What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2022-01-13 11:00:00 | Le parcours du cyber-risque, première partie: où allons-nous d'ici? The Cyber Risk Journey, Part One: Where Do We Go From Here? (lien direct) |
Le cyber-risque peut être un gros point d'arrêt pour les organisations.Heureusement, les conseils d'administration et les hauts dirigeants sont plus engagés que jamais et travaillent à développer une meilleure compréhension de la gestion des cyber-risques au sein de leurs organisations.Plus de dialogue avec la gestion des cadres concernant le cyber-risque et les impacts que les mesures proactives et réactives ont sur un profil de risque d'organisation est une excellente tendance à voir.
Les équipes de cybersécurité-Office en arrière-plan sur les tâches écrasantes de soutenir les opérations quotidiennes tout en étant constamment préparées pour les attaquants dans leur environnement.Équilibrage
Cyber risk can be a big blindspot for organizations. Fortunately, Boards and senior leaders are more engaged than ever before and working to develop a better understanding of how cyber risk is being managed within their organizations. More dialogue with executive management around cyber risk and the impacts proactive and reactive measures have on an organization\'s risk profile is a great trend to see. Cyber security teams-often in the background-take on the overwhelming tasks of supporting day-to-day operations while constantly being prepared for attackers in their environment. Balancing |
Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2021-12-20 00:00:00 | 7 Rapports qui peuvent vous aider à comprendre l'assurance contre le paysage de cyber-assurance continue de faire face à des marges d'érodage, les assureurs ayant du mal à quantifier les risques 7 Reports That Can Help You Understand the Cyber Insurance LandscapeCyber insurance continues to face eroding margins, with insurers having trouble quantifying the risks enterprises faceRead More (lien direct) |
The explosion of ransomware attacks and cybersecurity risk as a whole have made life tough for so many organizations across industries globally. Enterprises need to face these risks in whatâs often a challenging business market anyway, and turning to potential solutions like cyber insurance comes with its own difficulties. The cyber insurance market continues to harden, with insurers facing eroding margins and often struggling to quantify the risk enterprises face. But itâs not all bad news. Cyber insurance companies and other enterprises who want to know the cyber landscape better have a wide range of resources to turn to. As the market matures, many quality research reports have emerged, including several that provide overviews and predictions for what will happen within cyber insurance and cybersecurity as a whole for 2021 and beyond. But which of these research reports should you read to strengthen your cyber knowledge and feel more prepared for what may come? In this article, weâll provide a brief overview of seven of the top cyber insurance research reports for you to consider diving into more.1) Munich Re: Cyber insurance: Risks and trends 2021In the report âCyber insurance: Risks and trends 2021,â the reinsurer Munich Re shares the results of the companyâs first âGlobal Cyber Risk and Insurance Survey.âSome of the key findings include that amidst rapid digitization within companies, approximately four out of five C-suite executives do not think their company has adequate cyber threat protection. The top cyber threats feared by this group include fraud, data breaches and ransomware. The survey also finds gaps in cyber insurance knowledge, but the market could soon grow, with 35% of C-level respondents likely to soon take out a policy.Munich Re also notes the importance of cyber risk accumulation. While the company mentions its own accumulation models, âit is important to monitor the market and seek external expertise from different vendors in order to assure state of the art accumulation management,â the company says.2) Aon: Cyber Insurance Market Insights Q1 2021In one report from Aon, âCyber Insurance Market Insights Q1 2021,â the firm highlights how the cyber insurance industry is changing amidst evolving cyber risks. In particular, the company highlights how issues such as ransomware, silent cyber exposure and the SolarWinds event have affected the cyber insurance market.With SolarWinds, for example, the âtheft of investigative tools from a globally recognised cyber security and forensics firm is likely to lead to improved hacking tools in the hands of cyber criminals,â notes Aon.Amidst this backdrop, Aon sees more hardening within the market through 2021 and 2022. Insurers are looking closely at their underwriting practices while also assessing retention, limits and premiums to figure out the right mix to make cyber insurance viable. 3) Aon: 2021 Cyber Security Risk ReportAnother report by Aon, the â2021 Cyber Security Risk Report,â focuses more on the overall risk landscape from an enterprise perspective. In particular, Aon highlights four main cyber-related risks facing organizations today:Digitization: As companies rapidly digitize, particularly with Covid-19 changing the way many companies work, only 40% say they have âadequate remote work strategies to manage this risk.âThird-Party Risk: Organizations need to be aware of risks in their supply chains and among the various vendors they work with, yet only 21% have implemented âbaseline measuresâ to oversee third-party risk.Ransomware: Ransomware attacks have been prevalent and damaging recently, and many are unprepared. Less than one-third of organizations say theyâve implemented âadequate business resilience measuresâ to handle this risk.Regulation: As stronger data security laws come into place, o | Ransomware Tool Threat Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2021-10-19 00:00:00 | A Sneak Peek into Kovrrâs Data SourcesA sneak peek into Kovrr\\\'s unique data sources used exclusively for modeling purposesRead More (lien direct) | Modeling impacts from cyber events requires extensive understanding of the cyber threat landscape. A core aspect of Kovrrâs cyber risk modeling data pipeline combines unique data sources to better inform the data points taken into account when building out the frequency and severity of cyber events. Access to these data sources is derived via partnerships reserved for Kovrrâs use exclusively for modeling purposes, developed among others with Israeli cybersecurity emerging vendors which continuously bring new exciting data and create a unique ecosystem. Hudson RockHudson Rock is a cybercrime intelligence startup with a database composed of millions of machines compromised in global malware spreading campaigns. The data is augmented monthly with tens of thousands, to hundreds of thousands of new compromised machines. Data includes Info Stealers, ransomware bots and other types of malware. Hudsonâs high-fidelity data help protect employees, partners, customers, and digital assets with unprecedented granularity of threat vectors including Ransomware, Business Espionage, Breaches & Network Overtakes.