What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2024-04-29 10:00:00 | Améliorer la sécurité financière grâce à la biométrie comportementale Enhancing Financial Security Through Behavioral Biometrics (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. The evolution of tech necessitates stronger cybersecurity. Financial information is appealing to hackers trying to steal identities and commit fraud. These bad actors are evolving with tech to figure out ways to bypass the increasingly robust cybersecurity measures. Organizations commonly use physical biometric applications, like fingerprinting and facial recognition, when they’re conducting transactions, when people are entering buildings, and when they’re logging into sites with sensitive information. However, you need a stronger layer of security to keep your information safe. This is where behavioral biometrics comes in. Possible Financial Security Issues Consumers lose millions of dollars due to fraud every year, according to the FTC. Online shopping is the number one avenue where this money is lost, with bad investments and illegitimate businesses falling close behind. There is an increasing amount of ways that scammers can have access to your information or social engineer you into spending money. Some examples include phishing emails, password attacks, and malware. Often, hackers will also target people whom they profile as gullible. Charity scams are unfortunately rampant, including scammers pretending to be charitable organizations like the Red Cross. These crop up when disaster strikes, and they masquerade as legitimate ways to donate. Other scammers will pretend to be individuals in need, family members, or even government organizations. Instead, the money goes to illegitimate scammers. To avoid this, you should always double-check links and, more importantly, log in to a reputable site when entering any credit card or banking information. Financial institutions are surprisingly not the most targeted, but they are still rife with sensitive info that can be vulnerable to hackers if not guarded correctly. Cybersecurity in online banking is extremely important. There can be data breaches, customer phishing scams, and even offshore banking transparency issues. Enhanced security must be in place to prevent these scams, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, threat detection, and biometrics. Why Stronger Biometrics Are Necessary Physical biometrics are the most common form of biometrics employed for financial security currently. However, bad actors have learned how to bypass these physical barriers. Printed-out photos can work for face identification, and fingerprints and palm prints can be stolen and imprinted onto soft surfaces and then used for sign-ins. Evolving threats demand cybersecurity measures that are as far advanced as possible. Behavioral biometrics takes things a step further by analyzing the behavior patterns of device users. Then, these patterns can be developed over time and set to be recognized by the device. These behaviors can be digital or in-person and include factors like: Gait; Posture; Signatures; | Malware Threat | Deloitte | ★★ | |
| 2024-03-25 10:00:00 | Décodage des implications de cybersécurité de l'avancement rapide de l'AI \\ Decoding the Cybersecurity Implications of AI\\'s Rapid Advancement (lien direct) |
The genius at the heart of AI—its ability to sift through mountains of data, actually spot a needle in a haystack, and act on threats before they blossom into full-scale emergencies—it’s undeniable. However, here’s the rub—every part of that impressive arsenal? It’s also up for grabs by the other side, and can (and will) arm them to launch attacks of unprecedented sophistication and elusiveness, the likes of which we’ve thankfully never seen up to now. How do we wield this impressive technology to fortify our defenses, while preventing it from falling into the wrong hands? Can such a thing even be accomplished? Join me below as we take a closer look at how AI’s rapid rise is changing the landscape of cybersecurity. AI as a Defense Tool AI is a reliable navigator for charting the digital deluge—it has the ability to handle vast quantities of information rapidly on a level that no human could ever hope to match. It doesn’t take a huge leap to come to the conclusion that those capabilities can very easily be leveraged for defense. Automated Threat Detection Think of AI as the ever-watchful eye, tirelessly scanning the horizon for signs of trouble in the vast sea of data. Its capability to detect threats with speed and precision beyond human ken is our first line of defense against the shadows that lurk in the network traffic, camouflaged in ordinary user behavior, or embedded within the seemingly benign activities of countless applications. AI isn’t just about spotting trouble; it’s about understanding it. Through machine learning, it constructs models that learn from the DNA of malware, enabling it to recognize new variants that bear the hallmarks of known threats. This is akin to recognizing an enemy’s tactics, even if their strategy evolves. All of what I’ve said also here applies to incident response—with AI’s ability to automatically meet threats head-on making a holistic cybersecurity posture both easier to achieve and less resource-intensive for organizations of all sizes. Predictive Analytics By understanding the patterns and techniques used in previous breaches, AI models can