What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2024-03-05 16:15:00 | GhostSec évolue avec des outils de compromis sur le site Web GhostSec Evolves With Website Compromise Tools (lien direct) |
Cisco Talos a découvert deux nouveaux outils développés par le groupe: «l'outil GhostSec Deep Scan» et «Ghostpresser»
Cisco Talos uncovered two new tools developed by the group: the “GhostSec Deep Scan tool” and “GhostPresser” |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-05 15:58:00 | US Sanctions Predator Spyware Makers pour cibler les fonctionnaires de Gov \\ ' US sanctions Predator spyware makers for targeting gov\\'t officials (lien direct) |
 Le gouvernement américain a annoncé mardi des sanctions contre deux personnes et cinq entités liées aux logiciels espions de Predator, quelques jours seulement après l'entreprise derrière l'outil a supprimé l'infrastructure en réponse à Nouvelles recherches sur ses opérations .Le département du Trésor a déclaré qu'il sanctionnait des personnes et des entités liées au consortium d'impression commerciale Intellexa - une tenue
Le gouvernement américain a annoncé mardi des sanctions contre deux personnes et cinq entités liées aux logiciels espions de Predator, quelques jours seulement après l'entreprise derrière l'outil a supprimé l'infrastructure en réponse à Nouvelles recherches sur ses opérations .Le département du Trésor a déclaré qu'il sanctionnait des personnes et des entités liées au consortium d'impression commerciale Intellexa - une tenue
 The U.S. government announced sanctions on Tuesday against two people and five entities tied to Predator spyware, just days after the company behind the tool took down infrastructure in response to new research about its operations. The Treasury Department said it sanctioned people and entities connected to the Intellexa Commercial Spyware Consortium - a holding
The U.S. government announced sanctions on Tuesday against two people and five entities tied to Predator spyware, just days after the company behind the tool took down infrastructure in response to new research about its operations. The Treasury Department said it sanctioned people and entities connected to the Intellexa Commercial Spyware Consortium - a holding |
Tool Legislation Commercial | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-05 15:30:00 | Maker des sanctions américaines du logiciel espion prédateur U.S. sanctions maker of Predator spyware (lien direct) |
> L'administration Biden sanctionne les individus et les entités derrière l'outil de surveillance commerciale impliquée dans les violations des droits de l'homme.
>The Biden administration sanctions individuals and entities behind the commercial surveillance tool implicated in human rights abuses. |
Tool Commercial | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-05 15:30:00 | La police sud-coréenne développe un outil de détection DeepFake avant les élections d'avril South Korean Police Develops Deepfake Detection Tool Ahead of April Elections (lien direct) |
Avec une efficacité revendiquée de 80%, le nouvel outil de détection d'IA sera utilisé pour informer la police lors d'enquêtes criminelles
With a claimed 80% efficiency, the new AI detection tool will be used to inform the police during criminal investigations |
Tool Legislation | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-05 12:05:53 | L'insécurité des sonnettes vidéo The Insecurity of Video Doorbells (lien direct) |
Consumer Reports a analysé Un tas de sonnettes vidéo connectées à Internet populaires.Leur sécurité est terrible.
Tout d'abord, ces sonnettes exposent votre adresse IP à domicile et votre nom de réseau wifi sur Internet sans cryptage, ouvrant potentiellement votre réseau domestique aux criminels en ligne.
[& # 8230;]
Quiconque peut accéder physiquement à l'une des sonnettes peut reprendre l'appareil & # 8212; Aucun outil ou compétences de piratage de fantaisie nécessaire.
