What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2022-02-03 02:58:35 | FBI Confirms It Bought Spyware From Israel\'s NSO Group (lien direct) | The FBI has confirmed purchasing NSO Group's powerful spyware tool Pegasus, whose chronic abuse to surveil journalists, dissidents and human rights activists has long been established. It suggested its motivation was to “stay abreast of emerging technologies and tradecraft.” | Tool | |||
| 2022-02-02 17:30:00 | Online Ad Association Fined for Privacy Violation (lien direct) | Belgian data watchdog penalizes IAB Europe over ad-targeting tool | Tool | |||
| 2022-02-02 12:15:07 | CVE-2020-26208 (lien direct) | JHEAD is a simple command line tool for displaying and some manipulation of EXIF header data embedded in Jpeg images from digital cameras. In affected versions there is a heap-buffer-overflow on jhead-3.04/jpgfile.c:285 ReadJpegSections. Crafted jpeg images can be provided to the user resulting in a program crash or potentially incorrect exif information retrieval. Users are advised to upgrade. There is no known workaround for this issue. | Tool | |||
| 2022-02-02 09:46:34 | SEO poisoning pushes malware-laced Zoom, TeamViewer, Visual Studio installers (lien direct) | A new SEO poisoning campaign is underway, dropping the Batloader and Atera Agent malware onto the systems of targeted professionals searching for productivity tool downloads, such as Zoom, TeamViewer, and Visual Studio. [...] | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-02-01 15:15:07 | CVE-2021-44746 (lien direct) | UNIVERGE DT 820 V3.2.7.0 and prior, UNIVERGE DT 830 V5.2.7.0 and prior, UNIVERGE DT 930 V2.4.0.0 and prior, IP Phone Manager V8.9.1 and prior, Data Maintenance Tool for DT900 Series V5.3.0.0 and prior, Data Maintenance Tool for DT800 Series V4.2.0.0 and prior allows a remote attacker who can access to the internal network, the configuration information may be obtained. | Tool | |||
| 2022-02-01 15:00:00 | Zoom pour vous - Empoisonnement du référencement pour distribuer Batloader et Atera Agent Zoom For You - SEO Poisoning to Distribute BATLOADER and Atera Agent (lien direct) |
Tout en défendant nos clients contre les menaces, manage managedDéfense continue de voir de nouvelles menaces qui abusent de la confiance dans les outils et les produits légitimes pour mener à bien leurs attaques.Ces attaques sont efficaces pour obtenir des défenses de sécurité passées et rester non détecté dans un réseau.
Grâce à la chasse à la menace proactive, notre équipe de première ligne de défense gérée a découvert une campagne qui a utilisé l'empoisonnement d'optimisation des moteurs de recherche (SEO) pour conduire les victimes à télécharger le Batloader MALWWare pour le compromis initial.Nous avons également observé une technique d'évasion de défense astucieuse à l'aide de mshta.exe, un utilitaire Windows-Native
While defending our customers against threats, Mandiant Managed Defense continues to see new threats that abuse trust in legitimate tools and products to carry out their attacks. These attacks are effective in getting past security defenses and staying undetected in a network. Through proactive threat hunting, our Managed Defense frontline team uncovered a campaign that used search engine optimization (SEO) poisoning to lead victims to download the BATLOADER malware for the initial compromise. We also observed a crafty defense evasion technique using mshta.exe, a Windows-native utility |
Malware Tool Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-02-01 14:37:29 | CyberheistNews Vol 12 #05 [Heads Up] DHS Sounds Alarm on New Russian Destructive Disk Wiper Attack Potential (lien direct) |
![CyberheistNews Vol 12 #05 [Heads Up] DHS Sounds Alarm on New Russian Destructive Disk Wiper Attack Potential](https://blog.knowbe4.com/hubfs/Stu_Headshot_2021_resize.png)
|
Ransomware Malware Hack Tool Threat Guideline | NotPetya NotPetya Wannacry Wannacry APT 27 APT 27 | ||
| 2022-01-31 17:49:42 | Microsoft PowerToys adds Mouse and File Explorer utilities (lien direct) | Microsoft has updated PowerToys with three new utilities, including a new mouse crosshair tool to quickly find the pointer on the screen and two new File Explorer add-ons. [...] | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-31 15:33:58 | No, a researcher didn\'t find Olympics app spying on you (lien direct) | For the Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics, the Chinese government requires everyone to download an app onto their phone. It has many security/privacy concerns, as CitizenLab documents. However, another researcher goes further, claiming his analysis proves the app is recording all audio all the time. His analysis is fraudulent. He shows a lot of technical content that looks plausible, but nowhere does he show anything that substantiates his claims.Average techies may not be able to see this. It all looks technical. Therefore, I thought I'd describe one example of the problems with this data -- something the average techie can recognize.His "evidence" consists screenshots from reverse-engineering tools, with red arrows pointing to the suspicious bits. An example of one of these screenshots is this on: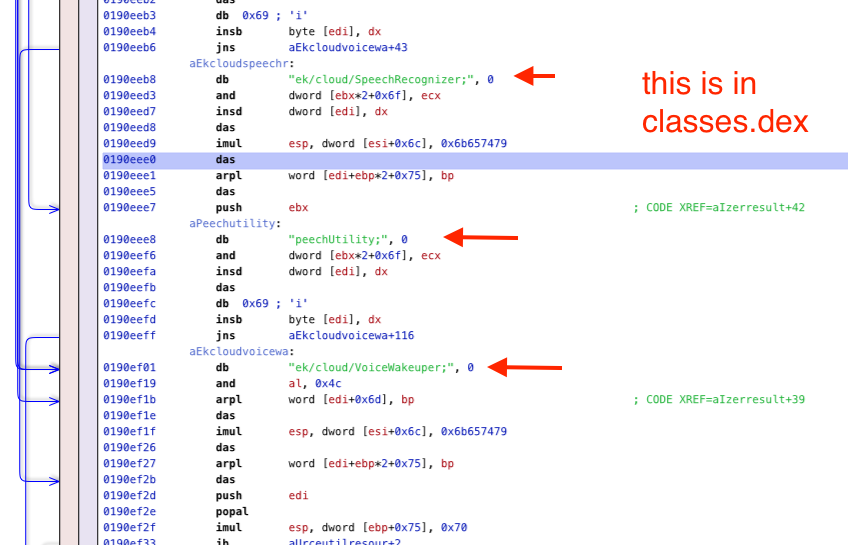 This screenshot is that of a reverse-engineering tool (Hopper, I think) that takes code and "disassembles" it. When you dump something into a reverse-engineering tool, it'll make a few assumptions about what it sees. These assumptions are usually wrong. There's a process where the human user looks at the analyzed output, does a "sniff-test" on whether it looks reasonable, and works with the tool until it gets the assumptions correct.That's the red flag above: the researcher has dumped the results of a reverse-engineering tool without recognizing that something is wrong in the analysis.It fails the sniff test. Different researchers will notice different things first. Famed google researcher Tavis Ormandy points out one flaw. In this post, I describe what jumps out first to me. That would be the 'imul' (multiplication) instruction shown in the blowup below: This screenshot is that of a reverse-engineering tool (Hopper, I think) that takes code and "disassembles" it. When you dump something into a reverse-engineering tool, it'll make a few assumptions about what it sees. These assumptions are usually wrong. There's a process where the human user looks at the analyzed output, does a "sniff-test" on whether it looks reasonable, and works with the tool until it gets the assumptions correct.That's the red flag above: the researcher has dumped the results of a reverse-engineering tool without recognizing that something is wrong in the analysis.It fails the sniff test. Different researchers will notice different things first. Famed google researcher Tavis Ormandy points out one flaw. In this post, I describe what jumps out first to me. That would be the 'imul' (multiplication) instruction shown in the blowup below: It's obviously ASCII. In other words, it's a series of bytes. The tool has tried to interpret these bytes as Intel x86 instructions (like 'and', 'insd', 'das', 'imul', etc.). But it's obviously not Intel x86, because those instructions make no sense.That 'imul' instruction is multiplying something by the (hex) number 0x6b657479. That doesn't look like a number -- it looks like four lower-case ASCII letters. ASCII lower-case letters are in the range 0x61 through 0x7A, so it's not the single 4-byte number 0x6b657479 but the 4 individual bytes 6b 65 74 79, which map to the ASCII letters 'k', 'e', 't It's obviously ASCII. In other words, it's a series of bytes. The tool has tried to interpret these bytes as Intel x86 instructions (like 'and', 'insd', 'das', 'imul', etc.). But it's obviously not Intel x86, because those instructions make no sense.That 'imul' instruction is multiplying something by the (hex) number 0x6b657479. That doesn't look like a number -- it looks like four lower-case ASCII letters. ASCII lower-case letters are in the range 0x61 through 0x7A, so it's not the single 4-byte number 0x6b657479 but the 4 individual bytes 6b 65 74 79, which map to the ASCII letters 'k', 'e', 't |