âHow Kovrr uses this dataâKovrr has extended capabilities to recognize ransomware trends and emerging techniques. This information is crucial for formulating accurate attack distributions. Kovrr leverages the data in order to enrich different parameters of its datasets. We can improve our understanding of the target audience profile by applying additional analytics on the data, Kovrr can deduct the entities who have suffered from the breach, this information may include location, job description and company. We also have extended information on the attack vector. Kovrr uses metadata regarding the attack to understand the attack vector used to install the malware, which is critical to understanding attack and exploitation patterns. Cynerio Medical and IoT devices in healthcare environments grow more numerous and vulnerable every day, and mitigating their risk is becoming more complex. The Cynerio platform uses a granular inventory classification taxonomy which tracks device types, functions, vendors, models, serial numbers, firmware/OS, MAC, and IP+ methods of medical devices. Drilldowns into VLANs, ports, kernels, HW, services, browsers, and FDA class, classification, and recalls are also provided. Cynerio then leverages this data to monitor, verify, and reduce the risk of IoT and IoMT device vulnerabilities through direct communication with vendors, third-party solution providers, and cybersecurity governance organizations.How Kovrr uses this dataKovrr has secured unique cyber information sources per industry to have more detailed data reflecting the cyber risk landscape. Kovrr receives aggregated data on compromised medical IoT devices and relevant vulnerabilities, corresponding to companiesâ geographic location, size and industry that shows instances of potential attack per type of device. For this specific source, Kovrrâs extended insights surrounding healthcare cybersecurity feeds into the industry exposure database. In turn this provides more accurate data on the frequency and severity of events affecting organizations in the healthcare industry and assists in better analysis of understanding a companyâs cyber resilience.Sedric.me Sedric integrates into all communication systems of organizations and provides cyber risk management teams with a solution to securely store company interactions with internal and external users. By monitoring a wide range of interactions, Sedric uses AI to detect intentions related to regulatory, compliance, and company misconduct without the need for explicit exact phrase or rule matches.  The platform securely cleans ,encrypts and stores data associated with GDPR, PCI, PHI, and other violations before it enters a companyâs system.âHow Kovrr uses this dataKovrr receives aggregated data of sensitive data records corresponding to companiesâ g | Ransomware Malware Vulnerability Threat Prediction Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2021-10-12 17:41:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Aerospace and Telecoms Targeted by Iranian MalKamak Group, Cozy Bear Refocuses on Cyberespionage, Wicked Panda is Traced by Malleable C2 Profiles, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Data leak, Ransomware, Phishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Russian Cyberattacks Pose Greater Risk to Governments and Other Insights from Our Annual Report
(published: October 7, 2021)
Approximately 58% of all nation-state attacks observed by Microsoft between July 2020 and June 2021 have been attributed to the Russian-sponsored threat groups, specifically to Cozy Bear (APT29, Nobelium) associated with the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR). The United States, Ukraine, and the UK were the top three targeted by them. Russian Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) actors increased their effectiveness from a 21% successful compromise rate to a 32% rate comparing year to year. They achieve it by starting an attack with supply-chain compromise, utilizing effective tools such as web shells, and increasing their skills with the cloud environment targeting. Russian APTs are increasingly targeting government agencies for intelligence gathering, which jumped from 3% of their targets a year ago to 53% – largely agencies involved in foreign policy, national security, or defense. Following Russia by the number of APT cyberattacks were North Korea (23%), Iran (11%), and China (8%).
Analyst Comment: As the collection of intrusions for potential disruption operations via critical infrastructure attacks became too risky for Russia, it refocused back to gaining access to and harvesting intelligence. The scale and growing effectiveness of the cyberespionage requires a defence-in-depth approach and tools such as Anomali Match that provide real-time forensics capability to identify potential breaches and known actor attributions.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Brute Force - T1110
Tags: Fancy Bear, APT28, APT29, The Dukes, Strontium, Nobelium, Energetic Bear, Cozy Bear, Government, APT, Russia, SVR, China, North Korea, USA, UK, Ukraine, Iran
Ransomware in the CIS
(published: October 7, 2021)
Many prominent ransomware groups have members located in Russia and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) - and they avoid targeting this region. Still, businesses in the CIS are under the risk of being targeted by dozens of lesser-known ransomware groups. Researchers from Kaspersky Labs have published a report detailing nine business-oriented ransomware trojans that were most active in the CIS in the first half of 2021. These ransomware families are BigBobRoss (TheDMR), Cryakl (CryLock), CryptConsole, Crysis (Dharma), Fonix (XINOF), Limbozar (VoidCrypt), Phobos (Eking), Thanos (Hakbit), and XMRLocker. The oldest, Cryakl, has been around since April 2014, and the newest, XMRLocker, was first detected in August 2020. Most of them were mainly distributed via the cracking of Remote Deskto
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Russian Cyberattacks Pose Greater Risk to Governments and Other Insights from Our Annual Report
(published: October 7, 2021)
Approximately 58% of all nation-state attacks observed by Microsoft between July 2020 and June 2021 have been attributed to the Russian-sponsored threat groups, specifically to Cozy Bear (APT29, Nobelium) associated with the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR). The United States, Ukraine, and the UK were the top three targeted by them. Russian Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) actors increased their effectiveness from a 21% successful compromise rate to a 32% rate comparing year to year. They achieve it by starting an attack with supply-chain compromise, utilizing effective tools such as web shells, and increasing their skills with the cloud environment targeting. Russian APTs are increasingly targeting government agencies for intelligence gathering, which jumped from 3% of their targets a year ago to 53% – largely agencies involved in foreign policy, national security, or defense. Following Russia by the number of APT cyberattacks were North Korea (23%), Iran (11%), and China (8%).