predict where and how cybercriminals might strike next. This foresight enables organizations to reinforce their defenses before an attack occurs, transforming cybersecurity from a reactive discipline into a proactive strategy that helps prevent breaches rather than merely responding to them. The sophistication of predictive analytics lies in its use of diverse data sources, including threat intelligence feeds, anomaly detection reports, and global cybersecurity trends. This comprehensive view allows AI systems to identify correlations and causations that might elude human analysts. Phishing Detection and Email Filtering AI has stepped up as a pivotal ally in the ongoing skirmish against phishing and other forms of social engineering attacks, which too often lay the groundwork for more invasive security breaches. Through meticulous analysis of email content, context, and even the | Spam Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction Technical | Deloitte | ★★ | |
| 2023-12-15 13:00:05 | Apprendre à connaître: Royce Ho Getting to Know: Royce Ho (lien direct) |
> Royce Ho est consultant régional en matière de sécurité de la prévention des menaces pour l'Asie du Sud-Est & # 38;Région de la Corée (Seak) chez Check Point Software Technologies.Avant le point de contrôle, il a travaillé chez CSintelligence, Deloitte, F5 Networks et StarHub.Royce a obtenu un baccalauréat \\ de sciences en systèmes d'information et de la sécurité et de l'assurance de l'information de la Singapore Management University.Royce, comment êtes-vous entré dans la cybersécurité?J'ai obtenu mon diplôme de Singapore Management University (SMU) avec une double majeure en systèmes d'information et en sécurité et assurance de l'information.C'est à ce moment-là que ma curiosité dans la cybersécurité a été piquée, et les connaissances que j'ai acquises tout au long de mes journées académiques m'ont permis [& # 8230;]
>Royce Ho is a Regional Threat Prevention Security Consultant for the Southeast Asia & Korea (SEAK) region at Check Point Software Technologies. Prior to Check Point, he worked at CSIntelligence, Deloitte, F5 Networks and StarHub. Royce received a Bachelor\'s of Science in Information Systems and Information Security and Assurance from Singapore Management University. Royce, how did you get into cybersecurity? I graduated from Singapore Management University (SMU) with a double major in Information Systems and Information Security and Assurance. That was when my curiosity in cybersecurity was piqued, and the knowledge that I gained throughout my academic days enabled me […] |
Threat | Deloitte | ★★★ | |
| 2023-09-27 10:00:00 | Combiner la sécurité et la sécurité des OT pour une gestion des cyber-risques améliorée Combining IT and OT security for enhanced cyber risk management (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Integrating IT and OT security for a comprehensive approach to cyber threats in the digital age. Historically, IT and OT have operated in separate worlds, each with distinct goals and protocols. IT, shaped by the digital age, has always emphasized the protection of data integrity and confidentiality. In this space, a data breach can lead to significant consequences, making it crucial to strengthen digital defenses. On the other hand, OT, a legacy of the Industrial Revolution, is all about ensuring machinery and processes run without interruptions. Any machine downtime can result in major production losses, making system availability and safety a top priority. This difference in focus has created a noticeable cultural gap. IT teams, often deep into data management, might not fully grasp the real-world impact of a stopped production line. Similarly, OT teams, closely connected to their machines, might not see the broader impact of a data breach. The technical challenges are just as significant. OT systems are made up of specialized equipment, many from a time before cybersecurity became a priority. When these older systems connect to modern IT networks, they can become weak points, open to today\'s cyber threats. This risk is even higher because many OT systems use unique protocols and hardware. These systems, once isolated, are now part of more extensive networks, making them accessible and vulnerable through different points in an organization\'s network. Additionally, common IT tasks, like updating software, can be more complex in OT. The equipment in OT often has specific requirements from their manufacturers. What\'s standard in IT can become a complicated task in OT because of the particular nature of its systems. Combining IT and OT is more than just a technical task; it\'s a significant change in how companies see and manage risks. From the physical risks during the Industrial Revolution, we\'ve moved to a time when online threats can have real-world effects. As companies become part of bigger digital networks and supply chains, the risks increase. The real challenge is how to unify IT and OT security strategies to manage cyber risks effectively. The imperative of unified security strategies According to a Deloitte study, a staggering 97% of organizations attribute many of their security challenges to their IT/OT convergence efforts. This suggests that the convergence of IT and OT presents significant challenges, highlighting the need for more effective security strategies that integrate both domains. Steps to integrate IT and OT security: Acknowledge the divide: The historical trajectories