Tool | |||
| 2022-01-31 13:03:41 | The Third Building Block for the SOC of the Future: Balanced Automation (lien direct) | When automation is balanced between humans and machines, we can ensure teams always have the best tool for the job | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-31 12:18:55 | Twelve-Year-Old Linux Vulnerability Discovered and Patched (lien direct) | It’s a privilege escalation vulnerability: Linux users on Tuesday got a major dose of bad news — a 12-year-old vulnerability in a system tool called Polkit gives attackers unfettered root privileges on machines running most major distributions of the open source operating system. Previously called PolicyKit, Polkit manages system-wide privileges in Unix-like OSes. It provides a mechanism for nonprivileged processes to safely interact with privileged processes. It also allows users to execute commands with high privileges by using a component called pkexec, followed by the command... | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-01-28 20:15:12 | CVE-2021-4034 (lien direct) | A local privilege escalation vulnerability was found on polkit's pkexec utility. The pkexec application is a setuid tool designed to allow unprivileged users to run commands as privileged users according predefined policies. The current version of pkexec doesn't handle the calling parameters count correctly and ends trying to execute environment variables as commands. An attacker can leverage this by crafting environment variables in such a way it'll induce pkexec to execute arbitrary code. When successfully executed the attack can cause a local privilege escalation given unprivileged users administrative rights on the target machine. | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-01-27 16:00:33 | .NET Remoting Revisited (lien direct) | .NET Remoting is the built-in architecture for remote method invocation in .NET. It is also the origin of the (in-)famous BinaryFormatter and SoapFormatter serializers and not just for that reason a promising target to watch for. This blog post attempts to give insights into its features, security measures, and especially its weaknesses/vulnerabilities that often result in remote code execution. We're also introducing major additions to the ExploitRemotingService tool, a new ObjRef gadget for YSoSerial.Net, and finally a RogueRemotingServer as counterpart to the ObjRef gadget. If you already understand the internal of .NET Remoting, you may skip the introduction and proceed right with Security Features, Pitfalls, and Bypasses. Introduction .NET Remoting is deeply integrated into the .NET Framework and allows invocation of methods across so called remoting boundaries. These can be different app domains within a single process, different processes on the same computer, or different processes on different computers. Supported transports between the client and server are HTTP, IPC (named pipes), and TCP. Here is a simple example for illustration: the server creates and registers a transport server channel and then registers the class as a service with a well-known name at the server's registry: var channel = new TcpServerChannel(12345);ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel);RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType( typeof(MyRemotingClass), "MyRemotingClass"); Then a client just needs the URL of the registered service to do remoting with the server: var remote = (MyRemotingClass)RemotingServices.Connect( typeof(MyRemotingClass), "tcp://remoting-server:12345/MyRemotingClass"); With this, every invocation of a method or property accessor on remote gets forwarded to the remoting server, executed there, and the result gets returned to the client. This all happens transparently to the developer. And although .NET Remoting has already been deprecated with the release of .NET Framework 3.0 in 2009 and is no longer available on .NET Core and .NET 5+, it is still around, even in contemporary enterprise level software products. Remoting Internals If you are interested in how .NET Remoting works under the hood, here are some insights. In simple terms: when the client connects to the remoting object provided by the server, it creates a RemotingProxy that implements the specified type MyRemotingClass. All method invocations on remote at the client (except for GetType() and GetHashCode()) will get sent to the server as remoting calls. When a method gets invoked on remote, the proxy creates a MethodCall object that holds the information of the method and passed parameters. It is then passed to a chain of sinks that prepare the MethodCall and handle the remoting communication with the server over the given transport. On the server side, the received request is also passed to a chain of sinks that reverses the process, which also includes deserialization of the MethodCall object. It ends in a dispatcher sink, which invokes the actual implementation of the method with the passed parameters. The result of the method invocation is then put in a MethodResponse object and gets returned to the client where the client s | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-26 22:39:34 | TrickBot Crashes Security Researchers\' Browsers in Latest Upgrade (lien direct) | The malware has added an anti-debugging tool that crashes browser tabs when researchers use code beautifying for analysis. | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-01-26 16:09:43 | New Open Source Tool Helps Identify EtherNet/IP Stacks for ICS Research, Analysis (lien direct) | Industrial cybersecurity firm Claroty on Wednesday announced a new open source tool designed for identifying EtherNet/IP stacks. According to the company, the new “EtherNet/IP & CIP Stack Detector” tool can be useful to security researchers, operational technology (OT) engineers, and asset owners. | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-25 16:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: MoonBounce, AccessPress, QR Code Scams and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Linux Malware, Supply-Chain Attacks, Malspam, Phishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
FBI Warns Of Malicious QR Codes Used To Steal Your Money
(published: January 23, 2022)
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) recently released a notice that malicious QR codes have been found in the wild. These codes, when scanned, will redirect the victim to a site where they are prompted to enter personal and payment details. The site will then harvest these credentials for cybercriminals to commit fraud and empty bank accounts. This threat vector has been seen in Germany as of December 2021.