Analyst Comment: As the collection of intrusions for potential disruption operations via critical infrastructure attacks became too risky for Russia, it refocused back to gaining access to and harvesting intelligence. The scale and growing effectiveness of the cyberespionage requires a defence-in-depth approach and tools such as Anomali Match that provide real-time forensics capability to identify potential breaches and known actor attributions.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Brute Force - T1110
Tags: Fancy Bear, APT28, APT29, The Dukes, Strontium, Nobelium, Energetic Bear, Cozy Bear, Government, APT, Russia, SVR, China, North Korea, USA, UK, Ukraine, Iran
Ransomware in the CIS
(published: October 7, 2021)
Many prominent ransomware groups have members located in Russia and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) - and they avoid targeting this region. Still, businesses in the CIS are under the risk of being targeted by dozens of lesser-known ransomware groups. Researchers from Kaspersky Labs have published a report detailing nine business-oriented ransomware trojans that were most active in the CIS in the first half of 2021. These ransomware families are BigBobRoss (TheDMR), Cryakl (CryLock), CryptConsole, Crysis (Dharma), Fonix (XINOF), Limbozar (VoidCrypt), Phobos (Eking), Thanos (Hakbit), and XMRLocker. The oldest, Cryakl, has been around since April 2014, and the newest, XMRLocker, was first detected in August 2020. Most of them were mainly distributed via the cracking of Remote Deskto |
Ransomware Malware Tool Threat Guideline Prediction | APT 41 APT 41 APT 39 APT 29 APT 29 APT 28 | ||
| 2021-09-12 00:00:00 | Règlements et ransomwares: un aperçu rapide de la vue d'ensemble de ce que les entreprises doivent savoir sur les ransomwares et les réglementations connexes. Regulations & Ransomware: A Quick OverviewAn overview of what enterprises need to know about ransomware and related regulations.Read More (lien direct) |
As cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, ransomware has recently come into focus as one of the more prominent and challenging types of attacks to deal with. Not only do companies need to face the security implications of having their data fall into the hands of cybercriminals, but there can be significant costs around paying ransoms and/or recovering systems and files. Plus, paying ransoms can raise some ethical if not legal issues. There are already several existing regulations that enterprises need to keep in mind if hit with a ransomware attack. And as the risk grows, a number of new regulations are under consideration around the world.In this brief overview, weâll explore what enterprises need to know about ransomware and related regulations.What Is Ransomware?Before diving into what to do about ransomware and what regulations to follow, itâs important to understand what ransomware is.âRansomware is a form of malware designed to encrypt files on a device, rendering any files and the systems that rely on them unusable. Malicious actors then demand ransom in exchange for decryption,â explains the U.S. Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).In other words, ransomware can lock a user out of their own files/systems, which can bring work to a halt. Even if the ransom is paid and everything gets unlocked, itâs possible that the cybercriminals stole data meanwhile. While some of the more headline-grabbing attacks have been at large, well-known companies, ransomware can essentially affect anyone, regardless of size, industry or location.How to Reduce the Risk of RansomwareAlthough ransomware is on the rise, there are still several steps organizations can take to reduce the risk of a ransomware attack or at least mitigate the damage.âAs with all risks posed by external actors, the likelihood that a ransomware attack is successful can be drastically reduced by tightening the security of the data controlling environment,â notes the European Data Protection Board (EDPB).From updating software and systems with appropriate security patches, to using anti-malware software or related monitoring services, there are many cybersecurity best practices that can potentially keep ransomware out, as the EDPB highlights.If ransomware does take hold, having complete backups can help. As the EDPB notes, the impact of ransomware âcould effectively be contained,â by resetting systems to wipe out the ransomware and then âfixing the vulnerabilities and restoring the affected data soon after the attack.âOrganizations can also get a better handle on ransomware risk via cyber risk quantification (CRQ), such as through Kovrrâs insurance-validated risk models. CRQ works by analyzing factors such as past cyber events and the technologies and service providers that a company uses to then quantify what companies might lose if a cyber attack like ransomware occurs. Part of being prepared means knowing how much is at stake financially, and CRQ can help organizations focus on the areas that present the largest financial risk. âWhat Ransomware Regulations Exist?Current ransomware regulations differ around the world, so the specific rules an enterprise needs to follow depends on factors like what markets they operate in and whether they fall under certain jurisdictions.Communicating AttacksOne of the more notable rules that relates to ransomware is the EUâs General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which can still apply to companies outside Europe, such as those that have customers in the EU. Under GDPR, explains the EDPB, a personal data breach needs to be reported to relevant authorities and potentially to the people whose data gets exposed. So, for example, if a ransomware incident involves a cybercriminal locking up files that contain personal information, such as financial or medical records, then the affected company may need to report that to those affected.In the U.S. the | Ransomware Data Breach Malware Vulnerability Prediction Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2021-05-10 06:00:29 | Ep. 145 – Baking a Human Behavior Cake with Jack Schafer (lien direct) | In this episode, Chris Hadnagy and Maxie Reynolds are joined by industry professional Jack Schafer, PhD. Dr. Schafer is a psychologist, professor, intelligence consultant, and former FBI Special Agent. Dr. Schafer spent fifteen years conducting counter-intelligence and counterterrorism investigations, and seven years as a behavioral analyst for the FBI’s National Security Division’s Behavioral Analysis Program. May 10, 2021 Download Ep. 145 […] | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2021-03-16 16:32:50 | BSidesSF CTF 2021 Author writeup: Hangman Battle Royale, where you defeat 1023 AI players! (lien direct) | Hi Everybody! This is going to be a challenge-author writeup for the Hangman Battle Royale challenge from BSides San Francisco 2021. This is actually a reasonable simple challenge, overall. I got the idea of using a bad mt19937 implementation (the Mersenne Twister PRNG used by Ruby and Python) from SANS Holiday Hack Challenge 2020 (which is still online if you want to play!), and wanted to build a challenge around it. I had the idea of Battleship originally, but ended up deciding on Hangman for reasons I no longer remember, but that I'm sure made sense at the time. The game When you run the game, it prompts for the number of rounds: $ ruby ./hangman.rb Welcome to Hangman Battle Royale! ================================ MAIN MENU ================================ How many rounds do you want to play? (2 - 16) If you play at least 8 rounds, you win the special prize! When you choose a round count, it picks a bunch of CPU names to build brackets: ================================ ROUND 1! ================================ This game's match-ups are: Meirina Tresvalles -vs- Gelbert Chhangte Kebede Boehmer -vs- Karthic Cassity Mairtin Piedrahita -vs- Winston Pawlowski Brendaliz Lumbang -vs- Josipa Perlow Unusual Ballenger -vs- Carmellia Agregado Jinnie Khalif -vs- Jeegar Madela Vjeran Saltarelli -vs- Rachella Newfield And finally... YOU -vs- Patience Saravana! The vulnerability The actual code powering the list of players uses Ruby's built-in PRNG, which uses a predictable Mersenne Twister to generate random numbers. I don't love how the name-choosing code was a little bit contrived, but it can leak enough state to predict future random numbers: def get_opponents(count) return 0.upto(count-1).map do || i = rand(0xFFFFFFFF) "#{ FIRST_NAMES[i & 0xFFFF] } #{ LAST_NAMES[i >> 16] }" end end Each pair of names is a single 32-bit integer from the Mersenne Twister PRNG. It turns out, if you can leak 624 32-bit outputs, you can recover the full state! That means if you play at least 10 rounds, you end up with 210-1 names, or 1023 32-bit numbers (because you're the 1024th player). Once you've gotten the state of the PRNG, you can predict everything else that's going to happen! The exploit My exploit is super quick and dirty. It can parse the output from the game and grab the seed using mt19937predict: predictor = MT19937Predictor() for _ in range(511): (a, b) = read_names(i) predictor.setrandbits(a, 32) predictor.setrandbits(b, 32) (and yes, this is probably the first time I've ever written a Python solution!) Then does a final validation on your opponent's name to make sure the solution is working: (_, actual) = read_names(i) first_actual = FIRST_NAMES[actual & 0x0000FFFF] last_actual = LAST_NAMES[actual >> 16] final_name_actual = "%s %s" % (first_actual, last_actual) print("Validating...") print(" -> Final name (predicted):", final_name_predicted) print(" -> Final name (actual): ", final_name_actual) assert(final_name_predicted == final_name_actual) And prints out the 10 words that will be chosen: for i in range(10, 0, -1): word = predictor.getrandbits(32) print("Round %d: %s" % (10 - i + 1, WORDS[word & 0xFFFF])) # Waste RNG cycles for _ in range(1, (2**i) >> 1): predictor.getrandbits(64) To use it, I just connect to the game and tee the outpu | Hack Prediction | ★★★★ | ||
| 2021-02-02 00:00:00 | (Déjà vu) Mélanges clés de la montée des ransomwares en 2020: Ransomware-as-a-service et double extorse. Key Drivers of Rise of Ransomware in 2020: Ransomware-as-a-Service and Double ExtortionThe key drivers in the rise of ransomware have been double extortion and RaaS.Read More (lien direct) |
Ransomware-as-a-Service and Double ExtortionâRansomware has been a known method for cyber attacks for more than 30 years and has significantly evolved within this timespan. The growth in the number of ransomware attacks in 2020 has marked a pivotal milestone in the ransomware evolution. According to a Check Point study, Global Surges in Ransomware Attacks, in Q3 2020 the daily average of ransomware attacks has increased by 50%, and has specifically increased by 98.1% in the United States. Additionally, the average amount of money requested by attackers in Q3 2020 increased by 178% compared to Q4 of 2019. Supporting this trend, Coalitionâs Cyber Insurance Claims Report stated that more than 40% of the cyber incident claims in Q1 and Q2 2020 were due to ransomware attacks. âTaking into account these statistics, Kovrr has conducted research that included monitoring the activity of trending threats actors, the attacks they were involved with and the victims of these operations through 2020. The research included data from various proprietary and third party data sources including leaked data from the dark web. The research revealed that ransomware attacks have evolved in the following two areas:âMethodology - unlike ransomware attacks witnessed in the past, the last half year of 2020 was characterized by adoption of a new attack method which includes - stealing the companyâs data along with encrypting the attacked companyâs data. This practice is also known as âDouble Extortionâ because the attacker not only encrypts the data but also threatens to publish the companyâs stolen data.  Ransomware as - a - service (RaaS) - a method that recently became popular, which enables potential attackers to purchase already existing ransomware and use it for their desired purposes. âKovrr has researched 16 active âdouble extortionâ ransomware attack campaigns in the last year. Of the campaigns studied, 75% use social engineering (phishing emails) to propagate, while 25% of them involve exploiting a vulnerability in remote access software. In order to fully understand the effect of the ransomware campaigns, Kovrr applied the CRIMZON⢠framework to better analyze and report findings of the research. CRIMZON are an easy to use open framework to measure and understand cyber risk exposure that focus on the minimal elements needed to describe cyber risk accumulation. Elements of the CRIMZON include location, industry, and entity size. Applying the CRIMZON framework to the ransomware campaign research found the top 5 CRIMZON exposed were: âUS_NY_I_S [United States_New York_Services_Small Company]GB_I_S [Great Britain_Services_Small Company] CA_I_S [Canada_Services_Small Company] CA_E_S [Canada_Transportation & Communications_Small Company] US_CA_I_S [United States_California_Services_Small Company]âMost of the attacked companies are located in the U.S. (more than 50% of the targets), followed by Canada, the United Kingdom, Germany and France. Within the U.S., the main states affected were California, Texas, Florida and New York. The industries to which most of the attacked companies belong to are Services (20% of the services category is attributed to educational services), Transportation and Communication, and Manufacturing. âThese findings have a significant impact on the cyber insurance market both in terms of rising claim numbers and entity of the amount claimed. The increase in attacks is more concentrated in particular combinations of location, industry, and entity size (CRIMZON), meaning certain CRIMZON are more susceptible to an attack than others. This paper addresses new ransomware trend characteristics by providing an overview of two major ransomware campaigns encountered in the research; provides examples of ways in which a portfolio can be influenced as a result of the wide a | Ransomware Data Breach Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2020-09-17 23:41:21 | US sanctions Iranian government front company hiding major hacking operations (lien direct) | US says the Iranian government used the "Rana Intelligence Computing Company" as a front for the APT39 hacking group. | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-09-17 17:10:00 | Iranian Hackers Indicted for Stealing Aerospace & Satellite Tracking Data (lien direct) | Also, the US Treasury sanctioned Iranian attack group APT39 following a years-long malware campaign. | Malware Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-07-24 13:00:18 | Check Point CloudGuard Connect Protects Microsoft Azure Branch Office Internet Connections from Cyber Attacks (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms Enterprises are moving their applications, workloads and services out of the data center into the cloud. As enterprises become more distributed, organizations need flexible solutions that deliver secure and predictable application performance across a global footprint. Companies need to securely connect their branch offices to the… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-07-17 10:00:58 | Check Point IoT Protect Uses Automation and Threat Intelligence to Prevent the most advanced IoT cyber-attacks (lien direct) | Integrated solution prevents attacks at both IoT network and device level, even on unpatchable devices: protects critical infrastructure, industrial, healthcare, smart city and smart building environments By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms It is estimated that over 41 billion IoT devices will be connected in the next few years. Given 127 new… | Threat Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-05-21 11:49:49 | Iran-linked Chafer APT group targets governments in Kuwait and Saudi Arabia (lien direct) | Cybersecurity researchers uncovered an Iranian cyber espionage campaign conducted by Chafer APT and aimed at critical infrastructures in Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. Cybersecurity researchers from Bitdefender published a detailed report on an Iranian cyber espionage campaign directed against critical infrastructures in Kuwait and Saudi Arabia. The cyber espionage campaigns were carried out by Iran-linked Chafer […] | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-05-21 01:11:42 | Iranian APT Group Targets Governments in Kuwait and Saudi Arabia (lien direct) | Today, cybersecurity researchers shed light on an Iranian cyber espionage campaign directed against critical infrastructures in Kuwait and Saudi Arabia.