Consumer Reports has analyzed a bunch of popular Internet-connected video doorbells. Their security is terrible. First, these doorbells expose your home IP address and WiFi network name to the internet without encryption, potentially opening your home network to online criminals. […] Anyone who can physically access one of the doorbells can take over the device—no tools or fancy hacking skills needed. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-05 11:00:00 | Explorer les techniques de découverte d'hôtes dans un réseau Exploring host discovery techniques in a network (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. In a network assessment, one of the first tasks is to narrow down a large set of IP addresses to a list of active or interesting hosts. It\'s like trying to find specific houses in a big neighbourhood without knocking on every door. Scanning every possible connection of every single IP address can be slow and often unnecessary. What makes a host interesting depends on what you\'re looking for. For example, network administrators might only care about devices running specific services, while security experts might want to know about every device with an IP address. Imagine a scenario, where a network administrator wants to find all the computers in their office network. They might just want to send a quick signal (like a ping) to see if each computer responds. But if someone outside the network is testing security, they might try different tricks to avoid detection by firewalls and uncover every possible connection. Host discovery serves as the initial phase of network reconnaissance, laying the groundwork for subsequent analysis and exploitation. Host discovery refers to the technique used in a network assessment to find live hosts (online systems) and narrow down the scope of assessment to live hosts only in a network. In this article, we will delve into various ways to perform host discovery in a network using Nmap, netdiscover and angry ip scanner. For this exercise I have used a virtual local area network (LAN) network configured on my local system. The IP range I will use in this exercise is for my network. You have to find your IP before starting a scan for hosts in your LAN. I have used host only as network adapter in my virtual machines, but you can al | Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 23:05:43 | Critical TeamCity Bugs met en danger la chaîne d'approvisionnement des logiciels Critical TeamCity Bugs Endanger Software Supply Chain (lien direct) |
Les clients doivent immédiatement corriger les vulnérabilités critiques dans les déploiements sur site de l'outil de pipeline CI / CD JetBrains TeamCity qui pourrait permettre aux acteurs de menace de prendre le contrôle des administrateurs sur les serveurs.
Customers should immediately patch critical vulnerabilities in on-prem deployments of the CI/CD pipeline tool JetBrains TeamCity that could allow threat actors to gain admin control over servers. |
Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 19:20:00 | Comment les cybercriminels exploitent les opérations de l'Inde \\ 's pour le blanchiment d'argent How Cybercriminals are Exploiting India\\'s UPI for Money Laundering Operations (lien direct) |
Les cybercriminels utilisent un réseau de mules d'argent embauché en Inde en utilisant une application basée sur Android pour orchestrer un système massif de blanchiment d'argent.
L'application malveillante, appelée & nbsp; Xhelper, est un "outil clé pour l'intégration et la gestion de ces mules de l'argent", les chercheurs de Cloudsek Sparh Kulshrestha, Abhishek Mathew et Santripti Bhujel & nbsp; a dit & nbsp; dans un rapport.
Détails sur l'escroquerie & nbsp;
Cybercriminals are using a network of hired money mules in India using an Android-based application to orchestrate a massive money laundering scheme. The malicious application, called XHelper, is a "key tool for onboarding and managing these money mules," CloudSEK researchers Sparsh Kulshrestha, Abhishek Mathew, and Santripti Bhujel said in a report. Details about the scam |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 17:15:00 | Hacktivist Collective Noname057 frappe les cibles européennes Hacktivist Collective NoName057 Strikes European Targets (lien direct) |
Sekoia.io a observé des développements dans les outils DDOS du groupe \\, y compris les mises à jour améliorant la compatibilité avec différentes architectures de processeur et OS
Sekoia.io observed developments in the group\'s DDoS tools, including updates enhancing compatibility with different processor architectures and OS |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 12:48:36 | Les risques de génération de code automatisés et la nécessité d'une correction alimentée par l'IA The Risks of Automated Code Generation and the Necessity of AI-Powered Remediation (lien direct) |
Les techniques de développement de logiciels modernes créent des défauts plus rapidement qu'ils ne peuvent être fixés.Bien que l'utilisation de bibliothèques tierces, de microservices, de générateurs de code, de modèles de langage grand (LLM), etc., a une productivité et une flexibilité remarquablement accrues dans le développement, il a également augmenté le taux de génération de code non sécurisé.Une solution automatisée et intelligente est nécessaire pour combler l'écart d'élargissement entre l'introduction et l'assainissement des défauts.
Soit \\ explorer les dangers potentiels des méthodes modernes de génération de code automatisées et la nécessité d'un mode sécurisé et automatisé de correction des défauts.