Analyst Comment: Always be sure to check that emails have been sent from a legitimate source, and that any financial details or method of payment is done through the website. While QR codes are useful and being used by businesses more often, it is easy for cybercriminals to perform this kind of scam. If scanning a physical QR code, ensure the code has not been replaced with a sticker placed on top of the original code. Check the final URL to make sure it is the intended site and looks authentic.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566
Tags: EU & UK, Banking and Finance
MoonBounce: The Dark Side Of UEFI Firmware
(published: January 20, 2022)
Kaspersky has reported that in September 2021, a bootloader malware infection had been discovered that embeds itself into UEFI firmware. The malware patches existing UEFI drivers and resides in the SPI flash memory located on the motherboard. This means that it will persist even if the hard drive is replaced. Code snippets and IP addresses link the activity to APT41, a group that is operated by a group of Chinese-speaking individuals. MoonBounce is highly sophisticated and very difficult to detect.
Analyst Comment: Systems should be configured to take advantage of Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware security chips to secure their systems' boot image and firmware, where available. Secure boot is also a viable option to mitigate against attacks that would patch, reconfigure, or flash existing UEFI firmware to implant malicious code.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Pre-OS Boot - T1542 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Obfuscation - T1001 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation of Remote Services - T1210 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Services - T1021 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Shared Modules - T1129 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hijack Execution Flow - T1574 |
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
FBI Warns Of Malicious QR Codes Used To Steal Your Money
(published: January 23, 2022)
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) recently released a notice that malicious QR codes have been found in the wild. These codes, when scanned, will redirect the victim to a site where they are prompted to enter personal and payment details. The site will then harvest these credentials for cybercriminals to commit fraud and empty bank accounts. This threat vector has been seen in Germany as of December 2021.
Analyst Comment: Always be sure to check that emails have been sent from a legitimate source, and that any financial details or method of payment is done through the website. While QR codes are useful and being used by businesses more often, it is easy for cybercriminals to perform this kind of scam. If scanning a physical QR code, ensure the code has not been replaced with a sticker placed on top of the original code. Check the final URL to make sure it is the intended site and looks authentic.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566
Tags: EU & UK, Banking and Finance
MoonBounce: The Dark Side Of UEFI Firmware
(published: January 20, 2022)
Kaspersky has reported that in September 2021, a bootloader malware infection had been discovered that embeds itself into UEFI firmware. The malware patches existing UEFI drivers and resides in the SPI flash memory located on the motherboard. This means that it will persist even if the hard drive is replaced. Code snippets and IP addresses link the activity to APT41, a group that is operated by a group of Chinese-speaking individuals. MoonBounce is highly sophisticated and very difficult to detect.
Analyst Comment: Systems should be configured to take advantage of Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware security chips to secure their systems' boot image and firmware, where available. Secure boot is also a viable option to mitigate against attacks that would patch, reconfigure, or flash existing UEFI firmware to implant malicious code.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Pre-OS Boot - T1542 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Obfuscation - T1001 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation of Remote Services - T1210 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Services - T1021 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Shared Modules - T1129 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hijack Execution Flow - T1574 | |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | APT 41 APT 28 | ||
| 2022-01-24 08:15:09 | CVE-2021-24976 (lien direct) | The Smart SEO Tool WordPress plugin before 3.0.6 does not sanitise and escape the search parameter before outputting it back in an attribute when the TDK optimisation setting is enabled, leading to a Reflected Cross-Site Scripting | Tool Guideline | |||
| 2022-01-23 17:15:41 | CFRipper – CloudFormation Security Scanning & Audit Tool (lien direct) |  CFRipper is a Python-based Library and CLI security analyzer that functions as an AWS CloudFormation security scanning and audit tool, it aims to prevent vulnerabilities from getting to production infrastructure through vulnerable CloudFormation scripts.
You can use CFRipper to prevent deploying insecure AWS resources into your Cloud environment. You can write your own compliance checks by adding new custom plugins.
CFRipper should be part of your CI/CD pipeline. It runs just before a CloudFormation stack is deployed or updated and if the CloudFormation script fails to pass the security check it fails the deployment and notifies the team that owns the stack.
Read the rest of CFRipper – CloudFormation Security Scanning & Audit Tool now! Only available at Darknet. CFRipper is a Python-based Library and CLI security analyzer that functions as an AWS CloudFormation security scanning and audit tool, it aims to prevent vulnerabilities from getting to production infrastructure through vulnerable CloudFormation scripts.
You can use CFRipper to prevent deploying insecure AWS resources into your Cloud environment. You can write your own compliance checks by adding new custom plugins.
CFRipper should be part of your CI/CD pipeline. It runs just before a CloudFormation stack is deployed or updated and if the CloudFormation script fails to pass the security check it fails the deployment and notifies the team that owns the stack.
Read the rest of CFRipper – CloudFormation Security Scanning & Audit Tool now! Only available at Darknet.
|
Tool | |||
| 2022-01-20 00:00:00 | Rapport WatchGuard Threat Lab : 2021, l\'année de l\'explosion du nombre de malwares et ransomwares ciblant les endpoints (lien direct) | Paris, le 19 janvier 2022 - WatchGuard® Technologies, leader mondial en matière de sécurité et d\'intelligence réseau, de Wi-Fi sécurisé, d\'authentification multifacteur et de protection avancée des postes de travail, publie aujourd\'hui les résultats de son dernier rapport trimestriel sur la sécurité Internet. Ce rapport met en évidence les principales tendances en matière de malwares et menaces pour la sécurité réseau au troisième trimestre 2021, analysées par les chercheurs du Threat Lab de WatchGuard. Les données indiquent que si le volume total de détections de malwares dans le périmètre a diminué par rapport aux sommets atteints au trimestre précédent, les détections de malwares sur les endpoints ont quant à elles déjà dépassé le volume total observé en 2020 (les données du quatrième trimestre 2021 n\'ayant pas encore été communiquées). En outre, un pourcentage important de malwares continue de mettre à profit des connexions chiffrées, confirmant la tendance des trimestres précédents. Les rapports de recherche trimestriels de WatchGuard sont basés sur des données anonymisées provenant d\'appliances Firebox actives chez les clients WatchGuard et dont les propriétaires ont choisi de partager les données pour soutenir directement les efforts de recherche du Threat Lab. Au troisième trimestre 2021, WatchGuard a bloqué plus de 16,6 millions de variantes de malwares et près de 4 millions de menaces réseau. Corey Nachreiner, Chief Security Officer chez WatchGuard commente : " Alors que le volume total d\'attaques réseau a légèrement diminué au troisième trimestre, le nombre de malwares détectés par terminal a progressé pour la première fois depuis le début de la pandémie. Mais il est important que les entreprises voient plus loin que les fluctuations à court terme pour se concentrer sur les tendances persistantes et préoccupantes telles que l\'utilisation accélérée des connexions chiffrées dans les attaques Zero-Day ". Parmi ses conclusions les plus notables, le rapport sur la sécurité Internet du troisième trimestre 2021 de WatchGuard révèle ce qui suit : Près de la moitié des malwares Zero-Day sont désormais diffusés via des connexions chiffrées – Alors que le nombre total de malwares 0-Day a connu une augmentation modeste de 3 % pour atteindre 67,2 % de l\'ensemble des malwares au troisième trimestre, le pourcentage de malwares diffusés via le protocole TLS (Transport Layer Security) a grimpé de 31,6 % à 47 %. Même si une moindre proportion des attaques Zero-Day chiffrées sont considérées comme avancées, la situation reste préoccupante d\'après les données de WatchGuard : celles-ci montrent en effet qu\'un grand nombre d\'organisations ne déchiffrent pas ces connexions et ont donc une mauvaise visibilité sur la quantité de malwares qui pénètrent leurs réseaux. Les cybercriminels ciblent les nouvelles vulnérabilités au fur et à mesure que les utilisateurs passent à des versions plus récentes de Microsoft Windows et Office – Si les vulnérabilités non corrigées des anciens logiciels restent un terrain de chasse prisé des cybercriminels, ces derniers cherchent également à exploiter les faiblesses des toutes dernières versions des produits Microsoft les plus répandus. Au troisième trimestre, CVE-2018-0802, qui exploite une vulné | Ransomware Tool Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-01-19 22:45:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Russia-Sponsored Cyber Threats, China-Based Earth Lusca Active in Cyberespionage and Cybertheft, BlueNoroff Hunts Cryptocurrency-Related Businesses, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, China, HTTP Stack, Malspam, North Korea, Phishing, Russia and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Earth Lusca Employs Sophisticated Infrastructure, Varied Tools and Techniques
(published: January 17, 2022)
The Earth Lusca threat group is part of the Winnti cluster. It is one of different Chinese groups that share aspects of their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) including the use of Winnti malware. Earth Lusca were active throughout 2021 committing both cyberespionage operations against government-connected organizations and financially-motivated intrusions targeting gambling and cryptocurrency-related sectors. For intrusion, the group tries different ways in including: spearphishing, watering hole attacks, and exploiting publicly facing servers. Cobalt Strike is one of the group’s preferred post-exploitation tools. It is followed by the use of the BioPass RAT, the Doraemon backdoor, the FunnySwitch backdoor, ShadowPad, and Winnti. The group employs two separate infrastructure clusters, first one is rented Vultr VPS servers used for command-and-control (C2), second one is compromised web servers used to scan for vulnerabilities, tunnel traffic, and Cobalt Strike C2.