Bitdefender said the intelligence-gathering operations were conducted by Chafer APT (also known as APT39 or Remix Kitten), a threat actor known for its attacks on telecommunication and travel industries in the Middle East to collect personal |
Threat Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-05-20 13:00:40 | Check Point and Citrix: Securing the SD-WAN Edge with Multi-layered Security (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms The coronavirus has challenged enterprises to quickly enable their employees to work productively from home. Enterprises are turning away from traditional WAN architectures and adopting SD-WAN to provide better support for cloud SaaS applications. SD-WAN enables users to connect through their local Internet providers instead of… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2020-03-31 00:00:00 | Cyber Risk - du péril au produit adoptant une nouvelle approche pour gérer le cyber-risque silencieux Lire la suite Cyber Risk - From Peril to ProductTaking a New Approach for Managing Silent Cyber RiskRead More (lien direct) |
A New Approach for Managing Silent Cyber RiskâCyber is a multifaceted peril that is both a threat and an opportunity for the insurance industry: an opportunity because of the ever-evolving needs of coverage for businesses of any size, and a threat because of the systemic risk arising from its potential for overlap with other lines of business. Silent cyber refers to covered losses triggered by cyber events in P&C policies that were not specifically designed to cover cyber risk. Affirmative cyber refers to coverages specifically provided to protect policyholders against cyber events and presents a premium growth opportunity for insurance companies. As exposures to cyber continue to grow, insurance companies need tools to quantify the impact on allocated capital for cyber risk, regardless of whether the risk is silent or affirmative.With some estimates for accumulation across commercial lines running in the hundreds of billions, exposure managers are under pressure to more accurately estimate the potential impact of cyber events to ensure appropriate capital is held for this risk and enable decision makers, investors and regulators to quantify financial returns on a risk adjusted basis. Additionally, they are being forced to provide more transparency into methods used for measuring and controlling cyber accumulations. With various stakeholders and types of practitioners involved, the topic of cyber risk often presents seemingly conflicting priorities around managing capital at risk, estimating potential losses in existing lines of business, and finding new ways to market, through pricing new cyber specific business.Cyber events across different lines of business share a common trait. The key is to build tools capable of estimating realistic losses for both silent and affirmative cyber based on these shared traits. The focus of cyber risk for insurers should be gaining unique insights into events that truly matter -events capable of generating equity depleting losses. Measuring the impact of cyber events on capital is a three step process: identify, quantify and manage.Lately, the insurance industry seeks to consolidate most cyber risk into one dedicated line of business by implementing exclusion clauses in existing policies and inviting policy holders to âbuy backâ coverage. Several different wordings for such exclusions and endorsements have been introduced to the market. While intending to clearly define the scope of a cyber event and the coverage provided, the introduction of some of these clauses has produced unintended consequences. One example of this would be coverage for damage to a server due to flooding. In this example, the common expectation would be for the physical damage to the server as well as recovery of the data to be covered under flood insurance, however, the latest trend suggests data recovery might be excluded, as it relates to âdataâ, leaving a gap in coverage for property which some sources consider excessive.âSilent and AffirmativeThe issue with silent cyber, as with any circumstance presenting unexpected claims activity, is ensuring the premium charged is commensurate with the level of risk, usually referred to as pricing adequacy. Both cyber exposure and the potential impact of losses triggered by cyber perils continues to trend upwards annually. Unexpected claims lead to unexpectedly high loss ratios which clearly erode profits but can also lead to significant damage to an insurerâs financial stability.Insurance companies protect their balance sheets by purchasing reinsurance, but reinsurers face similar issues, they are also vulnerable to silent cyber. Therefore, insurers face the prospect of being denied recoveries from cyber losses and reinsurers are stepping up demands for clarity of coverage. Efforts to resolve the situation have taken two complementary directions: a conscious attempt to price for cyber risk and the introduction of increasingly restrictive exclusion clauses.âThe Status of Cyber ExclusionsCyber | Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2020-03-23 07:00:00 | Surveillance des outils de cyber-opération ICS et des modules d'exploitation de logiciels pour anticiper les menaces futures Monitoring ICS Cyber Operation Tools and Software Exploit Modules To Anticipate Future Threats (lien direct) |
Il n'y a eu qu'un petit nombre de cyberattaques largement documentées ciblant les technologies opérationnelles (OT) / systèmes de contrôle industriel (ICS) au cours de la dernière décennie.Bien que moins d'attaques soit clairement une bonne chose, l'absence d'une taille d'échantillon adéquate pour déterminer les seuils de risque peut rendre difficile pour les défenseurs de comprendre l'environnement de menace, de hiérarchiser les efforts de sécurité et de justifier l'allocation des ressources.