of IT and OT have been distinct. IT has emerged as a standardized facilitator of business processes, while OT has steadfastly managed tangible assets like production mechanisms and HVAC systems. Therefore, the first step towards a unified front is recognizing these inherent differences and fostering dialogues that bridge the understanding gap between IT and OT teams and leaders. Develop a unified security framework: Optimized architecture: Given the distinct design principles of OT, which traditionally prioritized isolated operations, it\'s crucial to devise an architecture that inherently safeguards each component. By doing so, any vulnerability in one part of the system won\'t jeopardize the overall network\'s stability and security. Regular vulnerability assessments: Both environments should be subjected to periodic assessments to identify and address potential weak links. Multi-factor authentication: For systems pivotal to critical inf | Data Breach Tool Vulnerability Threat Industrial | Deloitte | ★★ | |
| 2023-02-21 11:00:00 | 7 reasons why Endpoint Security and Response shouldn\'t be ignored (lien direct) | The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. When strategizing a security approach for the coming year, many solutions will cross a CISO’s desk, all useful in covering some part of the network. Organizations must scrutinize every layer and each solution to make sure their security stack runs efficiently while still boasting a Defense-in-Depth approach. There cannot be an overload of alerts, the learning curve must be worth the cost, and all solutions must integrate with each other. Not surprisingly, the search can be tedious, complex, and confusing. Broadly speaking, cybersecurity defends the network and the devices on that network. Both are key and must be protected. Endpoint security and response includes “not only the automated monitoring and detection of threats on the endpoint, but also a combination of autonomous and manual investigation, remediation, and response.” While not every tool will make the cut, here are seven reasons why Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) should not be ignored. Cybercriminals aren’t ignoring endpoints. It’s not surprising that in a recent study, 76% of IT decision-makers reported their company use of endpoint devices has gone up. This can include workstations, servers, tablets, smartphones and a host of IoT devices like cameras, smart speakers, and lighting. However, it is equally unsurprising that bad actors have capitalized on this gain, and consequently, 79% of IT teams have seen a rise in endpoint-related security breaches. The cyber talent crisis creates the need for autonomous response on the endpoint. With an increase of both endpoints and endpoint-related attacks, a proportional increase in endpoint security measures is needed; unfortunately, the ongoing cyber talent deficit hamstrings those efforts and makes whatever qualified cybersecurity experts are available difficult to attain for many small to medium-sized businesses. Endpoint security solutions use automatic investigation and monitoring techniques to spot threat 24/7/365 and often respond autonomously to mitigate them. This cuts back significantly on the work remaining for already-strapped security teams to do. EDR offers cloud-based security for end-user devices. One of the primary security problems facing fast-expanding, digitally native, and mid-transition companies is how to secure both on-premises and cloud-based assets. Endpoints, while not in the cloud, connect to it and bad actors can use vulnerabilities in device software to pivot to the rest of your network. State of the industry endpoint security platforms can deploy patches and run reboots from the cloud and offer enterprise-wide centralized cloud management. Remote device security trends downward as workers mix personal with professional. The rise of BYOD has been significant and ubiquitous in the wake of the remote-work migration, and a study by Gartner revealed that over 50% of workers used their own laptop or smartphone for work activity. Interestingly, a Ponemon study indicated that 67% of respondents reported that personal mobile devices have negatively impacted their company’s security posture, and 55% cite smartphones as | Tool Threat | Deloitte | ★★ | |
| 2022-11-29 11:00:00 | 5 Tips for protecting your connected vehicle against Cyberattacks (lien direct) | The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. As more connected vehicles hit the road, cyberattacks are increasing. Deloitte estimates that there will be over 470 million connected cars in use by 2025 if their popularity continues to grow at the current rate. And because each connected car produces about 25 GB of data every hour, they are a tempting challenge for cybercriminals and bad actors with malicious intent. Connected vehicles come with enhanced features that give drivers more to love about their favorite car brands, but cybersecurity in automobiles has a long way to go. If you drive a connected car or are considering buying one, you need to know how to protect your new car against a potential cyberattack. In this article, we’ll talk about how hackers can infiltrate your vehicle and what you can do to protect yourself and your car from a serious attack. Can your car get hacked? Cars today are built using hundreds of sensors connected to computers that help monitor how your car operates, add internet capabilities, and