Analyst Comment: Earth Lusca often relies on tried-and-true techniques that can be stopped by security best practices, such as avoiding clicking on suspicious email/website links and or reacting on random banners urging to update important public-facing applications. Don’t be tricked to download Adobe Flash update, it was discontinued at the end of December 2020. Administrators should keep their important public-facing applications (such as Microsoft Exchange and Oracle GlassFish Server) updated.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Drive-by Compromise - T1189 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Services - T1569 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Windows Management Instrumentation - T1047 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Account Manipulation - T1098 | [MITRE ATT&CK] BITS Jobs - T1197 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create Account - T1136 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create or Modify System Process - T1543 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hijack Execution Flow
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Earth Lusca Employs Sophisticated Infrastructure, Varied Tools and Techniques
(published: January 17, 2022)
The Earth Lusca threat group is part of the Winnti cluster. It is one of different Chinese groups that share aspects of their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) including the use of Winnti malware. Earth Lusca were active throughout 2021 committing both cyberespionage operations against government-connected organizations and financially-motivated intrusions targeting gambling and cryptocurrency-related sectors. For intrusion, the group tries different ways in including: spearphishing, watering hole attacks, and exploiting publicly facing servers. Cobalt Strike is one of the group’s preferred post-exploitation tools. It is followed by the use of the BioPass RAT, the Doraemon backdoor, the FunnySwitch backdoor, ShadowPad, and Winnti. The group employs two separate infrastructure clusters, first one is rented Vultr VPS servers used for command-and-control (C2), second one is compromised web servers used to scan for vulnerabilities, tunnel traffic, and Cobalt Strike C2.
Analyst Comment: Earth Lusca often relies on tried-and-true techniques that can be stopped by security best practices, such as avoiding clicking on suspicious email/website links and or reacting on random banners urging to update important public-facing applications. Don’t be tricked to download Adobe Flash update, it was discontinued at the end of December 2020. Administrators should keep their important public-facing applications (such as Microsoft Exchange and Oracle GlassFish Server) updated.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Drive-by Compromise - T1189 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Services - T1569 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Windows Management Instrumentation - T1047 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Account Manipulation - T1098 | [MITRE ATT&CK] BITS Jobs - T1197 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create Account - T1136 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create or Modify System Process - T1543 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hijack Execution Flow |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Patching Guideline | APT 41 APT 38 APT 29 APT 28 APT 28 | ||
| 2022-01-19 21:15:08 | CVE-2021-23843 (lien direct) | The Bosch software tools AccessIPConfig.exe and AmcIpConfig.exe are used to configure certains settings in AMC2 devices. The tool allows putting a password protection on configured devices to restrict access to the configuration of an AMC2. An attacker can circumvent this protection and make unauthorized changes to configuration data on the device. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability to manipulate the device\'s configuration or make it unresponsive in the local network. The attacker needs to have access to the local network, typically even the same subnet. | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-01-19 10:00:00 | Reducing Security Risks in Open Source Software at Scale: Scorecards Launches V4 (lien direct) |  Posted by Laurent Simon and Azeem Shaikh, Google Open Source Security Team (GOSST) Since our July announcement of Scorecards V2, the Scorecards project-an automated security tool to flag risky supply chain practices in open source projects-has grown steadily to over 40 unique contributors and 18 implemented security checks. Today we are proud to announce the V4 release of Scorecards, with larger scaling, a new security check, and a new Scorecards GitHub Action for easier security automation.The Scorecards Action is released in partnership with GitHub and is available from GitHub's Marketplace. The Action makes using Scorecards easier than ever: it runs automatically on repository changes to alert developers about risky supply-chain practices. Maintainers can view the alerts on GitHub's code scanning dashboard, which is available for free to public repositories on GitHub.com and via GitHub Advanced Security for private repositories. Additionally, we have scaled our weekly Scorecards scans to over one million GitHub repositories, and have partnered with the Open Source Insights website for easy user access to the data. For more details about the release, including the new Dangerous-Workflow security check, visit the OpenSSF's official blog post here. Posted by Laurent Simon and Azeem Shaikh, Google Open Source Security Team (GOSST) Since our July announcement of Scorecards V2, the Scorecards project-an automated security tool to flag risky supply chain practices in open source projects-has grown steadily to over 40 unique contributors and 18 implemented security checks. Today we are proud to announce the V4 release of Scorecards, with larger scaling, a new security check, and a new Scorecards GitHub Action for easier security automation.The Scorecards Action is released in partnership with GitHub and is available from GitHub's Marketplace. The Action makes using Scorecards easier than ever: it runs automatically on repository changes to alert developers about risky supply-chain practices. Maintainers can view the alerts on GitHub's code scanning dashboard, which is available for free to public repositories on GitHub.com and via GitHub Advanced Security for private repositories. Additionally, we have scaled our weekly Scorecards scans to over one million GitHub repositories, and have partnered with the Open Source Insights website for easy user access to the data. For more details about the release, including the new Dangerous-Workflow security check, visit the OpenSSF's official blog post here.