Méthodes automatisées qui produisent du code sans sécurité
Générateurs de code
Ces outils peuvent générer du code basé sur des entrées ou des modèles spécifiques que les développeurs fournissent, tels que les spécifications des fonctionnalités, les modèles de conception ou d'autres paramètres.Cela accélère les cycles de développement, réduit les erreurs et maintient la cohérence dans une application.Les exemples incluent Swagger…
Modern software development techniques are creating flaws faster than they can be fixed. While using third-party libraries, microservices, code generators, large language models (LLMs), etc., has remarkably increased productivity and flexibility in development, it has also increased the rate of generating insecure code. An automated and intelligent solution is needed to bridge the widening gap between the introduction and remediation of flaws. Let\'s explore the potential dangers of modern methods of automated code generation and the need for a secure and automated mode of flaw remediation. Automated Methods That Produce Insecure Code Code Generators These tools can generate code based on specific inputs or templates that developers provide, such as feature specifications, design patterns, or other parameters. This accelerates development cycles, reduces errors, and maintains consistency across an application. Examples include Swagger… |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 11:00:00 | Naviguer dans le paysage de la cybersécurité: une plongée profonde dans des stratégies efficaces SIEM Navigating the Cybersecurity landscape: A deep dive into effective SIEM strategies (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Comprehending and effectively addressing cybersecurity threats is paramount to organizational security. As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, how companies respond to cybersecurity threats and how they take proactive steps to mitigate them will factor heavily into profitability, reputation and long-term success. Within this context, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) emerges as a critical tool for fortifying your defense against cyber threats. This deep dive aims to guide you through the foundational concepts, the pivotal role of SIEM in cybersecurity, and strategies to ensure its effectiveness. SIEM stands at the forefront, offering a centralized solution for monitoring, analyzing, and responding to security events across your network. This article is designed to be your guide, providing insights into the components of SIEM, the challenges it addresses, and most importantly, how to wield it effectively. Understanding the foundations | Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-04 06:00:36 | La chaîne d'attaque inhabituelle de TA577 \\ mène au vol de données NTLM TA577\\'s Unusual Attack Chain Leads to NTLM Data Theft (lien direct) |
Ce qui s'est passé Proofpoint a identifié l'acteur de menace cybercriminale notable TA577 en utilisant une nouvelle chaîne d'attaque pour démontrer un objectif inhabituellement observé: voler des informations d'authentification NT LAN Manager (NTLM).Cette activité peut être utilisée à des fins de collecte d'informations sensibles et pour permettre l'activité de suivi. Proofpoint a identifié au moins deux campagnes en tirant parti de la même technique pour voler des hachages NTLM les 26 et 27 février 2024. Les campagnes comprenaient des dizaines de milliers de messages ciblant des centaines d'organisations dans le monde.Les messages sont apparus sous forme de réponses aux e-mails précédents, appelés détournement de fil, et contenaient des pièces jointes HTML zippées. Exemple de message utilisant le détournement de thread contenant une pièce jointe zippée contenant un fichier HTML. Chaque pièce jointe .zip a un hachage de fichiers unique, et les HTML dans les fichiers compressés sont personnalisés pour être spécifiques pour chaque destinataire.Lorsqu'il est ouvert, le fichier HTML a déclenché une tentative de connexion système à un serveur de blocs de messages (SMB) via un actualisation Meta à un schéma de fichier URI se terminant par .txt.Autrement dit, le fichier contacterait automatiquement une ressource SMB externe appartenant à l'acteur de menace.ProofPoint n'a pas observé la livraison de logiciels malveillants de ces URL, mais les chercheurs évaluent à la grande confiance que l'objectif de Ta577 \\ est de capturer les paires de défi / réponse NTLMV2 du serveur SMB pour voler des hachages NTLM en fonction des caractéristiques de la chaîne d'attaque et des outils utilisés. Exemple HTML contenant l'URL (en commençant par «File: //») pointant vers la ressource SMB. Ces hachages pourraient être exploités pour la fissuration du mot de passe ou faciliter les attaques "pass-the-hash" en utilisant d'autres vulnérabilités au sein de l'organisation ciblée pour se déplacer latéralement dans un environnement touché.Les indications à l'appui de cette théorie comprennent des artefacts sur les serveurs SMB pointant vers l'utilisation de l'impaquette de boîte à outils open source pour l'attaque.L'utilisation d'Impacket sur le serveur SMB peut être identifiée par le défi du serveur NTLM par défaut "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa" et le GUID par défaut observé dans le trafic.Ces pratiques sont rares dans les serveurs SMB standard. Capture de paquets observée (PCAP) de la campagne TA577. Toute tentative de connexion autorisée à ces serveurs SMB pourrait potentiellement compromettre les hachages NTLM, ainsi que la révélation d'autres informations sensibles telles que les noms d'ordinateurs, les noms de domaine et les noms d'utilisateur dans un texte clair. Il est à noter que TA577 a livré le HTML malveillant dans une archive zip pour générer un fichier local sur l'hôte.Si le schéma de fichiers URI était envoyé directement dans l'organisme de messagerie, l'attaque ne fonctionnerait pas sur les clients d'Outlook Mail patchés depuis juillet 2023. La désactivation de l'accès des clients à SMB n'atteint pas l'attaque, car le fichier doit tenter de s'authentifier auprès du serveur externe SMB ServerPour déterminer s'il doit utiliser l'accès des clients. Attribution TA577 est un acteur de menace de cybercriminalité éminent et l'un des principaux affiliés de QBOT avant la perturbation du botnet.Il est considéré comme un courtier d'accès initial (IAB) et Proofpoint a associé des campagnes TA577 avec des infections de ransomware de suivi, notamment Black Basta.Récemment, l'acteur favorise Pikabot comme charge utile initiale. Pourquoi est-ce important Proof Point observe généralement TA577 menant des attaques pour livrer des logiciels malveillants et n'a jamais observé cet acteur de menace démontrant la chaîne d'attaque utilisée pour voler des informations d'identification NTLM observées le 26 février.Récemment, TA577 a été observé pour fou | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 20:49:50 | Les opérateurs de logiciels espions prédateurs reconstruisent l'infrastructure à plusieurs niveaux pour cibler les appareils mobiles Predator Spyware Operators Rebuild Multi-Tier Infrastructure to Target Mobile Devices (lien direct) |
#### Description
Le groupe INSIKT de Future \\ a découvert de nouvelles infrastructures liées aux opérateurs de Predator, un logiciel spymétrique mobile mercenaire.L'infrastructure serait utilisée dans au moins onzepays, dont l'Angola, l'Arménie, le Botswana, l'Égypte, l'Indonésie, le Kazakhstan, la Mongolie, Oman, les Philippines, l'Arabie saoudite,et Trinidad et Tobago.Bien qu'il soit commercialisé pour la lutte contre le terrorisme et les forces de l'ordre, Predator est souvent utilisé contre la société civile, ciblant les journalistes, les politiciens et les militants.
L'utilisation de logiciels espions comme Predator présente des risques importants pour la confidentialité, la légalité et la sécurité physique, en particulier lorsqu'ils sont utilisés en dehors des contextes graves de criminalité et de lutte contre le terrorisme.La recherche du groupe INSIKT \\ a identifié une nouvelle infrastructure de livraison de prédateurs à plusieurs niveaux, avec des preuves de l'analyse du domaine et des données de renseignement du réseau.Malgré les divulgations publiques en septembre 2023, les opérateurs de Predator \\ ont poursuivi leurs opérations avec un minimum de changements.Predator, aux côtés de Pegasus de NSO Group \\, reste un principal fournisseur de logiciels espions mercenaires, avec des tactiques, des techniques et des procédures cohérentes au fil du temps.À mesure que le marché des logiciels espions mercenaires se développe, les risques s'étendent au-delà de la société civile à toute personne intéressée aux entités ayant accès à ces outils.Les innovations dans ce domaine sont susceptibles de conduire à des capacités de logiciels espions plus furtifs et plus complets.
