxy tool, and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
Analyst Comment: Network defenders should monitor for alerts related to web shell threats, suspicious RDP sessions, ASEP registry anomaly, and suspicious account creation. Similarly, SysAid users can monitor for webshells and abnormal processes related to SysAisServer instance. Even though Static Kitten was observed leveraging the Log4Shell vulnerabilities in the past (targeting VMware apps), most of their attacks still start with spearphishing, often from a compromised email account.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 |
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
LastPass Hackers Stole Source Code
(published: August 26, 2022)
In August 2022, an unidentified threat actor gained access to portions of the password management giant LastPass development environment. LastPass informed that it happened through a single compromised developer account and the attacker took portions of source code and some proprietary LastPass technical information. The company claims that this incident did not affect customer data or encrypted password vaults.
Analyst Comment: This incident doesn’t seem to have an immediate impact on LastPass users. Still, organizations relying on LastPass should raise the concern in their risk assessment since “white-box hacking” (when source code of the attacking system is known) is easier for threat actors. Organizations providing public-facing software should take maximum measures to block threat actors from their development environment and establish robust and transparent security protocols and practices with all third parties involved in their code development.
Tags: LastPass, Password manager, Data breach, Source code
Mercury Leveraging Log4j 2 Vulnerabilities in Unpatched Systems to Target Israeli
(published: August 25, 2022)
Starting in July 2022, a new campaign by Iran-sponsored group Static Kitten (Mercury, MuddyWater) was detected targeting Israeli organizations. Microsoft researchers detected that this campaign was leveraging exploitation of Log4j 2 vulnerabilities (CVE-2021-45046 and CVE-2021-44228) in SysAid applications (IT management tools). For persistence Static Kitten was dropping webshells, creating local administrator accounts, stealing credentials, and adding their tools in the startup folders and autostart extensibility point (ASEP) registry keys. Overall the group was heavily using various open-source and built-in operating system tools: eHorus remote management software, Ligolo reverse tunneling tool, Mimikatz credential theft tool, PowerShell programs, RemCom remote service, Venom proxy tool, and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI).
Analyst Comment: Network defenders should monitor for alerts related to web shell threats, suspicious RDP sessions, ASEP registry anomaly, and suspicious account creation. Similarly, SysAid users can monitor for webshells and abnormal processes related to SysAisServer instance. Even though Static Kitten was observed leveraging the Log4Shell vulnerabilities in the past (targeting VMware apps), most of their attacks still start with spearphishing, often from a compromised email account.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | |
Ransomware Hack Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline Cloud | APT 37 APT 29 LastPass | ||
| 2022-08-30 08:00:09 | ModernLoader delivers multiple stealers, cryptominers and RATs (lien direct) |  By Vanja SvajcerCisco Talos recently observed three separate, but related, campaigns between March and June 2022 delivering a variety of threats, including the ModernLoader bot, RedLine information-stealer and cryptocurrency-mining malware to victims. The actors use PowerShell, .NET assemblies, and HTA and VBS files to spread across a targeted network, eventually dropping other pieces of malware, such as the SystemBC trojan and DCRAT, to enable various stages of their operations. The attackers' use of a variety of off-the-shelf tools makes it difficult to attribute this activity to a specific adversary.The final payload appears to be ModernLoader, which acts as a remote access trojan (RAT) by collecting system information and deploying various modules. In the earlier campaigns from March, we also observed the attackers delivering the cryptocurrency mining malware XMRig. The March campaigns appeared to be targeting Eastern European users, as the constructor utility we analyzed had predefined script templates written in Bulgarian, Polish, Hungarian and Russian.The actors are attempting to compromise