Pour résoudre ce problème, Fireeye Mandiant Threat Intelligence produit une gamme de rapports pour abonnement Les clients qui se concentrent sur différents indicateurs pour prédire les menaces futures
There has only been a small number of broadly documented cyber attacks targeting operational technologies (OT) / industrial control systems (ICS) over the last decade. While fewer attacks is clearly a good thing, the lack of an adequate sample size to determine risk thresholds can make it difficult for defenders to understand the threat environment, prioritize security efforts, and justify resource allocation. To address this problem, FireEye Mandiant Threat Intelligence produces a range of reports for subscription customers that focus on different indicators to predict future threats |
Tool Threat Industrial Prediction | ★★★★ | ||
| 2020-03-22 00:00:00 | Comment l'IoT industriel pourrait déclencher le prochain cyber-catastrophieffect d'urgence / 11 sur l'industrie manufacturière américaine révèle 7 milliards de dollars pour les eaux autres How Industrial IoT could Trigger the Next Cyber CatastropheEffect of URGENT/11 on the US Manufacturing Industry Reveals $7 Billion ExposureRead More (lien direct) |
IntroductionOn 29th July 2019, the cyber security firm Armis announced that it had found eleven different vulnerabilities in the operating system âVXworksâ which they believe exposed around 200 million critical devices. The team at Armis dubbed this group of vulnerabilities: URGENT/11. This report explores how the discovery of URGENT/11 demonstrates the susceptibility of global manufacturing businesses to large losses from a cyber-attack event and the potential impact on commercial P&C (re)insurers.âThe Operating System at the Heart of the IssueVxWorks is a widely used, but lesser known, lightweight IoT real-time operating system (RTOS). This operating system is embedded in over 2 billion devices in the US and worldwide. These range from large-scale industrial machinery controlling installations such as nuclear power stations and oil production platforms, to smaller systems throughout the worldâs automotive, aviation, agri-business, textile, logistics and pharmaceutical facilities. A malicious attack could affect what is known as the SupervisoryControl and Data Acquisition (SCADA), the system that allows industrial organizations to gather and monitor real-time data in their manufacturing and distribution systems. Critically, VxWorks is also part of what are known as Industrial Control Systems (ICS) â software that manages the industrial processes themselves.âNot a Quick FixAs with any type of software vulnerability, affected organizations need to patch vulnerabilities quickly. However, in the case of URGENT/11, the necessary patches can be very expensive to apply immediately, because the affected devices are critical to day-to-day operations. Patching a vulnerability requires stopping or interrupting the device, which could lead to significant business disruption. Furthermore, while very large organizations have the financial and technical resources to implement system patches quickly, smaller manufacturers â who may nevertheless be critical to the supply chain â often do not. They may buy equipment that happens to contain VxWorks, but do not expect to have to maintain the software or even be aware of its existence.âQuantifying URGENT/11âs Potential Loss Scenarios for the US Manufacturing IndustryTo understand the extent of companies that were vulnerable to URGENT/11, their susceptibility to being attacked, and the effect an attack might have industry wide, Kovrr deployed its proprietary technologies. The first step was to gather real-time information about the distribution of VxWorks in the US manufacturing sector. To achieve this, Kovrr leveraged its ability to continuously collect relevant business intelligence, cyber threat intelligence, external and internal security data. As a result, we were able to identify companies with devices that were utilizing the VxWorks operating system. For internal mapping, access to multiple security vendors\' data is essential because each vendor has its own expertise and distribution, in terms of geolocation, served industries, defense level focus, mapped devices, etc. In the case below involving an industrial sector, unique data focused on IoT devices is needed. Kovrr partners with a diverse range of data providers to detect and map beyond the firewall devices and security control mechanisms. By having access to Armis\' proprietary IoT fingerprinting technology, we were able to produce a highly granular map of any IoT device being used by one organization.We can then accurately assess any IoT related emerging vulnerability on clients\' portfolios. In order to understand the nature of these businesses, including their sector, size and place in the supply chain; we use publicly available information linked to a variety of proprietary data-sources including our own. This technique is similar in principle to the exposure-data cleansing and augmentation used by catastrophe modelers. Having developed a sophisticated view of the affected businesses, we have selected a series of events fro | Ransomware Vulnerability Threat Industrial Prediction | ★★★★ | ||
| 2019-12-06 13:00:09 | Protect Your Network Edge with VMware SD-WAN and Check Point Security (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms, published December 6th, 2019 As enterprise branch offices expand their use of cloud applications, they are adopting software defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) to improve application performance by intelligently routing traffic directly to the Internet without passing it through the data center. Connecting branch offices directly… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-11-05 19:13:49 | Check Point Protects Branch Office Microsoft Azure Internet Connections and SaaS Applications from Cyber Attacks (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms, published November 5, 2019 Enterprises are moving their applications, workloads and services out of the data center into the cloud. As enterprises become more distributed, organizations need flexible solutions that deliver secure and predictable application performance across a global footprint. Companies need to securely connect their… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-10-01 15:00:44 | Check Point and VMware Partner to Secure Branch Office SD-WAN Connections to the Cloud (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms As more applications move from the datacenter to the cloud, enterprise users rely on these applications to do their daily jobs. These SaaS applications range from productivity software like Office 365 to virtual meeting and collaboration tools like Zoom and Slack. Applications that include voice and… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-09-05 13:00:43 | (Déjà vu) Check Point, VMware and Silver Peak Transform Branch Office SD-WAN with Cloud Security Services (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms Enterprise security solutions enable branch offices to connect safely and reliably to the data center, the Internet and cloud applications. In the past, branches relied on centralized security gateways at their data center to protect the entire enterprise. Enterprises sent branch traffic to the data center… | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-09-05 13:00:04 | Transforming Branch Security with Top-Rated Threat Prevention Cloud Services Integrated with VMware and Silver Peak SD-WAN (lien direct) | By Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms Enterprise security solutions enable branch offices to connect safely and reliably to the data center, the Internet and cloud applications. In the past, branches relied on centralized security gateways at their data center to protect the entire enterprise. Enterprises sent branch traffic to the data center… | Threat Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-04-12 13:00:00 | Things I hearted this week 12th April 2019 (lien direct) |
Hello again to another weekly security roundup. This week, I have a slightly different spin on the roundup in that the net has been slightly widened to include broader technology topics from more than just this last week. However, all of the articles were written by ladies. With that, let’s dive straight in.