enable connected apps. While these technologies are helpful and convenient for drivers, they can also lead to data theft and even threaten your safety while driving. For example, remote manipulation, identity theft, and vehicle theft are all ways that bad actors can exploit the security vulnerabilities of your connected car. The push toward electric vehicles also poses a unique threat to connected car owners. A recent survey revealed that 79% of two-car households are considering an electric car for their next purchase, but ethical hacking exercises have shown that electric vehicles can easily be drained by remote hackers. This can potentially put drivers in a dangerous situation if they are stranded without a means of charging their vehicle. There are many ways that bad actors can hack into your car. They can manipulate the signal from a key fob to unlock your doors, change the code in the apps to create a backdoor to steal your data, learn about your driving habits, control your vehicle’s security response systems, and much more. Cars today are essentially human-assisted computers, which means they can be hacked just as easily as any other IoT device. How to protect your connected vehicle from a cyberattack Connected vehicles provide users convenience and peace of mind while traveling across the country or making their daily commute. But they also pose a significant threat when bad actors execute attacks for data theft, taking over vehicle controls, and even tracking your location. If you’re going to take advantage of connected vehicle features, you need to know how to protect yourself from becoming the victim of an automotive cyberattack. Here are five tips to protect your connected vehicle from an attack: Remove dongles Dongles are small devices that plug into the diagnostic port and allow companies to monitor your driving habits for various reasons. It can be used to monitor vehicle performance, improve gas mileage, and set more accurate insurance rates based on driving activity. Many people choose to use dongles to save money and ensure their car is running at top performance, but these devices can be an | Hack Threat Guideline | Deloitte Deloitte | ★★★ | |
| 2022-10-25 13:07:27 | Face à l\'hyperconnectivité de notre société, ESET protège les internautes de bout en bout (lien direct) | ESET annonce la disponibilité de ses solutions destinées au grand public. Un grand nombre d'améliorations et de nouvelles fonctionnalités y sont ajoutées. Elles sont destinées à renforcer la confidentialité, améliorer la protection des routeurs, empêcher les attaques par force brute et sécuriser les navigateurs. La suite logicielle intègre également la technologie Intel® Threat Detection qui ajoute une couche de protection contre les rançongiciels. L'enquête Deloitte sur les tendances en matière de (...) - Marchés | Threat | Deloitte Deloitte | ||
| 2022-08-09 10:00:00 | Are SASE and Zero Trust the key for manufacturers grappling with IoT cyber risks? (lien direct) | As manufacturers dash headlong into smart factory initiatives, the number of IoT devices operating in factories, warehouses, and across supply chain infrastructure is exploding. Manufacturers seek to utilize IoT in a range of places, be it video camera inspection devices on the assembly line, temperature sensors on refrigeration units, or maintenance telemetry sensors on factory equipment. But as they seek to reap tremendous business gains from smart devices in industrial IoT, they also must balance that upside with the potential risks that IoT is increasingly introducing to manufacturing environments. New cyber challenges are arising in the face of this explosion of IoT in manufacturing. They require organizations in this sector to design modern security architecture that can meet them head on. Smart manufacturing and the rise in IoT Consensus across recent industry studies shows that manufacturers are making big bets on smart manufacturing and IoT as the lynchpins to their success in the coming years. According to Deloitte’s 2022 Manufacturing Industry Outlook, some 45% of manufacturing executives expect increases in operational efficiency from investments in IoT that connects machines and automates processes. Meantime, the State of Smart Manufacturing report published in 2022 by Plex found that 83% of manufacturers say that smart manufacturing is a key to their organization’s future success. Smart devices and IIoT are among the most used projects to bring smart manufacturing to fruition. Some 49% of organizations have already deployed smart devices and 45% have put IIoT into production, with another 35% and 36%, respectively, planning to use these technologies. This is rapidly pushing a lot of manufacturing compute out to the edge. AT&T’s own recent analysis for the AT&T Cybersecurity Insights Report: Securing the Edge-A Focus on Manufacturing study found that the manufacturing vertical is one of the furthest along in implementing edge use cases. The report reveals that 78% of manufacturers globally are planning, have partially, or have fully implemented an edge use case - that’s ahead of energy, finance, and healthcare industry organizations. This kind of progress noted by the report is in sync with other industry studies watching the progress of digital transformation in manufacturing. For example, a study by Palo Alto Networks says the demand for secure remote access in manufacturing is rapidly outstripping other industries. Amid many