vulnerable web applications to serve malware and deliver threats via files masquerading as fake Amazon gift cards. Technical detailsInitial findingsIn June 2022, Cisco Talos identified an unusual command line execution in our telemetry. The decoded base64 command is below: By Vanja SvajcerCisco Talos recently observed three separate, but related, campaigns between March and June 2022 delivering a variety of threats, including the ModernLoader bot, RedLine information-stealer and cryptocurrency-mining malware to victims. The actors use PowerShell, .NET assemblies, and HTA and VBS files to spread across a targeted network, eventually dropping other pieces of malware, such as the SystemBC trojan and DCRAT, to enable various stages of their operations. The attackers' use of a variety of off-the-shelf tools makes it difficult to attribute this activity to a specific adversary.The final payload appears to be ModernLoader, which acts as a remote access trojan (RAT) by collecting system information and deploying various modules. In the earlier campaigns from March, we also observed the attackers delivering the cryptocurrency mining malware XMRig. The March campaigns appeared to be targeting Eastern European users, as the constructor utility we analyzed had predefined script templates written in Bulgarian, Polish, Hungarian and Russian.The actors are attempting to compromise vulnerable web applications to serve malware and deliver threats via files masquerading as fake Amazon gift cards. Technical detailsInitial findingsIn June 2022, Cisco Talos identified an unusual command line execution in our telemetry. The decoded base64 command is below: Initial finding: A command executed on the system.The 31.41.244[.]231 IP is a Russian IP and hosts several other URLs with similar naming conventions. Autostart commandFollowing the discovery of the initial command, we identified two other command lines. They are a result of an autorun registered executable and the execution of a scheduled task. Initial finding: A command executed on the system.The 31.41.244[.]231 IP is a Russian IP and hosts several other URLs with similar naming conventions. Autostart commandFollowing the discovery of the initial command, we identified two other command lines. They are a result of an autorun registered executable and the execution of a scheduled task. |
Malware Tool Threat | Yahoo | ||
| 2022-08-29 15:15:09 | CVE-2022-0485 (lien direct) | A flaw was found in the copying tool `nbdcopy` of libnbd. When performing multi-threaded copies using asynchronous nbd calls, nbdcopy was blindly treating the completion of an asynchronous command as successful, rather than checking the *error parameter. This could result in the silent creation of a corrupted destination image. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-28 11:24:43 | Dealing With False Positives when Scanning Memory Dumps for Cobalt Strike Beacons, (Sun, Aug 28th) (lien direct) | I updated my Cobalt Strike beacon analysis tool 1768.py to deal with false positives in Windows system&#;x26;#;39;s memory dumps. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-26 15:45:25 | \'Sliver\' Emerges as Cobalt Strike Alternative for Malicious C2 (lien direct) | Microsoft and others say they have observed nation-state actors, ransomware purveyors, and assorted cybercriminals pivoting to an open source attack-emulation tool in recent campaigns. | Ransomware Tool | |||
| 2022-08-25 16:09:19 | ReasonLabs Launches Free Online Security Tool to Power Secure Web Experience for Millions of Global Users (lien direct) | Online Security autonomously blocks malicious URLs, extensions, ad trackers, and pop-ups 24/7, protecting consumers from complex and rapidly evolving cyber threats online. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-25 10:16:06 | Microsoft Details New Post-Compromise Malware Used by Russian Cyberspies (lien direct) | Microsoft this week published technical details on 'MagicWeb', a new post-exploitation tool used by Russia-linked cyberespionage group APT29. | Malware Tool | APT 29 | ||