A beginner's guide to test automation
If you’re new to automated testing, you’re probably starting off with a lot of questions: How do I know which tests to automate? Why is automated testing useful for me and my team? How do I choose a tool or framework? The options for automated testing are wide open, and you may feel overwhelmed.
If so, this is a great article on how to get started.
A Beginner's Guide to Test Automation | Sticky Minds
_500_353.jpg) All roads lead to exploratory testing
When I’m faced with something to test – be it a feature in a software application or a collection of features in a release, my general preference is weighted strongly towards exploratory testing. When someone who doesn’t know a great deal about testing wants me or my team to do testing for them, I would love to educate them on why exploratory testing could be a strong part of the test strategy.
All roads lead to exploratory testing | Womentesters
While on the topic of testing
Testing Behaviours — Writing A Good Gherkin Script | Medium, Jo Mahadevan
Single-page, server-side, static… say what?
An emoji-filled learning journey about the trade-offs of different website architectures, complete with gifs, diagrams, and demo apps.
If you’ve been hanging around the internet, trying to build websites and apps, you may have heard some words in conversation like static site or server-side rendered (SSR) or single-page app (SPA).
But what do all of these words mean? How does each type of application architecture differ? What are the tradeoffs of each approach and which one should you use when building your website?
Single-Page, Server-Side, Static… say what? | Marie Chatfield
If, like me you enjoyed this post by Marie, check out some of her other posts which are great. Quick plug to Protocol-andia: Welcome to the Networking Neighborhood. A whimsical introduction to how computers talk to each other, and what exactly your requests are up to.
Strengthen your security posture: start with a cybersecurity framework
The 2017 Equifax data breach is expected to break all previous records for data breach costs, with Larry Ponemon, chairman of the Ponemon Institute, estimating the final cost to be more than $600 million.
Even non-enterprise-level organizations suffer severe consequences for data breaches. According to the National Cyber Security Alliance, mid-market companies pay more than $1 million in post-attack mitigation, and the average cost of a data breach to an SMB is $117,000 per incident. While estimates vary, approximately 60% of businesses who suffer a breach are forced to shut down business within 6 months.
It is mor
All roads lead to exploratory testing
When I’m faced with something to test – be it a feature in a software application or a collection of features in a release, my general preference is weighted strongly towards exploratory testing. When someone who doesn’t know a great deal about testing wants me or my team to do testing for them, I would love to educate them on why exploratory testing could be a strong part of the test strategy.
All roads lead to exploratory testing | Womentesters
While on the topic of testing
Testing Behaviours — Writing A Good Gherkin Script | Medium, Jo Mahadevan
Single-page, server-side, static… say what?
An emoji-filled learning journey about the trade-offs of different website architectures, complete with gifs, diagrams, and demo apps.
If you’ve been hanging around the internet, trying to build websites and apps, you may have heard some words in conversation like static site or server-side rendered (SSR) or single-page app (SPA).
But what do all of these words mean? How does each type of application architecture differ? What are the tradeoffs of each approach and which one should you use when building your website?
Single-Page, Server-Side, Static… say what? | Marie Chatfield
If, like me you enjoyed this post by Marie, check out some of her other posts which are great. Quick plug to Protocol-andia: Welcome to the Networking Neighborhood. A whimsical introduction to how computers talk to each other, and what exactly your requests are up to.
Strengthen your security posture: start with a cybersecurity framework
The 2017 Equifax data breach is expected to break all previous records for data breach costs, with Larry Ponemon, chairman of the Ponemon Institute, estimating the final cost to be more than $600 million.
Even non-enterprise-level organizations suffer severe consequences for data breaches. According to the National Cyber Security Alliance, mid-market companies pay more than $1 million in post-attack mitigation, and the average cost of a data breach to an SMB is $117,000 per incident. While estimates vary, approximately 60% of businesses who suffer a breach are forced to shut down business within 6 months.
It is mor |
Guideline Prediction | Equifax APT 39 | ||
| 2019-04-11 13:00:03 | Protect Your Business by Managing Network Security from the Palm of Your Hand (lien direct) | by Russ Schafer, Head of Product Marketing, Security Platforms, published April 11th 2019 Next generation cyber security attacks can happen at any time to any size business, so you need to be prepared to react immediately. Based on the 2018 Verizon Data Breach report, 58% of security breach victims are categorized as small… | Data Breach Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-03-05 21:23:03 | Iran-Linked Chafer APT recently used python-based backdoor (lien direct) | The Iran-linked Chafer APT group used a new Python-based backdoor in recent attacks aimed at a Turkish government entity. The Iran-linked Chafer APT group used a new Python-based backdoor in attacks carried out in November 2018 that targeted a Turkish government entity. The Chafer APT group has distributed data stealer malware since at least mid-2014, […] | Malware Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-03-05 15:30:05 | Iran-Linked Hackers Use Python-Based Backdoor in Recent Attacks (lien direct) | The Iran-linked Chafer threat group has used a new Python-based backdoor in November 2018 attacks targeting a Turkish government entity, Palo Alto Networks reveals. | Threat Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2019-01-30 08:58:00 | Iran-Linked APT39 group use off-the-shelf tools to steal data (lien direct) | An Iran-linked cyber-espionage group tracked as APT39 is carrying out a widespread campaign using a broad range of custom and off-the-shelf tools. The APT39 cyberespionage group is carrying out a widespread campaign using a broad range of custom and off-the-shelf tools. The group has been active at least since November 2014, its operations are aligned […] | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2018-03-08 21:11:01 | Chafer : un groupe de cyber attaquants basé en Iran (lien direct) | Un groupe de pirates informatiques, baptisé Chafer s’attaquerait aux entreprises du monde entier. Des amateurs du blackmarket... L'article Chafer : un groupe de cyber attaquants basé en Iran est apparu en premier sur Data Security Breach. | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2018-03-01 19:06:00 | Iran-Linked Chafer Group Expands Toolset, Targets List (lien direct) | The Iran-based targeted attack group known as "Chafer" has been expanding its target list in the Middle East and beyond and adding new tools to its cyberweapon arsenal, Symantec warns. | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2018-03-01 15:32:02 | Iran Taps Chafer APT Group amid Civil Aviation Crisis (lien direct) | Iran’s Chafer hacking group is targeting aviation repair and maintenance firms in an apparent effort to obtain information needed to shore up the safety of that country’s fleet of domestic aircraft, according to research by the firm Symantec. When an Aseman Airlines flight crashed in bad weather in a mountainous region of southern Iran...Read the whole entry... _!fbztxtlnk!_ https://feeds.feedblitz.com/~/529622610/0/thesecurityledger -->» | Prediction | APT 39 | ||
| 2017-10-19 09:00:00 | Magnber Ransomware veut infecter uniquement les bonnes personnes Magniber Ransomware Wants to Infect Only the Right People (lien direct) |
L'utilisation du kit d'exploitation (EK) est en baisse depuis la fin de 2016;Cependant, une certaine activité reste cohérente.Le kit d'exploitation de magnitude est un tel exemple qui continue d'affecter les utilisateurs, en particulier dans la région de l'APAC.
