One Article Review
| Source | |
|---|---|
| Identifiant | 8455968 |
| Date de publication | 2024-02-27 11:00:00 (vue: 2024-02-27 17:08:06) |
| Titre | L'évolution du point de terminaison - passant des critères de terminaison traditionnels aux charges de travail cloud ou conteneurisées et les solutions de sécurité pour les protéger The endpoint evolution - Evolving from traditional endpoints to cloud or containerized workloads and the security solutions to protect them |
| Texte | As organizations grow and more endpoints are added across the enterprise, they create an increasingly broad attack surface sophisticated attackers are looking to compromise. According to the 2019 Endpoint Security Trends Report 70% of breaches originate at the endpoint¹. That is likely because endpoints typically represent the Intersection between humans and machines creating vulnerable points of entry for cybercriminals. This is why it is increasingly important to secure your endpoints.
Growth in endpoints
An endpoint is defined as any computing device that communicates back and forth with a network to which it is connected. Some end user devices serve as an interface with human users while others are servers that communicate with other endpoints on the network. Traditional endpoints began as physical devices including servers, workstations, desktops, and laptops, all connected to a corporate network. When smartphones and tablets became handheld computing devices with access to corporate email, document sharing and collaboration tools the number of endpoints at least doubled.
Then came the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) including devices like printers, webcams, smartwatches, and thermostats, all of which are connected to the network. Industries like healthcare and manufacturing are using millions of IoT sensors to collect and exchange data. This continued growth in IoT only increases the number of endpoints that need to be protected.
Another contribution to the growth in endpoints is the migration to the cloud. It is estimated that 67% of enterprise infrastructure is cloud-based². This cloud transformation is the evolution from physical devices to virtualization and containerization.
Endpoint virtualization
The cloud is a multi-tenant environment where multiple users run services on the same server hardware. Virtualization and containerization are both virtualization technologies that separate the host operating system from the programs that run in them.
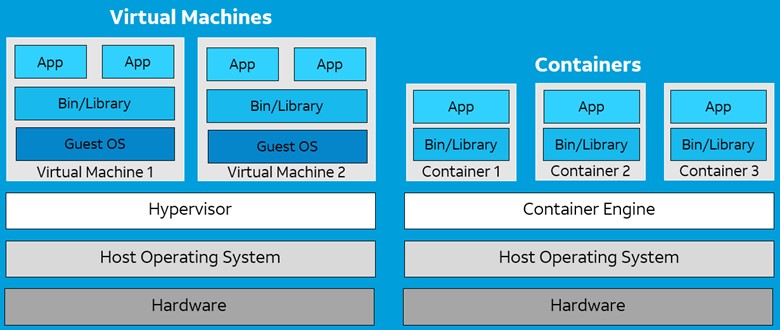 Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi
Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi |
| Envoyé | Oui |
| Condensat | “must “nice these ¹absolute ²saasworthy 2019 2023 access according achieved across activity added addition advances against all allows also analysis analytics analyzes another anti antivirus any app application applications apps architectures are attack attackers attacks back based based² became because becoming began behaves behavior behavioral behaviors being between beyond blocking both breaches broad broader build businesses but came can capacity case certificates challenges checking ci/cd cloud clusters code collaboration collect combined common communicate communicates compel completing complex compliance compromise compromised computer computing configurations connected connections considerations container containerization containerized containers containing continue continued continues contribution controls corporate could cpu create creating cspm current customer cwpp cybercriminals data database decades defense defined deliver delivering demand deployed desktops detect detection detects device devices devops different discovery document does doubled downloads dynamic each easily edr efficiency email emulation enable encryption end endpoint endpoint¹ endpoints engine engineering engineers enterprise entry environment environments epp escalations estimated evolution evolve evolving exchange exploit expose facet features feeds fileless filtering flexibility forensic forth from function future gets grow growth guest hand handheld hardware have have” healthcare heavily help helps host however human humans hunting hybrid hypervisor identified images important improve incident including increases increasingly independent independently individual industries infrastructure inject innovative instance instances integrating integration intelligence interface internet intersection invalid investigations iot just keeps known kubernetes laptops layered learning least less let’s level libraries lifecycle like likely longer look looking lured machine machines malicious malware man management manages manufacturing matching meet metadata microservice middle migration millions mobile modern monitoring more most mtd much multi multiple native need needed needs network not number offer often one only onto operate operating optimize orchestration organization’s organizations originate other others overlooked package parameters phishing physical pipeline platform platforms points posture potential present prevent prevents printers private privilege process programs protect protected protection protects provide provides providing public ram range recording regulation relied remediate report reporting represent resilience resources respond responders response reverse rise risky run runs runtime safe same scalability scale secure securing security selecting sensitive sensors separate serve server servers services sharing signature signatures single smartphones smartwatches software solution solutions some sophisticated splits splitting standards statistics storage storing support surface system tablets techniques technologies technology tenant testing them then thermostats these things threat threats throughout today today’s tools traditional transformation transformations trends typically use used user users uses using various vendors versions very virtual virtualization virtualization visibility vms vulnerabilities vulnerable web webcams websites went when where which why will worked workload workloads workstations your |
| Tags | Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Cloud |
| Stories | |
| Notes | ★★ |
| Move | 

|
L'article ne semble pas avoir été repris aprés sa publication.
L'article ne semble pas avoir été repris sur un précédent.