|
Tool | |||
| 2022-01-19 06:39:32 | Russian Hackers Heavily Using Malicious Traffic Direction System to Distribute Malware (lien direct) | Potential connections between a subscription-based crimeware-as-a-service (Caas) solution and a cracked copy of Cobalt Strike have been established in what the researchers suspect is being offered as a tool for its customers to stage post-exploitation activities. Prometheus, as the service is called, first came to light in August 2021 when cybersecurity company Group-IB disclosed details of | Malware Tool | |||
| 2022-01-19 00:00:00 | Quelles tendances émergentes de cybersécurité devraient-elles être conscientes? Alors que le monde devient plus connecté numériquement, les entreprises doivent être conscientes des risques croissants de cybersécurité. What Emerging Cybersecurity Trends Should Enterprises Be Aware Of?As the world becomes more digitally connected, enterprises need to be aware of the growing cybersecurity risks.Read More (lien direct) |
As the world becomes more digitally connected every year â and with the pandemic further accelerating digital transformation â all types of enterprises need to be aware of the growing cybersecurity risks that come with this shift. In Europe, for example, significant attacks on critical sectors more than doubled in 2020 compared to 2019, according to data from the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity, as reported by CNN. In 2021, the picture arguably became even bleaker around the world, with major ransomware attacks causing disruption to companies in industries ranging from energy to meat processing.In the first six months of 2021 alone, ransomware-related reported activity in the U.S. had a higher total value ($590 million) than all ransomware-related reported suspicious activity in the U.S. in 2020, according to the U.S. Department of Treasury\'s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). The total number of suspicious events filed in the first six months of 2021 in the U.S. also exceeded all of what occurred in the country in 2020 by 30%, the agency reports. Yet itâs not just ransomware thatâs wreaking havoc. Enterprises also need to be prepared for cyber threats like denial of service (DoS) attacks, where a flood of network activity can interrupt servers, thereby causing business interruption. Cisco predicts that distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks (a subset of DoS, which involves using multiple devices to send a flood of traffic, as opposed to just using one device with a DoS attack) globally will roughly âdouble from 7.9 million in 2018 to 15.4 million by 2023.âIn addition to preparing for these types of cyberattacks, enterprises will also increasingly need to be aware of and comply with privacy-related regulations. As governments around the world try to bolster their cybersecurity responses, they are passing or at least considering new rules and guidance around how companies need to handle sensitive data and privacy issues. Amidst this preparation, enterprises also need to recognize that cybersecurity plans arenât foolproof, especially as attacks evolve. That means assets could be at risk even with solid defenses in place. So, enterprises increasingly need to think about not just how to prevent cyber attacks but also consider the dollar-value cost of risk, given that events will inevitably occur. This process, known as cyber risk quantification â a form of financial quantification â helps enterprises think about and discuss cyber risk in definitive business terms. Knowing how much money is at stake and how different cyber events could affect revenue and profit can help businesses prioritize defenses and take mitigating action like securing cyber insurance. In this report, weâll take a closer look at these emerging cybersecurity trends that enterprises should be aware of. Understanding these areas can help organizations potentially improve their risk management, both from a cybersecurity and overall governance standpoint. ââEvolving Ransomware RisksWhile ransomware is not a new type of threat, the scale and intensity of ransomware continue to broaden. Enterprises large and small, across all types of industries, need to be prepared for these cyber attacks.For one, ransomware-as-a-service, âwhere ransomware variants are licensed to individuals and accomplices to execute attacks,â as Reuters explains, has been on the rise. Based on suspicious activity reports, FinCEN identified 68 ransomware variants in the first half of 2021.âThe resulting emergence of new attackers has led to increased uncertainty and volatility for companies in responding to attacks due to the lack of information on the growing number of ransomware threat actors,â adds Reuters.Part of the problem is also that ransomware attacks arenât just being launched on an ad-hoc basis by individuals. Instead, thereâs in | Ransomware Tool Threat Prediction Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-01-18 23:15:08 | CVE-2022-21694 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. The website mode of the onionshare allows to use a hardened CSP, which will block any scripts and external resources. It is not possible to configure this CSP for individual pages and therefore the security enhancement cannot be used for websites using javascript or external resources like fonts or images. | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-18 23:15:08 | CVE-2022-21690 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions The path parameter of the requested URL is not sanitized before being passed to the QT frontend. This path is used in all components for displaying the server access history. This leads to a rendered HTML4 Subset (QT RichText editor) in the Onionshare frontend. | Tool Guideline | |||
| 2022-01-18 23:15:08 | CVE-2022-21692 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions anyone with access to the chat environment can write messages disguised as another chat participant. | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-18 22:15:08 | CVE-2022-21693 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions an adversary with a primitive that allows for filesystem access from the context of the Onionshare process can access sensitive files in the entire user home folder. This could lead to the leaking of sensitive data. Due to the automatic exclusion of hidden folders, the impact is reduced. This can be mitigated by usage of the flatpak release. | Tool Guideline | ★★★★★ | ||
| 2022-01-18 22:15:08 | CVE-2022-21691 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions chat participants can spoof their channel leave message, tricking others into assuming they left the chatroom. | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2022-01-18 22:15:08 | CVE-2022-21695 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions authenticated users (or unauthenticated in public mode) can send messages without being visible in the list of chat participants. This issue has been resolved in version 2.5. | Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-01-18 22:15:07 | CVE-2022-21688 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. Affected versions of the desktop application were found to be vulnerable to denial of service via an undisclosed vulnerability in the QT image parsing. Roughly 20 bytes lead to 2GB memory consumption and this can be triggered multiple times. To be abused, this vulnerability requires rendering in the history tab, so some user interaction is required. An adversary with knowledge of the Onion service address in public mode or with authentication in private mode can perform a Denial of Service attack, which quickly results in out-of-memory for the server. This requires the desktop application with rendered history, therefore the impact is only elevated. This issue has been patched in version 2.5. | Tool Vulnerability Guideline | |||
| 2022-01-18 22:15:07 | CVE-2022-21689 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions the receive mode limits concurrent uploads to 100 per second and blocks other uploads in the same second, which can be triggered by a simple script. An adversary with access to the receive mode can block file upload for others. There is no way to block this attack in public mode due to the anonymity properties of the tor network. | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2022-01-18 20:15:07 | CVE-2022-21696 (lien direct) | OnionShare is an open source tool that lets you securely and anonymously share files, host websites, and chat with friends using the Tor network. In affected versions it is possible to change the username to that of another chat participant with an additional space character at the end of the name string. An adversary with access to the chat environment can use the rename feature to impersonate other participants by adding whitespace characters at the end of the username. | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-18 17:23:12 | \'White Rabbit\' Ransomware May Be FIN8 Tool (lien direct) | It's a double-extortion play that uses the command-line password 'KissMe' to hide its nasty acts and adorns its ransom note with cutesy ASCII bunny art. | Ransomware Tool | |||
| 2022-01-13 00:37:23 | Iranian Hackers Exploit Log4j Vulnerability to Deploy PowerShell Backdoor (lien direct) | An Iranian state-sponsored actor has been observed scanning and attempting to abuse the Log4Shell flaw in publicly-exposed Java applications to deploy a hitherto undocumented PowerShell-based modular backdoor dubbed "CharmPower" for follow-on post-exploitation. "The actor's attack setup was obviously rushed, as they used the basic open-source tool for the exploitation and based their operations | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-01-12 16:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: FluBot, iOS, Ransomware, Zloader, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Data breach, Phishing, Ransomware and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Attack Misuses Google Docs Comments to Spew Out “Massive Wave” of Malicious Links
(published: January 7, 2022)
Security researchers have seen a very large number of attacks leveraging the comment features of Google Docs to send emails to users containing malicious content. The attackers can create a document, sheet, or slides and add comments tagging any user's email address. Google then sends an email to the tagged user account. These emails come from Google itself and are more likely to be trusted than some other phishing avenues.