cited edge use cases such as smart warehousing, remote operations, and augmented maintenance, video-based inspection was the number one edge priority cited by manufacturing respondents to the AT&T Cybersecurity Insights Report . This is a prime example of how IoT is being leveraged to improve efficiency, quality and speed on factory floor, while helping manufacturers also overcome workforce challenges. Unpatchable IoT devices raises manufacturing risk profile Video-based inspection also provides an excellent example of how IoT devices can at the same time potentially increase cyber risk in manufacturing environments. In use cases like this one, IoT devices such as cameras are increasingly connected to OT networks and devices on the manufacturing shop floor. Simultaneously, they’re also opening up access outside th | Threat Studies Patching Guideline | Deloitte | ||
| 2022-07-21 11:38:00 | Deloitte expands its managed XDR platform (lien direct) | Deloitte announced an update this week to its Managed Extended Detection and Response platform. The upgrade boosts the platform's capabilities to collect intelligence, hunt for threats, and secure mobile devices. Among the new modules added to Deloitte's MXDR offering: Cyber Security Intelligence, which adds to Deloitte's tools and proprietary sources intelligence from CrowdStrike Falcon X. The combination will provide users with actionable indicators of compromise (IoCs), threat notifications, threat actor profiles, industry landscapes, automated sandbox analysis, and threat briefing requests for information. "CSI allows us to be much more proactive in our detection, prevention, and understanding of threats so we can be more proactive in planning with our clients," says Deloitte MXDR leader Curt Aubley. Dynamic Adversary Intelligence, which provides clients with "over-the-horizon" adversary investigations. DAI uses passive intelligence collection methods, including global telemetry, industry-leading application programming interface integrations, refined tradecraft, proprietary analytics of publicly available information, and proprietary sources via Splunk. "DAI gives clients an inside-out view of attackers," Aubley explains. "It can also give a client the information they need to give to authorities to track down adversaries." Digital Risk Protection, which lets a client follow their digital footprint online. "We can fingerprint a client's intellectual property," Aubley says. "Using that information, along with data like domain names, email addresses, and others, we can look on the open web, deep web, and dark web and see if that information has gotten into the hands of an adversary. Then we can let a client know how to best manage any potential crisis that might arise from that leak. We can also look inside their environment to determine how the leak happened." Active Hunt and Response, which includes the use of a "dissolvable agent" that can be planted in the memory of an endpoint and collect data about an attacker while remaining invisible to them. In addition, a new Mobile Prevent, Detection, and Response module has been added to the MXDR platform. It has expanded hunting capabilities and is fully integrated with CrowdStrike Falcon for Mobile Endpoint Detection and Response and CrowdStrike's mobile threat defense.To read this article in full, please click here | Threat Guideline | Deloitte Deloitte | ||
| 2022-07-13 02:09:00 | Consulting firms jump on the Zero Trust bandwagon (lien direct) | Within a day of each other, the consulting and outsourcing firms Deloitte and HCL Technologies have both launched new managed cybersecurity services, as consultants look to capitalize on the growing appetite for the Zero Trust security model.On Tuesday, Deloitte unveiled its Zero Trust Access managed service, which is heavily influenced by its recent acquisition of TransientX. Then, on Wednesday, HCL announced a collaboration with Palo Alto Networks to offer managed SASE, cloud security, and threat detection and response for its customers.To read this article in full, please click here | Threat | Deloitte Deloitte | ||
| 2022-01-19 17:00:02 | Deloitte launches new SaaS cyber threat detection and response platform (lien direct) | AWS, CrowdStrike, Exabeam, and Google Cloud Chronicle are operationalizing the new platform. | Threat | Deloitte | ||
| 2021-06-04 05:01:00 | Digital transformation explained (lien direct) |
This article was written by an independent guest author.
No matter what sector your organization does business in, you’ve probably heard the term digital transformation. In every industry, digital transformation is going to be critical to remain competitive and resilient.
But what does digital transformation mean? And how does cybersecurity fit in? Today’s organizations are facing an increasingly complex environment of securing everything attached to the network; applications, data, and endpoints.
What is digital transformation?
At its most basic definition, digital transformation (or DX) is the process of improving your business by leveraging the latest technologies and solutions.
Digital transformation harnesses third platform technologies - think cloud and data analytics, and acceleration technologies - think IoT and mobile apps to transform business operations.
The primary goals of digital transformation are to increase agility for customer responsiveness, flexibility to accommodate new ways of working, and scalability to help your business do more.