| 2022-08-24 19:29:23 | Efficient \'MagicWeb\' Malware Subverts AD FS Authentication, Microsoft Warns (lien direct) | The Russia-backed Nobelium APT has pioneered a post-exploitation tool allowing attackers to authenticate as any user. | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-08-24 12:08:43 | Racing against the clock -- hitting a tiny kernel race window (lien direct) | TL;DR: How to make a tiny kernel race window really large even on kernels without CONFIG_PREEMPT:use a cache miss to widen the race window a little bitmake a timerfd expire in that window (which will run in an interrupt handler - in other words, in hardirq context)make sure that the wakeup triggered by the timerfd has to churn through 50000 waitqueue items created by epoll Racing one thread against a timer also avoids accumulating timing variations from two threads in each race attempt - hence the title. On the other hand, it also means you now have to deal with how hardware timers actually work, which introduces its own flavors of weird timing variations.Introduction I recently discovered a race condition (https://crbug.com/project-zero/2247) in the Linux kernel. (While trying to explain to someone how the fix for CVE-2021-0920 worked - I was explaining why the Unix GC is now safe, and then got confused because I couldn't actually figure out why it's safe after that fix, eventually realizing that it actually isn't safe.) It's a fairly narrow race window, so I was wondering whether it could be hit with a small number of attempts - especially on kernels that aren't built with CONFIG_PREEMPT, which would make it possible to preempt a thread with another thread, as I described at LSSEU2019. This is a writeup of how I managed to hit the race on a normal Linux desktop kernel, with a hit rate somewhere around 30% if the proof of concept has been tuned for the specific machine. I didn't do a full exploit though, I stopped at getting evidence of use-after-free (UAF) accesses (with the help of a very large file descriptor table and userfaultfd, which might not be available to normal users depending on system configuration) because that's the part I was curious about. This also demonstrates that even very small race conditions can still be exploitable if someone sinks enough time into writing an exploit, so be careful if you dismiss very small race windows as unexploitable or don't treat such issues as security bugs. The UAF reproducer is in our bugtracker.The bug In the UNIX domain socket garbage collection code (which is needed to deal with reference loops formed by UNIX domain sockets that use SCM_RIGHTS | Tool Guideline | APT 25 | ★★ | |
| 2022-08-24 12:02:07 | CVE-2021-1782, an iOS in-the-wild vulnerability in vouchers (lien direct) | Posted by Ian Beer, Google Project Zero This blog post is my analysis of a vulnerability exploited in the wild and patched in early 2021. Like the writeup published last week looking at an ASN.1 parser bug, this blog post is based on the notes I took as I was analyzing the patch and trying to understand the XNU vouchers subsystem. I hope that this writeup serves as the missing documentation for how some of the internals of the voucher subsystem works and its quirks which lead to this vulnerability. CVE-2021-1782 was fixed in iOS 14.4, as noted by @s1guza on twitter: 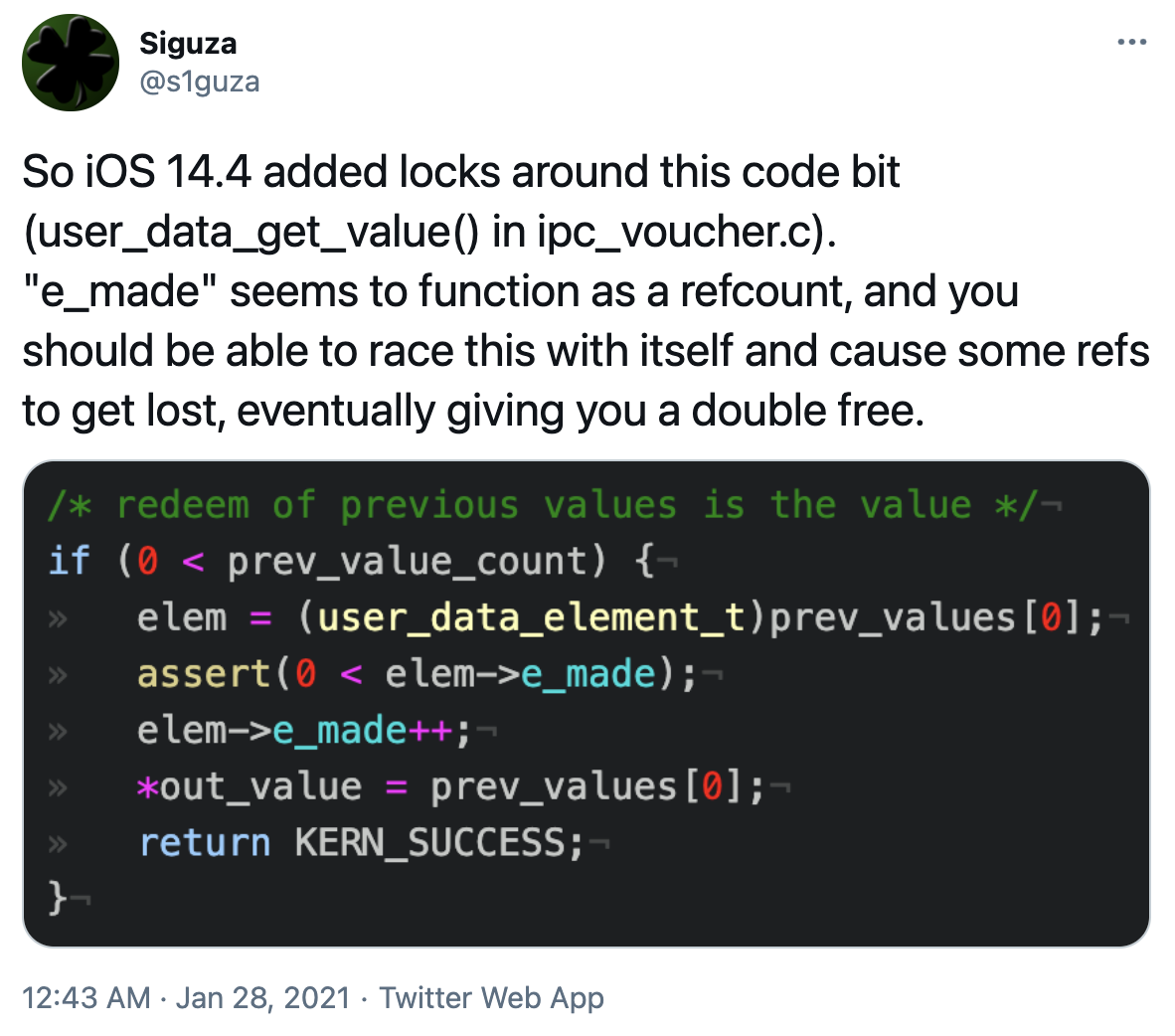 This vulnerability was fixed on January 26th 2021, and Apple updated the iOS 14.4 release notes on May 28th 2021 to indicate that the issue may have been actively exploited: This vulnerability was fixed on January 26th 2021, and Apple updated the iOS 14.4 release notes on May 28th 2021 to indicate that the issue may have been actively exploited: |
Hack Tool Vulnerability Guideline | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-08-24 04:26:37 | BitRAT and XMRig CoinMiner Being Distributed via Windows License Verification Tool (lien direct) | The ASEC analysis team has recently discovered the distribution of BitRAT and XMRig CoinMiner disguised as a Windows license verification tool. As introduced in previous posts, BitRAT has a history of being distributed on webhards as MS Windows license verification tools and MS Office installation programs. It is likely that the case covered by this post is being done by the same attacker. One thing to note is that a BitRAT remote control tool is installed in the environment without... | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-23 18:02:04 | Pirated 3DMark benchmark tool delivering info-stealer malware (lien direct) | Cybersecurity researchers have discovered multiple ongoing malware distribution campaigns that target internet users who seek to download copies of pirated software. [...] | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-08-23 17:35:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Emissary Panda Adds New Operation Systems to Its Supply-Chain Attacks, Russia-Sponsored Seaborgium Spies on NATO Countries, TA558 Switches from Macros to Container Files, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: China, Cyberespionage, DDoS, Russia, Spearphishing, Supply chain, Taiwan, and Ukraine. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Reservations Requested: TA558 Targets Hospitality and Travel
