One Article Review
| Source | |
|---|---|
| Identifiant | 8388447 |
| Date de publication | 2023-09-27 12:51:29 (vue: 2023-09-27 17:06:49) |
| Titre | Les lacunes de sécurité et de confidentialité SMS montrent clairement que les utilisateurs ont besoin d'une mise à niveau de messagerie SMS Security & Privacy Gaps Make It Clear Users Need a Messaging Upgrade |
| Texte | Posted by Eugene Liderman and Roger Piqueras Jover
SMS texting is frozen in time.
People still use and rely on trillions of SMS texts each year to exchange messages with friends, share family photos, and copy two-factor authentication codes to access sensitive data in their bank accounts. It\'s hard to believe that at a time where technologies like AI are transforming our world, a forty-year old mobile messaging standard is still so prevalent.
Like any forty-year-old technology, SMS is antiquated compared to its modern counterparts. That\'s especially concerning when it comes to security.
The World Has Changed, But SMS Hasn\'t Changed With It
According to a recent whitepaper from Dekra, a safety certifications and testing lab, the security shortcomings of SMS can notably lead to:
SMS Interception: Attackers can intercept SMS messages by exploiting vulnerabilities in mobile carrier networks. This can allow them to read the contents of SMS messages, including sensitive information such as two-factor authentication codes, passwords, and credit card numbers due to the lack of encryption offered by SMS.
SMS Spoofing: Attackers can spoof SMS messages to launch phishing attacks to make it appear as if they are from a legitimate sender. This can be used to trick users into clicking on malicious links or revealing sensitive information. And because carrier networks have independently developed their approaches to deploying SMS texts over the years, the inability for carriers to exchange reputation signals to help identify fraudulent messages has made it tough to detect spoofed senders distributing potentially malicious messages.
These findings add to the well-established facts about SMS\' weaknesses, lack of encryption chief among them.
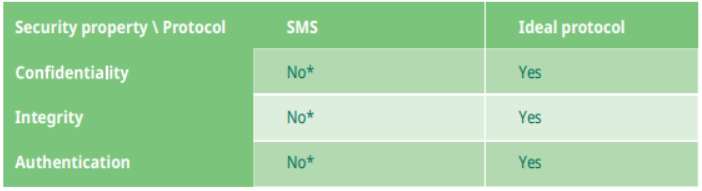
Dekra also compared SMS against a modern secure messaging protocol and found it lacked any built-in security functionality. According to Dekra, SMS users can\'t answer \'yes\' to any of the following basic security questions:
Confidentiality: Can I trust that no one else can read my SMSs?
Integrity: Can I trust that the content of the SMS that I receive is not modified?
Authentication: Can I trust the identity of the sender of the SMS that I receive?
 But this isn\'t just theoretical: cybercriminals have also caught on to the lack of security protections SMS provides and have repeatedly exploited its weakness. Both novice hackers and advanced threat actor groups (such as UNC3944 / Scattered Spider and APT41 investigated by Mandiant, part of Google Cloud) leverage the security deficiencies in SMS to launch different
But this isn\'t just theoretical: cybercriminals have also caught on to the lack of security protections SMS provides and have repeatedly exploited its weakness. Both novice hackers and advanced threat actor groups (such as UNC3944 / Scattered Spider and APT41 investigated by Mandiant, part of Google Cloud) leverage the security deficiencies in SMS to launch different |
| Envoyé | Oui |
| Condensat | 500 ability about abused access according accounts across actor add advanced against alike all allow already also among android androids answer antiquated any appear approaches apt41 are attackers attacks authentication authentication: bank basic because been before began believe between both built but can card care carrier carriers caught certifications chain changed chief clear clicking cloud codes collectively comes compared concerning confidentiality: content contents continued copy corporate corporations counterparts credit cyber cybercriminals data default deficiencies dekra depend deploying desire detect developed device different distributing drastically due each easily ecosystem else enable enabled encryption era especially established eugene ever everyone evolution examined exchange exploit exploited exploiting factor facts family feel financial findings fixed following forty found fraudulent friends from frozen functionality gaps global google groups hackers hard has hasn have help how however identify identity importance important improve inability including independently industry information insecurity integrity: intercept interception: investigated ios iphones isn its jover just lab lack lacked landscape large largely launch lead legitimate leverage liderman like link links losses made make malicious mandiant manufacturers may messages messaging mobile modern modified more most move moves need networks new not notably novice now numbers offered old one only over owe part particularly passwords people personal phishing phone photos piqueras platforms possible posted potentially prevalent privacy problem prominent protect protection protections protocol protocols provide provides questions: rcs read receive receiving recent regardless relates rely remains repeatedly reputation resulted revealing revert roger safe safety scattered secure security sender senders sending sensitive services shame share shortcomings should signals simple: smartphone sms smss solution something spider spoof spoofed spoofing: standard strong study such support technologies technology testing text texting texts than that theft them theoretical: these think threat time to: today tough towards transforming trick trillions trust two types unauthorized unc3944 understand unfortunately upgrade use used users using vulnerabilities want weak weakest weakness weaknesses well what when where whether whitepaper widely will world worse would year years yes yougov |
| Tags | Vulnerability Threat Studies |
| Stories | APT 41 |
| Notes | ★★★ |
| Move | 

|
L'article ne semble pas avoir été repris aprés sa publication.
L'article ne semble pas avoir été repris sur un précédent.