What’s driving digital transformation?
The main drivers of digital transformation are:
Skyrocketing data transmission speeds
Increased storage capacities
Expansion of mobile functionality
All these signs point to a rapid decrease of on-premises computing and storage.
With the cloud, the amount of time and resources spent on hardware maintenance and upkeep is drastically reduced because you no longer need to own, maintain, and upgrade these resources in your own data center.
Rebuffing the maintenance mindset, the preference for most IT departments is to spend more on innovation vs. the traditional “keep the lights on” tasks. However, because “turning the lights off” isn’t feasible, the bulk of IT budgets continue to be allocated to maintenance. A 2020 Deloitte Inisights report underscores the reality: the average IT department allocates over half its budget on maintenance but only 19 percent on innovation.
And according to a 2021 State of IT Spiceworks Ziff Davis study, updating outdated IT infrastructure is the number one factor driving IT budget increases — cited by 56% of organizations planning on growing IT spend.
Also driving cloud adoption is the need to address disaster recovery (DR). While DR has not been typically cost-effective for small to mid-sized businesses, many cloud vendors and providers offer DR solutions like DRaaS (Disaster Recovery as a Service) that address those challenges.
But perhaps the greatest driver of cloud adoption today is COVID-19. The pandemic’s disruption to the business landscape forced organizations to consider advanced technologies. The work from home or remote work model is here to stay, and the demand for software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that allow teams to collaborate from anywhere is steadily increasing.
The main spheres of digital transformation
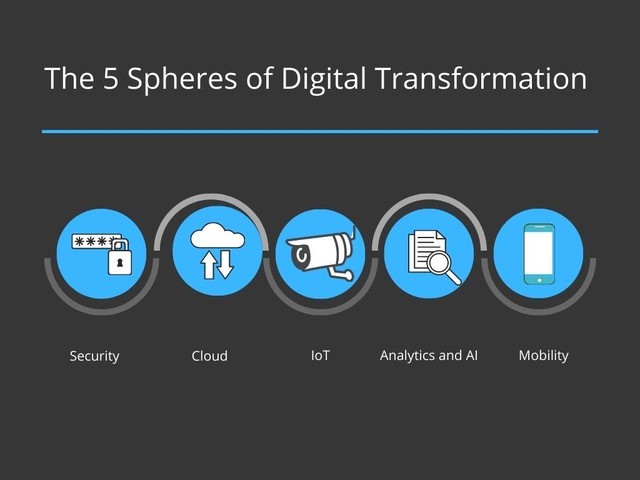 While one can argue that the components of digital transformation are numerous, we are highlighting five important spheres.
Security
As network access moves beyond the office perimeter to meet the demands of a remote workforce, robust security measures are required to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of corporate and customer data.
While one can argue that the components of digital transformation are numerous, we are highlighting five important spheres.
Security
As network access moves beyond the office perimeter to meet the demands of a remote workforce, robust security measures are required to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of corporate and customer data. |
Data Breach Threat | Deloitte | ||
| 2020-12-15 11:00:00 | Why application-layer encryption is essential for securing confidential data (lien direct) | This blog was written by an independent guest blogger. Your business is growing at a steady rate, and you have big plans for the future. Then, your organization gets hit by a cyberattack, causing a massive data breach. Suddenly, your company’s focus is shifted to sending out letters to angry customers informing them of the incident - which is required by law in most states - and devising strategies to deal with the backlash. This is an all too common scenario for many businesses, and the unfortunate truth is that most organizations fail to adopt the correct cybersecurity procedures until after an attack. The good news is that with a proactive approach to protecting your data, these kinds of nightmares can be avoided. New technology is constantly providing hackers new opportunities to commit cybercrimes. Most organizations have encrypted their data whether it’s stored on the cloud or in a server provided by their web host, but this isn’t enough. Even properly encrypted disc level encryption is vulnerable to security breaches. In this article, we will discuss the weaknesses found in disc level encryption and why it’s best to ensure your data is encrypted at the application layer. We’ll also discuss the importance of active involvement from a cybersecurity team in the beginning stages of application development, and why developers need to have a renewed focus on cybersecurity in a “security-as-code” culture. The importance of application-layer security Organizations all too often have a piecemeal, siloed approach to security. Increasingly competitive tech environments have pushed developers into building new products at a pace cybersecurity experts sometimes can’t keep up with. This is why it’s becoming more common for vulnerabilities to be detected only after an application launches or a data breach occurs. Application layer encryption reduces surface area and encrypts data at the application level. That means if one application is compromised, the entire system does not become at risk. To reduce attack surfaces, individual users and third parties should not have access to encrypted data or