(published: August 18, 2022)
Since 2018, financially-motivated threat group TA558 has targeted hospitality and travel with reservation-themed, business-relevant phishing emails. The group concentrates on targeting Latin America using lures written in Portuguese and Spanish, and sometimes uses English and wider targeting (North America, Western Europe). TA558 was seen leveraging at least 15 different malware payloads, most often AsyncRAT, Loda RAT, Revenge RAT, and Vjw0rm. In 2022, Proofpoint researchers detected that TA558 increased its activity and moved from using malicious macros to URLs and container files (ISO, RAR).
Analyst Comment: Microsoft’s preparations to disable macros by default in Office products caused multiple threat groups including TA558 to adopt new filetypes to deliver payloads. It is crucial for personnel working with invoices and other external attachments to use updated, secured systems and be trained on phishing threats. Anomali Match can be used to quickly search your infrastructure for known TA558 IOCs.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105
Tags: TA558, AsyncRAT, Loda, RAT, Vjw0rm, BluStealer, Revenge RAT, XtremeRAT, Hospitality, Travel, Phishing, ISO, RAR, PowerShell, CVE-2017-11882, CVE-2017-8570
Estonia Subjected to 'Extensive' Cyberattacks after Moving Soviet Monuments
(published: August 18, 2022)
On August 17, 2022, Russian hacktivist group KillNet launched distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks targeting Estonia. The Estonian government confirmed receiving the “most extensive” DDoS attacks in 15 years, but stressed that all services are back online after just some minor interruptions. Small and medium-sized DDoS attacks targeted 16 state and private organizations in the country, with seven of them experiencing downtime as a result. Specifically, the Estonian Tax and Customs Board website was unavailable for about 70 minutes.
Analyst Comment: Russian cyber activity follows political tensions, this time coinciding with the removal of a Red Army memorial. Estonia seemingly easily fended off this Russian DDoS attack, but the country is one of the top in cyber preparedness, and Russia limited it’s strike to using hacktivist groups that give plausible deniability when attributing the cyber attack on a NATO country. Organizations that rely on stable work of their I
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Reservations Requested: TA558 Targets Hospitality and Travel
(published: August 18, 2022)
Since 2018, financially-motivated threat group TA558 has targeted hospitality and travel with reservation-themed, business-relevant phishing emails. The group concentrates on targeting Latin America using lures written in Portuguese and Spanish, and sometimes uses English and wider targeting (North America, Western Europe). TA558 was seen leveraging at least 15 different malware payloads, most often AsyncRAT, Loda RAT, Revenge RAT, and Vjw0rm. In 2022, Proofpoint researchers detected that TA558 increased its activity and moved from using malicious macros to URLs and container files (ISO, RAR).
Analyst Comment: Microsoft’s preparations to disable macros by default in Office products caused multiple threat groups including TA558 to adopt new filetypes to deliver payloads. It is crucial for personnel working with invoices and other external attachments to use updated, secured systems and be trained on phishing threats. Anomali Match can be used to quickly search your infrastructure for known TA558 IOCs.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105
Tags: TA558, AsyncRAT, Loda, RAT, Vjw0rm, BluStealer, Revenge RAT, XtremeRAT, Hospitality, Travel, Phishing, ISO, RAR, PowerShell, CVE-2017-11882, CVE-2017-8570
Estonia Subjected to 'Extensive' Cyberattacks after Moving Soviet Monuments
(published: August 18, 2022)
On August 17, 2022, Russian hacktivist group KillNet launched distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks targeting Estonia. The Estonian government confirmed receiving the “most extensive” DDoS attacks in 15 years, but stressed that all services are back online after just some minor interruptions. Small and medium-sized DDoS attacks targeted 16 state and private organizations in the country, with seven of them experiencing downtime as a result. Specifically, the Estonian Tax and Customs Board website was unavailable for about 70 minutes.