Analyst Comment: Phishing education can often help users identify and prevent phishing attacks. Specific to this attack method, users should verify that any unsolicited comments that are received come from the user indicated, and if unsure, reach out separately to the user that appears to have sent the comment to verify that it is real. Links in email should be treated with caution.
MITRE ATT&CK:[MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1156
Tags: Google, Impersonation, Phishing
Finalsite Ransomware Attack Forces 5,000 School Websites Offline
(published: January 7, 2022)
Finalsite, a firm used by schools for website content management, design, and hosting, has been hit by an unknown strain of ransomware that affected approximately 5,000 of their 8,000 customers. The company has said in a statement that many of the affected sites were preemptively shut down to protect user's data, that there is no evidence of that data was breached (although they did not confirm that they had the needed telemetry in place to detect that), and that most of the sites and services have been restored.
Analyst Comment: Verified backup and disaster recovery processes are an important aspect of protecting organizations and allowing for remediation of successful attacks. Monitoring and telemetry can aid in detection and prevention from attacks, and provide evidence as to whether data has been exfiltrated.
MITRE ATT&CK:[MITRE ATT&CK] Web Service - T1102 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Education, Finalsite, Ransomware, Web hosting
FluBot’s Authors Employ Creative and Sophisticated Techniques to Achieve Their Goals in Version 5.0 and Beyond
(published: January 6, 2022)
Security researchers have analyzed a new and more sophisticated version of the FluBot Android malware first detected in early 2020. Once installed on a device, the malware can full
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Attack Misuses Google Docs Comments to Spew Out “Massive Wave” of Malicious Links
(published: January 7, 2022)
Security researchers have seen a very large number of attacks leveraging the comment features of Google Docs to send emails to users containing malicious content. The attackers can create a document, sheet, or slides and add comments tagging any user's email address. Google then sends an email to the tagged user account. These emails come from Google itself and are more likely to be trusted than some other phishing avenues.
Analyst Comment: Phishing education can often help users identify and prevent phishing attacks. Specific to this attack method, users should verify that any unsolicited comments that are received come from the user indicated, and if unsure, reach out separately to the user that appears to have sent the comment to verify that it is real. Links in email should be treated with caution.
MITRE ATT&CK:[MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1156
Tags: Google, Impersonation, Phishing
Finalsite Ransomware Attack Forces 5,000 School Websites Offline
(published: January 7, 2022)
Finalsite, a firm used by schools for website content management, design, and hosting, has been hit by an unknown strain of ransomware that affected approximately 5,000 of their 8,000 customers. The company has said in a statement that many of the affected sites were preemptively shut down to protect user's data, that there is no evidence of that data was breached (although they did not confirm that they had the needed telemetry in place to detect that), and that most of the sites and services have been restored.
Analyst Comment: Verified backup and disaster recovery processes are an important aspect of protecting organizations and allowing for remediation of successful attacks. Monitoring and telemetry can aid in detection and prevention from attacks, and provide evidence as to whether data has been exfiltrated.
MITRE ATT&CK:[MITRE ATT&CK] Web Service - T1102 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Education, Finalsite, Ransomware, Web hosting
FluBot’s Authors Employ Creative and Sophisticated Techniques to Achieve Their Goals in Version 5.0 and Beyond
(published: January 6, 2022)
Security researchers have analyzed a new and more sophisticated version of the FluBot Android malware first detected in early 2020. Once installed on a device, the malware can full |
Ransomware Data Breach Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | |||
| 2022-01-10 10:00:00 | Qu'est-ce qui est mieux que l'intelligence des menaces libres? What\\'s Better Than Free Threat Intelligence? (lien direct) |
Beaucoup diraient que la sécurité efficace n'est pas basée sur les contrôles de sécurité déployés, mais l'expertise et les renseignements derrière ces contrôles.Pour répondre à la question critique: «Notre organisation est-elle à risque?»nécessite un aperçu approfondi de l'évolution du paysage des menaces.Les praticiens de la sécurité doivent savoir qui sont les acteurs de menace les plus prolifiques, les outils qu'ils utilisent et les indicateurs et tactiques, techniques et procédures (TTP) associés à leurs attaques.
Pour aider les organisations de toutes tailles à répondre à beaucoup de ces questions, Mandiant propose un abonnement gratuit et gratuit de
Many would say that effective security is not based on the security controls deployed, but the expertise and the intelligence behind those controls. To answer the critical question, “Is our organization at risk?” requires deep insight into the evolving threat landscape. Security practitioners need to know who the most prolific threat actors are, the tools they are using, and the indicators and tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) associated with their attacks. To help organizations of all sizes better address many of these questions, Mandiant offers a limited, free subscription of |
Tool Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2022-01-07 22:36:52 | Digital Tool Estimates Software Firewall Credits for Your Environment (lien direct) | Our handy Software NGFW Credit Estimator tool can easily figure out when to dial up and down these instances of our industry-leading NGFWs. | Tool Guideline | |||
| 2022-01-06 12:15:08 | CVE-2021-44564 (lien direct) | A security vulnerability originally reported in the SYNC2101 product, and applicable to specific sub-families of SYNC devices, allows an attacker to download the configuration file used in the device and apply a modified configuration file back to the device. The attack requires network access to the SYNC device and knowledge of its IP address. The attack exploits the unsecured communication channel used between the administration tool Easyconnect and the SYNC device (in the affected family of SYNC products). | Tool Vulnerability | |||
| 2022-01-05 19:55:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: $5 Million Breach Extortion, APTs Using DGA Subdomains, Cyberespionage Group Incorporates A New Tool, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Cyberespionage, Data breach, DGA, Infostealer, Phishing, Rootkit, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Fintech Firm Hit by Log4j Hack Refuses to Pay $5 Million Ransom
(published: December 29, 2021)
The Vietnamese crypto trading, ONUS, was breached by unknown threat actor(s) by exploiting the Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228) vulnerability between December 11 and 13. The exploited target was an AWS server running Cyclos, which is a point-of-sale software provider, and the server was only intended for sandbox purposes. Actors were then able to steal information via the misconfigured AWS S3 buckets containing information on approximately two million customers. Threat actors then attempted to extort five million dollars (USD).
Analyst Comment: Although Cyclos issued a warning to patch on December 13, the threat actors had already gained illicit access. Even though Log4Shell provided initial access to the compromised server, it was the misconfigured buckets the actors took advantage of to steal data.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203
Tags: ONUS, Log4Shell, CVE-2021-44228,
Strategically Aged Domain Detection: Capture APT Attacks With DNS Traffic Trends
(published: December 29, 2021)
Palo Alto Networks Unit42 researchers have published a report based on their tracking of strategically-aged malicious domains (registered but not used until a specific time) and their domain generation algorithm (DGA) created subdomains. Researchers found two Pegasus spyware command and control domains that were registered in 2019 and were not active until July 2021. A phishing campaign using DGA subdomains that were similar to those used during the SolarWinds supply chain attack was also identified.