Dans la figure 1, qui est basée sur les données recueillies en mars 2017, nous pouvons voir les régions affectées par l'activité EK de magnitude au cours des trois derniers mois de 2016 et les trois premiers mois de 2017.
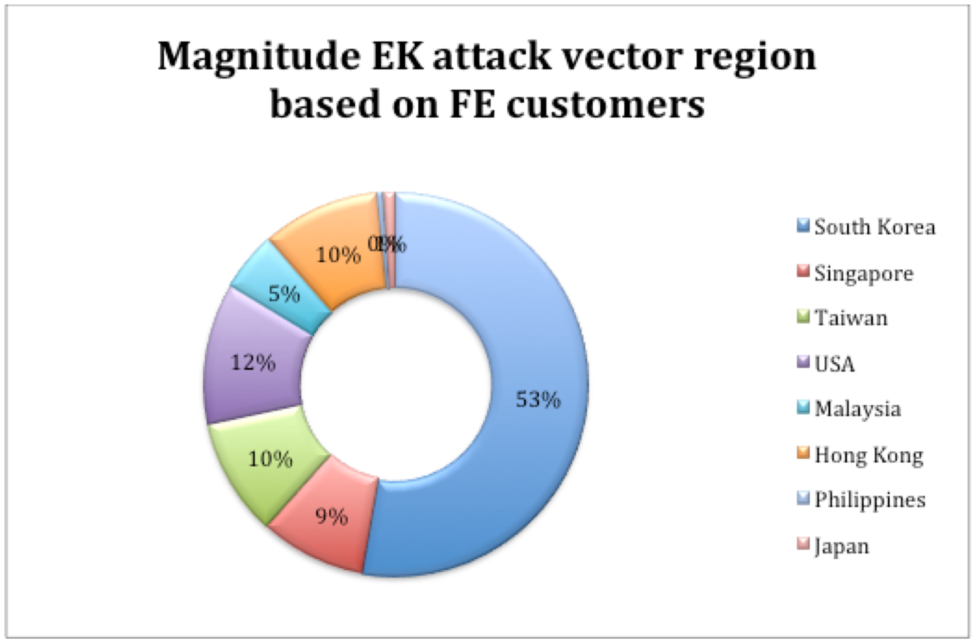 Figure 1: Distribution de l'amplitude EK comme le montre en mars 2017 Cette tendance s'est poursuivie jusqu'à la fin de septembre 2017, lorsque nous avons vu la magnitude EK se concentrer principalement sur la région de l'APAC, avec une grande partie ciblant la Corée du Sud.Activité EK de l'amplitude est ensuite tombée Figure 1: Distribution de l'amplitude EK comme le montre en mars 2017 Cette tendance s'est poursuivie jusqu'à la fin de septembre 2017, lorsque nous avons vu la magnitude EK se concentrer principalement sur la région de l'APAC, avec une grande partie ciblant la Corée du Sud.Activité EK de l'amplitude est ensuite tombée
Exploit kit (EK) use has been on the decline since late 2016; however, certain activity remains consistent. The Magnitude Exploit Kit is one such example that continues to affect users, particularly in the APAC region. In Figure 1, which is based on data gathered in March 2017, we can see the regions affected by Magnitude EK activity during the last three months of 2016 and the first three months of 2017.  Figure 1: Magnitude EK distribution as seen in March 2017This trend continued until late September 2017, when we saw Magnitude EK focus primarily on the APAC region, with a large chunk targeting South Korea. Magnitude EK activity then fell off Figure 1: Magnitude EK distribution as seen in March 2017This trend continued until late September 2017, when we saw Magnitude EK focus primarily on the APAC region, with a large chunk targeting South Korea. Magnitude EK activity then fell off |
Ransomware Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2016-08-22 07:00:00 | Piratage matériel intégré 101 & # 8211;Le lien Belkin Wemo Embedded Hardware Hacking 101 – The Belkin WeMo Link (lien direct) |
Pourquoi le piratage intégré?
Les appareils connectés à Internet ou exécutent un système d'exploitation complet deviennent de plus en plus répandus dans la société d'aujourd'hui.Des appareils pour les locomotives aux commutateurs d'éclairage sans fil, la tendance de l'Internet des objets (IoT) est en augmentation et ici pour rester.Cela a le potentiel de nous faciliter la vie;Cependant, la sensibilité croissante des appareils analogiques une fois permet également aux adversaires de les cibler et de les utiliser potentiellement.
Avec l'omniprésence de ces appareils connectés à Internet, il y a un excédent de «choses» à exploiter.L'intention principale de cet article de blog est
Why Embedded Hacking? Devices that are connected to the Internet or run a full operating system are becoming more and more prevalent in today\'s society. From devices for locomotives to wireless light switches, the Internet of Things (IoT) trend is on the rise and here to stay. This has the potential to make our lives much easier; however, the increasing sentience of once analog devices also enables adversaries to target them and potentially misuse them. With the ubiquity of these Internet-connected devices, there is a surplus of “Things” to exploit. The main intent of this blog post is |
Prediction Technical | ★★★★ |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