Analyst Comment: Russian cyber activity follows political tensions, this time coinciding with the removal of a Red Army memorial. Estonia seemingly easily fended off this Russian DDoS attack, but the country is one of the top in cyber preparedness, and Russia limited it’s strike to using hacktivist groups that give plausible deniability when attributing the cyber attack on a NATO country. Organizations that rely on stable work of their I |
Ransomware Malware Tool Threat | APT 27 | ||
| 2022-08-23 11:57:26 | Charming Kitten APT Wields New Scraper to Steal Email Inboxes (lien direct) | Google researchers say the nation-state hacking team is now employing a data-theft tool that targets Gmail, Yahoo!, and Microsoft Outlook accounts using previously acquired credentials. | Tool | Yahoo APT 35 | ||
| 2022-08-23 11:44:00 | True crime shows might be the biggest educational tool for cybercrime awareness (lien direct) | A survey of U.S. and UK residents conducted by Censuswide and commissioned by identity verification vendor Onfido released today said that popular culture – specifically, true-crime shows and movies – are having an outsized effect on the public's understanding of cybercrime.Two out of three survey respondents said that shows like Inventing Anna and documentaries like The Tinder Swindler have changed the way they view fraud in the modern day. Almost 60% of respondents also said that they're cautious about trusting other people online due to cultural depictions of fraud.Onfido CEO Mike Tuchen said in a press release that such programs have had a major impact on the public's view of fraud and cybercrime. “True crime and fraud-related entertainment stories have become widespread and popular. This is having a very real impact on how society views and perceives the prevalence and severity of fraud as a crime,” he said. “As a result, consumers are growing increasingly wary of online interactions, amid concerns over fraudster tactics and the security of their identities.”To read this article in full, please click here | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-23 11:00:00 | Google researchers expose Iranian hackers\' tool to steal emails from Gmail, Yahoo and Outlook (lien direct) | Security researchers linked the program to the so-called Charming Kitty Iranian hacker group known to carry out intelligence operations. | Tool | Yahoo Yahoo | ||
| 2022-08-23 10:00:00 | Establishing a mobile device vulnerability management program (lien direct) | The introduction of mobile devices has rapidly changed the world as we know it, as these small gadgets that are intended to fit into the palm of our hands rapidly gained dominance over our day-to-day activities. Thanks to these portable devices, we now have access to an abundance of information available to us on demand with minimal effort.
Mobile devices have become so powerful that your cellphone contains significant data about you as individual through your data storage, communication activities (social media, e-mail, text messages, audio calls), built-in health and fitness trackers, having access to financial accounts through NFC (near-field-communication) technology payment cards, GPS functionality. All this information that was once considered “personal data” is now contained on these portable devices that are more susceptible to physical theft, man-in-the-middle attacks when connected to unsecure wireless and cellular networks, as well as potential exploitation of vulnerabilities that are typically present on a mobile device operating system.
The periodic release of security updates for mobile devices is an attestation to the fact that the operating system software that runs on your mobile devices are never 100% secure. Data that is stored and processed by mobile devices are at high risk of potential breaches, and therefore business organizations are not factored out of this threat.
Businesses across a wide array of industry verticals are shifting their technological landscape to adapt to a portable ecosystem, by introducing mobile devices. While the presence of mobile devices in a business environment grows, these devices are not being effectively secured through appropriate patch update cycles, and that unauthorized users may also be accessing these company-owned devices.
These mobile devices typically have access to substantial amounts of information and may also literally serve as the “keys to the kingdom” through serving as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) tokens to business information systems. An organization may have invested countless hours and resources to secure information technology infrastructure, but all that effort is now simply undermined by the fact that data is longer static within the confines of your organizations firewall perimeter.
Your data is now always on the move with your employees’ mobile devices. As a result, the need for an effective mobile device vulnerability management program is more imperative than ever, in order to consistently identify, track and remediate vulnerabilities, as a way to prevent the exploitation of vulnerabilities that may allow malicious users to gain access to your resources.
 Mobile devices are not traditionally given a first thought when establishing a formal vulnerability management program. The devices that are typically given first thought include but are not limited to workstations, servers, networking appliances, web applications.