Analyst Comment: Monitor your networks for abnormal DNS requests, and have bandwidth limitations in place, if possible, to prevent numerous connections to DGA domains. Knowing which DGAs are most active in the wild will allow you to build a proactive defense by detecting any DGA that is in use. Anomali can detect DGA algorithms used by malware to assist in defending against these types of threats.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Dynamic Resolution - T1568 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Application Layer Protocol - T1071
Tags: DGA , Pegasus, Phishing
Implant.ARM.iLOBleed.a
(published: December 28, 2021)
Amnpardaz researchers discovered a new rootkit that has been targeting Hewlett-Packard Enterprise’s Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) server managemen
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Fintech Firm Hit by Log4j Hack Refuses to Pay $5 Million Ransom
(published: December 29, 2021)
The Vietnamese crypto trading, ONUS, was breached by unknown threat actor(s) by exploiting the Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228) vulnerability between December 11 and 13. The exploited target was an AWS server running Cyclos, which is a point-of-sale software provider, and the server was only intended for sandbox purposes. Actors were then able to steal information via the misconfigured AWS S3 buckets containing information on approximately two million customers. Threat actors then attempted to extort five million dollars (USD).
Analyst Comment: Although Cyclos issued a warning to patch on December 13, the threat actors had already gained illicit access. Even though Log4Shell provided initial access to the compromised server, it was the misconfigured buckets the actors took advantage of to steal data.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203
Tags: ONUS, Log4Shell, CVE-2021-44228,
Strategically Aged Domain Detection: Capture APT Attacks With DNS Traffic Trends
(published: December 29, 2021)
Palo Alto Networks Unit42 researchers have published a report based on their tracking of strategically-aged malicious domains (registered but not used until a specific time) and their domain generation algorithm (DGA) created subdomains. Researchers found two Pegasus spyware command and control domains that were registered in 2019 and were not active until July 2021. A phishing campaign using DGA subdomains that were similar to those used during the SolarWinds supply chain attack was also identified.
Analyst Comment: Monitor your networks for abnormal DNS requests, and have bandwidth limitations in place, if possible, to prevent numerous connections to DGA domains. Knowing which DGAs are most active in the wild will allow you to build a proactive defense by detecting any DGA that is in use. Anomali can detect DGA algorithms used by malware to assist in defending against these types of threats.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Dynamic Resolution - T1568 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Application Layer Protocol - T1071
Tags: DGA , Pegasus, Phishing
Implant.ARM.iLOBleed.a
(published: December 28, 2021)
Amnpardaz researchers discovered a new rootkit that has been targeting Hewlett-Packard Enterprise’s Integrated Lights-Out (iLO) server managemen |
Malware Hack Tool Vulnerability Threat | LastPass | ||
| 2022-01-05 17:24:24 | How to deploy the Portainer container management tool with persistent storage (lien direct) | Looking for a powerful web-based Docker container manager? Jack Wallen shows you how to deploy one of the best on the market. | Tool | |||
| 2022-01-05 09:55:56 | CredNinja – Test Credential Validity of Dumped Credentials or Hashes (lien direct) |  CredNinja is a tool to quickly test credential validity of dumped credentials (or hashes) across an entire network or domain very efficiently.
At the core of it, you provide it with a list of credentials you have dumped (or hashes, it can pass-the-hash) and a list of systems on the domain (the author suggests scanning for port 445 first, or you can use ââscanâ). It will tell you if the credentials you dumped are valid on the domain, and if you have local administrator access to a host.
Read the rest of CredNinja – Test Credential Validity of Dumped Credentials or Hashes now! Only available at Darknet. CredNinja is a tool to quickly test credential validity of dumped credentials (or hashes) across an entire network or domain very efficiently.
At the core of it, you provide it with a list of credentials you have dumped (or hashes, it can pass-the-hash) and a list of systems on the domain (the author suggests scanning for port 445 first, or you can use ââscanâ). It will tell you if the credentials you dumped are valid on the domain, and if you have local administrator access to a host.
Read the rest of CredNinja – Test Credential Validity of Dumped Credentials or Hashes now! Only available at Darknet.
|
Tool | |||
| 2022-01-03 13:15:08 | CVE-2021-24973 (lien direct) | The Site Reviews WordPress plugin before 5.17.3 does not sanitise and escape the site-reviews parameter of the glsr_action AJAX action (available to unauthenticated and any authenticated users), allowing them to perform Cross-Site Scripting attacks against logged in admins viewing the Tool dashboard of the plugin | Tool | |||
| 2021-12-30 14:15:07 | CVE-2021-43861 (lien direct) | Mermaid is a Javascript based diagramming and charting tool that uses Markdown-inspired text definitions and a renderer to create and modify complex diagrams. Prior to version 8.13.8, malicious diagrams can run javascript code at diagram readers' machines. Users should upgrade to version 8.13.8 to receive a patch. There are no known workarounds aside from upgrading. | Tool | |||
| 2021-12-30 12:11:04 | GUEST ESSAY: Here\'s how \'WFM\' tools can boost productivity - and security - of remote workers (lien direct) | Workforce management software (WFM) is an essential tool companies across industries can use to organize their workforce, track employee work and performance, forecast labor demand, and create schedules for employees. Related: Turning workers into security security sensors Most, … (more…) | Tool | |||
| 2021-12-29 17:05:47 | assetfinder – Find Related Domains and Subdomains (lien direct) |  assetfinder is a Go-based tool to find related domains and subdomains that are potentially related to a given domain from a variety of sources including Facebook, ThreatCrowd, Virustotal and more.
assetfinder uses a variety of sources including those in the infosec space and social networks which can give relevant info:
crt.sh
certspotter
hackertarget
threatcrowd
wayback machine
dns.bufferover.run
facebook â Needs FB_APP_ID and FB_APP_SECRET environment variables set (https://developers.facebook.com/) and you need to be careful with your appâs rate limits
virustotal â Needs VT_API_KEY environment variable set (https://developers.virustotal.com/reference)
findsubdomains â Needs SPYSE_API_TOKEN environment variable set (the free version always gives the first response page, and you also get â25 unlimited requestsâ) â (https://spyse.com/apidocs)
Sources to be implemented:
http://api.passivetotal.org/api/docs/
https://community.riskiq.com/ (?)
https://riddler.io/
http://www.dnsdb.org/
https://certdb.com/api-documentation
Usage of assetfinder to Find Related Domains and Subdomains
The usage is very simple with only one option basically, to limit the search to subdomains only â by default it will scan for all associated domains and subdomains.