keys. This leaves would-be cybercriminals with only the customer-facing end of the application for finding vulnerabilities, and this can be easily protected and audited for security. Building AI and application-layer security into code Application layer security and building security into the coding itself requires that your DevOps and cybersecurity experts work closely together to form a DevSecOps dream team. Developers are increasingly working hand-in-hand with cybersecurity experts from the very beginning stages of software development to ensure a “security-as-code” culture is upheld. However, there are some very interesting developments in AI that present opportunities to streamline this process. In fact, 78% of data scientists agree that artificial intelligence will have the greatest impact on data protection for the decade. Here are four ways AI is transforming application layer security: 1. Misuse detection or application security breach detection Also referred to as signature-based detection, AI systems alert teams when familiar attack patterns are noticed. | Data Breach Vulnerability Threat | Deloitte | ||
| 2019-10-18 13:25:14 | Bypassing LLMNR/NBT-NS honeypot (lien direct) | AbstractMITRE ATT&CK™ [https://attack.mitre.org/] “is a globally-accessible knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations” which recommends the Conveigh honeypot [https://github.com/Kevin-Robertson/Conveigh] for detection of the LLMNR/NBT-NS Poisoning and Relay | Threat Guideline | Deloitte | ★★ | |
| 2019-09-23 13:00:00 | How to justify your cybersecurity budget in 2019 (lien direct) |
It’s less expensive to prevent cyber attacks than it is to repair the damage when they happen. Companies and institutions across industries lose money from cyber attacks all the time. There are the more obvious ways like piracy, data breaches, and litigation. There are also ways that accountants can’t quite put a dollar figure on, such as reputational damage that makes customers and clientele less likely to want to buy a company’s products and services in the future.
Everything is digital these days, both on premises and in the cloud. So cybersecurity staff and security measures are things you have to spend money on. But how should your company determine how much money to budget for security? And how should your company determine how to spend it?
 Photo by Fabian Blank on Unsplash
What is a typical cybersecurity budget?
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer when trying to decide what a “typical budget” looks like for cybersecurity operations, there are a few studies that have been done that can provide some insight.
A recent study by Deloitte and the Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center found that financial services on average spend 10% of their IT budgets on cybersecurity. That’s approximately 0.2% to 0.9% of company revenue or $1,300 to $3,000 spent per full time employee. For a bigger picture benchmark, consider that Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella recently revealed in a statement that the tech behemoth “will invest more than $1 billion each year in cybersecurity for the foreseeable future”. Finally, it’s worth noting that the 2019 U.S. President’s budget allocated $15 billion in spending on cybersecurity, about 0.3% of the entire fiscal budget ($4.746 trillion).
And while none of these figures can clarify what a “typical” budget should look like for the average business or organization, they can at least provide a benchmark for how larger tech firms, financial service companies and governments are allocating cybersecurity spend as a percentage of overall budget.
Considerations for your cybersecurity budget
There are so many different variables and factors involved when it comes to determining your cybersecurity budget. I’ll offer you some tips which can be used as a starting point to help your company decide.
I asked Kate Brew, from AT&T Cybersecurity, to send a tweet to get views from various industry decision makers. The question was “Cybersecurity budgets come in many sizes. How does your company determine yours?” Here are some responses, which should illustrate what typical cybersecurity budgets are. Some of the responses were a bit tongue-in-cheek:
“They keep me far away from budget/financial decisions at my company but I’d like to think a d20 is involved somehow...” (I love Dungeons and Dragons references!)
“Yeah. They most often range in size from ‘miniscule,’ to ‘barely visible to the unaided eye.’”
“Pick a number and subtract that number from itself. That&
Photo by Fabian Blank on Unsplash
What is a typical cybersecurity budget?
While there is no one-size-fits-all answer when trying to decide what a “typical budget” looks like for cybersecurity operations, there are a few studies that have been done that can provide some insight.