However, new threatening vulnerabilities are discovered and published daily in various vulnerability databases, and many of these discoveries specifically impact mobile devices. Mobile devices must not be overlooked when establishing your vulnerability program. A vulnerability scan can typically discover hundreds of vulnerabilities on your mobile devices, but all it takes to hand over the keys to your kingdom to a malicious actor is the exploitation of one of those vulnerabilities.
Organizations invest a significant amount of resources to secure their IT infrastructure, however these mobile devices now serve as an entry-point directly into the environment, providing access to potentially petabytes of your data. Despite these security concerns in mind, mobile device vulnerability management unfortunately remains an afterthought.
Without a formal vulnerability assessment for mobile devices, undetected vulnerabilities on these
Mobile devices are not traditionally given a first thought when establishing a formal vulnerability management program. The devices that are typically given first thought include but are not limited to workstations, servers, networking appliances, web applications.
However, new threatening vulnerabilities are discovered and published daily in various vulnerability databases, and many of these discoveries specifically impact mobile devices. Mobile devices must not be overlooked when establishing your vulnerability program. A vulnerability scan can typically discover hundreds of vulnerabilities on your mobile devices, but all it takes to hand over the keys to your kingdom to a malicious actor is the exploitation of one of those vulnerabilities.
Organizations invest a significant amount of resources to secure their IT infrastructure, however these mobile devices now serve as an entry-point directly into the environment, providing access to potentially petabytes of your data. Despite these security concerns in mind, mobile device vulnerability management unfortunately remains an afterthought.
Without a formal vulnerability assessment for mobile devices, undetected vulnerabilities on these |
Tool Vulnerability Guideline | |||
| 2022-08-23 07:50:00 | Google Uncovers Tool Used by Iranian Hackers to Steal Data from Email Accounts (lien direct) | The Iranian government-backed actor known as Charming Kitten has added a new tool to its malware arsenal that allows it to retrieve user data from Gmail, Yahoo!, and Microsoft Outlook accounts. Dubbed HYPERSCRAPE by Google Threat Analysis Group (TAG), the actively in-development malicious software is said to have been used against less than two dozen accounts in Iran, with the oldest known | Malware Tool Threat Conference | Yahoo APT 35 | ||
| 2022-08-22 20:30:34 | Metasploit Creator Renames His Startup and IT Discovery Tool Rumble to \'runZero\' (lien direct) | HD Moore's company has rebranded its IT, IoT, and OT asset discovery tool as the platform rapidly evolves. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-22 14:00:00 | Threat Actor Deploys Raven Storm Tool to Perform DDoS Attacks (lien direct) | The malware is reportedly capable of server takedown, Wi-Fi attacks and application layer attacks | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-08-22 13:30:00 | How Qualys Reduces Risk and Enables Tool Consolidation (lien direct) | Sumedh Thakar, CEO of Qualys, explains how moving to a cloud-based asset management platform can simplify their strategies and improve overall security. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-20 13:00:00 | Janet Jackson\'s \'Rhythm Nation\' Can Crash Old Hard Drives (lien direct) | Plus: The Twilio hack snags a reporter, a new tool to check for spyware, and the Canadian weed pipeline gets hit by a cyberattack. | Hack Tool | |||
| 2022-08-18 18:34:08 | China\'s APT41 Embraces Baffling Approach for Dropping Cobalt Strike Payload (lien direct) | The state-sponsored threat actor has switched up its tactics, also adding an automated SQL-injection tool to its bag of tricks for initial access. | Tool Threat | APT 41 | ||
| 2022-08-18 11:45:45 | USB “Rubber Ducky” Attack Tool (lien direct) | The USB Rubber Ducky is getting better and better. Already, previous versions of the Rubber Ducky could carry out attacks like creating a fake Windows pop-up box to harvest a user’s login credentials or causing Chrome to send all saved passwords to an attacker’s webserver. But these attacks had to be carefully crafted for specific operating systems and software versions and lacked the flexibility to work across platforms. The newest Rubber Ducky aims to overcome these limitations. It ships with a major upgrade to the DuckyScript programming language, which is used to create the commands that the Rubber Ducky will enter into a target machine. While previous versions were mostly limited to writing keystroke sequences, DuckyScript 3.0 is a feature-rich language, letting users write functions, store variables, and use logic flow controls (i.e., if this… then that)... | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-17 22:15:08 | CVE-2022-2869 (lien direct) | libtiff's tiffcrop tool has a uint32_t underflow which leads to out of bounds read and write in the extractContigSamples8bits routine. An attacker who supplies a crafted file to tiffcrop could trigger this flaw, most likely by tricking a user into opening the crafted file with tiffcrop. Triggering this flaw could cause a crash or potentially further exploitation. | Tool Guideline | |||