Read the rest of assetfinder – Find Related Domains and Subdomains now! Only available at Darknet. assetfinder is a Go-based tool to find related domains and subdomains that are potentially related to a given domain from a variety of sources including Facebook, ThreatCrowd, Virustotal and more.
assetfinder uses a variety of sources including those in the infosec space and social networks which can give relevant info:
crt.sh
certspotter
hackertarget
threatcrowd
wayback machine
dns.bufferover.run
facebook â Needs FB_APP_ID and FB_APP_SECRET environment variables set (https://developers.facebook.com/) and you need to be careful with your appâs rate limits
virustotal â Needs VT_API_KEY environment variable set (https://developers.virustotal.com/reference)
findsubdomains â Needs SPYSE_API_TOKEN environment variable set (the free version always gives the first response page, and you also get â25 unlimited requestsâ) â (https://spyse.com/apidocs)
Sources to be implemented:
http://api.passivetotal.org/api/docs/
https://community.riskiq.com/ (?)
https://riddler.io/
http://www.dnsdb.org/
https://certdb.com/api-documentation
Usage of assetfinder to Find Related Domains and Subdomains
The usage is very simple with only one option basically, to limit the search to subdomains only â by default it will scan for all associated domains and subdomains.
Read the rest of assetfinder – Find Related Domains and Subdomains now! Only available at Darknet.
|
Tool | |||
| 2021-12-29 16:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Equation Group\'s Post-Exploitation Framework, Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Protocol Exploited, Third Log4j Vulnerability, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Apache Log4j 2, APT, Malspam, Ngrok relay, Phishing, Sandbox evasion, Scam, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
A Deep Dive into DoubleFeature, Equation Group’s Post-Exploitation Dashboard
(published: December 27, 2021)
Check Point researchers have published their findings on the Equation Group’s post-exploitation framework DanderSpritz — a major part of the “Lost in Translation” leak — with a focus on its DoubleFeature logging tool. DoubleFeature (similar to other Equation Group tools) employs several techniques to make forensic analysis difficult: function names are not passed explicitly, but instead a checksum of it; strings used in DoubleFeature are decrypted on-demand per function and they are re-encrypted once function execution completes. DoubleFeature also supports additional obfuscation methods, such as a simple substitution cipher and a stream cipher. In its information gathering DoubleFeature can monitor multiple additional plugins including: KillSuit (also known as KiSu and GrayFish) plugin that is running other plugins, providing a framework for persistence and evasion, MistyVeal (MV) implant verifying that the targeted system is indeed an authentic victim, StraitBizarre (SBZ) cross-platform implant, and UnitedRake remote access tool (UR, EquationDrug).
Analyst Comment: It is important to study Equation Group’s frameworks because some of the leaked exploits were seen exploited by other threat actors. Defense-in-depth (layering of security mechanisms, redundancy, fail-safe defense processes) is the best way to ensure safety from APTs, including a focus on both network and host-based security. Prevention and detection capabilities should also be in place.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Modify Registry - T1112 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rootkit - T1014 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion - T1497 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information - T1140
Tags: Equation Group, DanderSpritz, DoubleFeature, Shadow Brokers, EquationDrug, UnitedRake, DiveBar, KillSuit, GrayFish, StraitBizarre, MistyVeal, PeddleCheap, DiceDealer, FlewAvenue, DuneMessiah, CritterFrenzy, Elby loader, BroughtHotShot, USA, Russia, APT
Dridex Affiliate Dresses Up as Scrooge
(published: December 23, 2021)
Days before Christmas, an unidentified Dridex affiliate is using malspam emails with extremely emotion-provoking lures. One malicious email purports that 80% of the company’s employees have tested positive for Omicron, a variant of COVID-19, another email claims that the recipient was just terminated from his or her job. The attached malicious Microsoft Excel documents have two anti-sandbox features: they are password protected, and the macro doesn’t run until a user interacts with a pop-up dialog. If the user makes the macro run, it will drop an .rtf f
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
A Deep Dive into DoubleFeature, Equation Group’s Post-Exploitation Dashboard
(published: December 27, 2021)
Check Point researchers have published their findings on the Equation Group’s post-exploitation framework DanderSpritz — a major part of the “Lost in Translation” leak — with a focus on its DoubleFeature logging tool. DoubleFeature (similar to other Equation Group tools) employs several techniques to make forensic analysis difficult: function names are not passed explicitly, but instead a checksum of it; strings used in DoubleFeature are decrypted on-demand per function and they are re-encrypted once function execution completes. DoubleFeature also supports additional obfuscation methods, such as a simple substitution cipher and a stream cipher. In its information gathering DoubleFeature can monitor multiple additional plugins including: KillSuit (also known as KiSu and GrayFish) plugin that is running other plugins, providing a framework for persistence and evasion, MistyVeal (MV) implant verifying that the targeted system is indeed an authentic victim, StraitBizarre (SBZ) cross-platform implant, and UnitedRake remote access tool (UR, EquationDrug).
Analyst Comment: It is important to study Equation Group’s frameworks because some of the leaked exploits were seen exploited by other threat actors. Defense-in-depth (layering of security mechanisms, redundancy, fail-safe defense processes) is the best way to ensure safety from APTs, including a focus on both network and host-based security. Prevention and detection capabilities should also be in place.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Modify Registry - T1112 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rootkit - T1014 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion - T1497 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information - T1140
Tags: Equation Group, DanderSpritz, DoubleFeature, Shadow Brokers, EquationDrug, UnitedRake, DiveBar, KillSuit, GrayFish, StraitBizarre, MistyVeal, PeddleCheap, DiceDealer, FlewAvenue, DuneMessiah, CritterFrenzy, Elby loader, BroughtHotShot, USA, Russia, APT
Dridex Affiliate Dresses Up as Scrooge
(published: December 23, 2021)
Days before Christmas, an unidentified Dridex affiliate is using malspam emails with extremely emotion-provoking lures. One malicious email purports that 80% of the company’s employees have tested positive for Omicron, a variant of COVID-19, another email claims that the recipient was just terminated from his or her job. The attached malicious Microsoft Excel documents have two anti-sandbox features: they are password protected, and the macro doesn’t run until a user interacts with a pop-up dialog. If the user makes the macro run, it will drop an .rtf f |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Conference | APT 35 | ||
| 2021-12-28 21:00:00 | New Apache Log4j Update Released to Patch Newly Discovered Vulnerability (lien direct) | The Apache Software Foundation (ASF) on Tuesday rolled out fresh patches to contain an arbitrary code execution flaw in Log4j that could be abused by threat actors to run malicious code on affected systems, making it the fifth security shortcoming to be discovered in the tool in the span of a month. Tracked as CVE-2021-44832, the vulnerability is rated 6.6 in severity on a scale of 10 and | Tool Vulnerability Threat | |||
| 2021-12-28 19:23:29 | Researchers Dive Into Equation Group Tool \'DoubleFeature\' (lien direct) | Security researchers at Check Point are publicly documenting the Equation Group APT's DoubleFeature, a component of DanderSpritz post-exploitation framework. | Tool | |||
| 2021-12-28 14:18:05 | DoubleFeature, post-exploitation dashboard used by Equation Group APT (lien direct) | Researchers analyzed the DoubleFeature logging tool of DanderSpritz Framework that was used by the Equation Group APT group. Check Point researchers have published a detailed analysis of the DoubleFeature tool used to log post-exploitation activities in attacks conducted by the Equation Group and involving the DanderSpritz malware framework. DanderSpritz made the headlines on April 14, […] | Malware Tool |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