A recent study by Deloitte and the Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center found that financial services on average spend 10% of their IT budgets on cybersecurity. That’s approximately 0.2% to 0.9% of company revenue or $1,300 to $3,000 spent per full time employee. For a bigger picture benchmark, consider that Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella recently revealed in a statement that the tech behemoth “will invest more than $1 billion each year in cybersecurity for the foreseeable future”. Finally, it’s worth noting that the 2019 U.S. President’s budget allocated $15 billion in spending on cybersecurity, about 0.3% of the entire fiscal budget ($4.746 trillion).
And while none of these figures can clarify what a “typical” budget should look like for the average business or organization, they can at least provide a benchmark for how larger tech firms, financial service companies and governments are allocating cybersecurity spend as a percentage of overall budget.
Considerations for your cybersecurity budget
There are so many different variables and factors involved when it comes to determining your cybersecurity budget. I’ll offer you some tips which can be used as a starting point to help your company decide.
I asked Kate Brew, from AT&T Cybersecurity, to send a tweet to get views from various industry decision makers. The question was “Cybersecurity budgets come in many sizes. How does your company determine yours?” Here are some responses, which should illustrate what typical cybersecurity budgets are. Some of the responses were a bit tongue-in-cheek:
“They keep me far away from budget/financial decisions at my company but I’d like to think a d20 is involved somehow...” (I love Dungeons and Dragons references!)
“Yeah. They most often range in size from ‘miniscule,’ to ‘barely visible to the unaided eye.’”
“Pick a number and subtract that number from itself. That& |
Threat Studies | Deloitte | ||
| 2019-08-01 12:30:00 | For mid-sized enterprises to win the cybersecurity race, the game needs to change (lien direct) | Why does AT&T Cybersecurity get me so excited on behalf of the mid-sized enterprises that make up the bulk of business around the globe? Well, one example I like to share is from a bicycle manufacturer I had the pleasure of visiting a few years ago. As a cycling enthusiast myself, I know these manufacturers are true experts, with deep knowledge and passion for the businesses they run and technology they develop. Unsurprisingly, they were dismayed about the need to also become experts in cybersecurity. Even if they were experts, it still might not help. Could they really afford to follow the security blueprint defined by global banks and other elite security teams? According to a Deloitte survey, large enterprises spend thousands per employee and up to hundreds of millions of dollars per annum on cybersecurity, often deploying dozens or even hundreds of expensive and sophisticated security solutions along the way. For our bike manufacturer, it’s impossible to wade through all of the solutions on offer from the thousands of cybersecurity vendors out there. Their business is at risk through no fault of their own and the “solution” to mitigating that risk is beyond reasonable allocation of resources. Mind you, it’s not just the bicycle company in this race. There’s the contract manufacturer that actually assembles the bikes, the advertising agency that promotes them, the distributors that get them into stores and perhaps 20 other major partners and subcontractors who support the core business. And this is just one major bicycle brand! There are millions of other mid-sized enterprises around the globe with the exact same problem. Every business, including the Fortune 500, would relish the opportunity to be more efficient in cybersecurity and to put more money back into the business. But for mid-sized companies, who don’t have the same resources to protect themselves, it’s a matter of survival. Our bicycle brand should be focused on engineering the perfect machine to break a 36mph Tour de France stage speed, not on cybersecurity. This shouldn’t be something that soaks up resources and diverts attention from the core business. That’s precisely why AlienVault automated threat detection and streamlined response, and why we continue to focus on making security more accessible as AT&T Cybersecurity. What gets me excited for customers like the bicycle manufacturer is the ability to do all that and more, on a much grander scale, because of what AT&T brings to the table. With a core mission of connecting people where they live and work for more than 140 years, security is in AT&T’s DNA. Ever since there was something of value carried over a network, AT&T has been a leader—including what is now called cybersecurity. Serving more than 3 million companies globally from the smallest business to nearly all the Fortune 1000 has given AT&T unrivaled visibility into the threats and needs of business customers. And as a trusted advisor that provides countless integrated business solutions around the globe, AT&T has assembled a broad portfolio of nearly all of the leading security vendors to help in the mission. We now have the opportunity to integrate AT&T’s unparalleled threat intelligence, AlienVault’s proven strengths in automation, and the world’s best cybersecurity solutions into one unified platform that eliminates cost and complexity for millions of companies both large and small. The bicycle manufacturer can choose to use the platform to manage security themselves, outsource the work completely, or utilize a collaborative model that utilizes collective expertise and capabilities. This is enabled through the AT&T consulting and managed services teams or through | Threat Guideline | Deloitte |
1
We have: 16 articles.
We have: 16 articles.
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