| 2022-08-17 10:00:00 | A pragmatic approach to risk management & resilience (lien direct) | Cybersecurity starts with the ability to recognize your cyber risk. We will explore several topics related to taking a practical approach to managing risk and achieving cyber resilience. This is a blog series with collective thoughts from Bindu Sundaresan, Director AT&T Cybersecurity, and Nick Simmons, AVP, Cybersecurity. Cybercrime has become increasingly frequent, complex, and costly, posing a risk to all businesses regardless of size. How do you plan to respond when falling victim to a breach? Would you know who to call, how to react, or what to tell your employees, customers, and media? Could your organization absorb the potential financial and reputational impact of a lawsuit? The answer cannot be, "we store everything in the cloud, so we are good." Who owns the risk? Could your brand's image survive? What is acceptable, and how do you know your current plan will suffice? What more could your company do to understand better and manage the risk? These questions are all top of mind and need to be addressed from an overall business perspective. This blog summarizes the fundamental steps and offers suggestions to understand, manage, and respond to risk. Beyond technology, focus on risk and resilience It can be easy to deploy security technology and think you've mitigated risk to your business. Unfortunately, technology investment is no guarantee of protection against the latest threats. It is critical to take a risk-based approach to security, meaning leaders must identify and focus on specific elements of cyber risk to decrease enterprise risk. Specifically, the many components of cyber risk must be understood and prioritized for enterprise cybersecurity efforts. Organizations are increasingly aiming to shift from cybersecurity to cyber resilience, and the following recommendations can help forge this path: Understand the threats Measure the potential financial impact of cyber exposures compared to the company's risk appetite level; and Proactively manage cyber risks with clear action plans based on their capabilities and capacities to protect against cybercrime Risk-based approach Cyber resiliency requires a risk-based approach, accomplishing two critical things at once. First, it designates risk reduction as the primary goal, enabling the organization to prioritize investment, including implementation-related problem solving based squarely on a cyber program's effectiveness at reducing risk. Second, the program distills top management's risk-reduction targets into pragmatic implementation programs with precise alignment from senior executives to the front line. Following the risk-based approach, a company will no longer "build the control everywhere"; rather, the focus will be on building the appropriate controls for the worst vulnerabilities to defeat the most significant threats that target the business' most critical areas. The risk-based approach to cybersecurity is thus ultimately interactive and a dynamic tool to support strategic decision-making. Focused on business value, utilizing a common language among the interested parties, and directly linking enterprise risks to controls, the approach helps translate executive decisions about risk reduction into control implementation. The power of the risk-based approach to optimize risk reduction at any level of investment is enhanced by its flexibility, adjusting to an evolving risk-appetite strategy as needed. A risk-based approach recognizes that there are no perfect security solutions. Still, those that strategically balance security, scalability, access, usability, and cost can ultimately provide the best long-term protection against an evolving adversary. Fundamentally, risk transformation changes security strategy from an outside-in perspective, where external threats and regulations drive strategy, to an | Ransomware Data Breach Tool Vulnerability Threat Patching Guideline | |||
| 2022-08-16 15:30:00 | Healthcare Provider Issues Warning After Tracking Pixels Leak Patient Data (lien direct) | The leak was caused by incorrect configurations of an online tracking tool from Meta | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-16 15:06:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Ransomware Module Added to SOVA Android Trojan, Bitter APT Targets Mobile Phones with Dracarys, China-Sponsored TA428 Deploys Six Backdoors at Once, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Android, APT, China, Cyberespionage, India, Malspam, Ransomware, Spearphishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
APT-C-35: New Windows Framework Revealed
(published: August 11, 2022)
The DoNot Team (APT-C-35) are India-sponsored actors active since at least 2016. Morphisec Labs researchers discovered a new Windows framework used by the group in its campaign targeting Pakistani government and defense departments. The attack starts with a spearphishing RTF attachment. If opened in a Microsoft Office application, it downloads a malicious remote template. After the victim enables editing (macroses) a multi-stage framework deployment starts. It includes two shellcode stages followed by main DLL that, based on victim fingerprinting, downloads a custom set of additional information-stealing modules.
Analyst Comment: The described DoNot Team framework is pretty unique in its customisation, fingerprinting, and module implementation. At the same time, the general theme of spearphishing attachment that asks the targeted user to enable editing is not new and can be mitigated by anti-phishing training and Microsoft Office settings hardening.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion - T1497 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Template Injection - T1221 | [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Obfuscated Files or Information - T1027 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information - T1140 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Information Discovery - T1082 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Screen Capture - T1113 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Local System - T1005 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Removable Media - T1025 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Network Shared Drive - T1039 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Staged - T1074 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059
Tags: APT-C-35, DoNot Team, APT, India, source-country:IN, Government, Military, Pakistan, target-country:PK, Windows
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
APT-C-35: New Windows Framework Revealed
(published: August 11, 2022)
The DoNot Team (APT-C-35) are India-sponsored actors active since at least 2016. Morphisec Labs researchers discovered a new Windows framework used by the group in its campaign targeting Pakistani government and defense departments. The attack starts with a spearphishing RTF attachment. If opened in a Microsoft Office application, it downloads a malicious remote template. After the victim enables editing (macroses) a multi-stage framework deployment starts. It includes two shellcode stages followed by main DLL that, based on victim fingerprinting, downloads a custom set of additional information-stealing modules.
Analyst Comment: The described DoNot Team framework is pretty unique in its customisation, fingerprinting, and module implementation. At the same time, the general theme of spearphishing attachment that asks the targeted user to enable editing is not new and can be mitigated by anti-phishing training and Microsoft Office settings hardening.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion - T1497 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Template Injection - T1221 | [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Obfuscated Files or Information - T1027 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information - T1140 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Information Discovery - T1082 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Screen Capture - T1113 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Local System - T1005 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Removable Media - T1025 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data from Network Shared Drive - T1039 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Staged - T1074 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059
Tags: APT-C-35, DoNot Team, APT, India, source-country:IN, Government, Military, Pakistan, target-country:PK, Windows |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline Medical | APT 38 | ||
| 2022-08-16 10:03:51 | Vulnerability Spotlight: Three vulnerabilities in HDF5 file format could lead to remote code execution (lien direct) |  Dave McDaniel of Cisco Talos discovered these vulnerabilities. Blog by Jon Munshaw. Cisco Talos recently discovered three vulnerabilities in a library that works with the HDF5 file format that could allow an attacker to execute remote code on a targeted device. These issues arise in the libhdf5 gif2h5 tool that's normally used to convert a GIF file to the HDF5 format, commonly used to store large amounts of numerical data. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by tricking a user into opening a specially crafted, malicious file. TALOS-2022-1485 (CVE-2022-25972) and TALOS-2022-1486 (CVE-2022-25942) are out-of-bounds write vulnerabilities in the gif2h5 tool that trigger a specific crash, opening the door for code execution from the adversary. TALOS-2022-1487 (CVE-2022-26061) works similarly but is a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability. Cisco Talos is disclosing these vulnerabilities despite no official fix from HDF5 in adherence to the 90-day deadline outlined in Cisco's vulnerability disclosure policy. Dave McDaniel of Cisco Talos discovered these vulnerabilities. Blog by Jon Munshaw. Cisco Talos recently discovered three vulnerabilities in a library that works with the HDF5 file format that could allow an attacker to execute remote code on a targeted device. These issues arise in the libhdf5 gif2h5 tool that's normally used to convert a GIF file to the HDF5 format, commonly used to store large amounts of numerical data. An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities by tricking a user into opening a specially crafted, malicious file. TALOS-2022-1485 (CVE-2022-25972) and TALOS-2022-1486 (CVE-2022-25942) are out-of-bounds write vulnerabilities in the gif2h5 tool that trigger a specific crash, opening the door for code execution from the adversary. TALOS-2022-1487 (CVE-2022-26061) works similarly but is a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability. Cisco Talos is disclosing these vulnerabilities despite no official fix from HDF5 in adherence to the 90-day deadline outlined in Cisco's vulnerability disclosure policy. |
Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-08-12 21:00:00 | Anti-tracking tool tells you if you\'re being followed (lien direct) | >Categories: NewsCategories: PrivacyAt Black Hat, a cybersecurity expert presented an anti-stalking tool they made for a friend. (Read more...) | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-11 06:54:45 | InfoStealer Script Based on Curl and NSudo, (Thu, Aug 11th) (lien direct) | If sudo[1] is a well known tool used daily by most UNIX system administrators, NSudo[2] remains less below the radar. This is a tool running on Microsoft Windows which allows you to execute processes with different access tokens and privileges like: | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-10 14:14:08 | Why robotexts are scammers\' favorite new tool (lien direct) | Technology meant to limit robocalls has pushed scammers toward SMS-based attacks, which experts say can be even more dangerous. | Tool | |||
| 2022-08-10 13:10:00 | Sensitive data in the cloud gets new automated remediation tool from BigID (lien direct) | Data intelligence company BigID announced this week at the Black Hat conference in Las Vegas that it has rolled out new features for its privacy and data protection platform, allowing users to programmatically restrict access to sensitive cloud-based information when it's under threat.BigID's core product, its Data Intelligence platform, already boasts numerous capabilities focused on the privacy, organization and discovery of a company's data. The new features announced this week build on that framework, allowing IT staff to automatically lock down access to sensitive information tagged as having open or overprivileged access in the big three public cloud platforms.To read this article in full, please click here | Tool |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