#### URL de référence (s)
1. https://www.recordedfuture.com/predator-spyware-operators-rebuild-multi-tier-infrastructure-target-mobile-devices
#### Date de publication
1er mars 2024
#### Auteurs)
Groupe insikt
#### Description Recorded Future\'s Insikt Group has discovered new infrastructure related to the operators of Predator, a mercenary mobile spyware. The infrastructure is believed to be in use in at least eleven countries, including Angola, Armenia, Botswana, Egypt, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Oman, the Philippines, Saudi Arabia, and Trinidad and Tobago. Despite being marketed for counterterrorism and law enforcement, Predator is often used against civil society, targeting journalists, politicians, and activists. The use of spyware like Predator poses significant risks to privacy, legality, and physical safety, especially when used outside serious crime and counterterrorism contexts. The Insikt Group\'s research identified a new multi-tiered Predator delivery infrastructure, with evidence from domain analysis and network intelligence data. Despite public disclosures in September 2023, Predator\'s operators have continued their operations with minimal changes. Predator, alongside NSO Group\'s Pegasus, remains a leading provider of mercenary spyware, with consistent tactics, techniques, and procedures over time. As the mercenary spyware market expands, the risks extend beyond civil society to anyone of interest to entities with access to these tools. Innovations in this field are likely to lead to more stealthy and comprehensive spyware capabilities. #### Reference URL(s) 1. https://www.recordedfuture.com/predator-spyware-operators-rebuild-multi-tier-infrastructure-target-mobile-devices #### Publication Date March 1, 2024 #### Author(s) Insikt Group |
Tool Mobile Technical | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 13:32:01 | Le catalogue et les activités d\'un prestataire cyber privé du renseignement chinois révélés par la fuite de données I-Soon (lien direct) | Le catalogue et les activités d'un prestataire cyber privé du renseignement chinois révélés par la fuite de données I-Soon. Les chercheurs en sécurité d'HarfangLab ont étudié en profondeur les documents pour comprendre l'organisation, les tactiques et outils de l'acteur, ainsi que ses cibles et clients. - Interviews | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 12:00:00 | Cinq yeux mettent en garde contre l'exploitation des vulnérabilités d'Ivanti, les outils de détection insuffisants Five Eyes Warn of Ivanti Vulnerabilities Exploitation, Detection Tools Insufficient (lien direct) |
Les agences gouvernementales de la Five Eyes Coalition ont déclaré que les propres outils d'Ivanti ne sont pas suffisants pour détecter les compromis
Government agencies from the Five Eyes coalition said that Ivanti\'s own tools are not sufficient to detect compromise |
Tool Vulnerability | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 11:56:00 | Cinq agences des yeux mettent en garde contre l'exploitation active des vulnérabilités de la passerelle Ivanti Five Eyes Agencies Warn of Active Exploitation of Ivanti Gateway Vulnerabilities (lien direct) |
La Five Eyes (Fvey) Intelligence Alliance a émis un nouvel avertissement de conseil en cybersécurité des acteurs de cyber-menaces exploitant des fautes de sécurité connues dans Ivanti Connect Secure et Ivanti Policy Secure Gateways, notant que l'outil de vérificateur d'intégrité (ICT) peut être trompé pour fournir un faux sensde sécurité.
"Ivanti ICT n'est pas suffisant pour détecter les compromis et qu'un acteur de cybermenace peut être en mesure
The Five Eyes (FVEY) intelligence alliance has issued a new cybersecurity advisory warning of cyber threat actors exploiting known security flaws in Ivanti Connect Secure and Ivanti Policy Secure gateways, noting that the Integrity Checker Tool (ICT) can be deceived to provide a false sense of security. "Ivanti ICT is not sufficient to detect compromise and that a cyber threat actor may be able |
Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 08:00:00 | Kalker – La calculatrice scientifique de votre terminal (lien direct) | Contrairement aux idées reçues, je ne suis pas bon en maths malgré mes compétences informatiques. Je vous présente Kalker, une calculatrice scientifique pour terminal avec syntaxe mathématique, variables, fonctions, et opérations complexes. Disponible sur Windows, Linux, macOS, et en ligne, elle permet de personnaliser des fonctions pour simplifier des calculs avancés. | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-03-01 01:25:28 | Cutout.Pro AI Tool Data Breach: Hacker Faking 20 millions d'informations utilisateur CutOut.Pro AI Tool Data Breach: Hacker Leak 20 Million User Info (lien direct) |
> Par waqas
Dans une déclaration exclusive à HackRead.com, Cutout.pro a nié la violation et étiqueté la fuite comme une arnaque claire. \\ '
Ceci est un article de HackRead.com Lire le post original: Cutout.Pro Ai Tool Data Breach: Hacker Faking 20 millions d'informations utilisateur
>By Waqas In an exclusive statement to Hackread.com, CutOut.Pro denied the breach and labeled the leak as a \'clear scam.\' This is a post from HackRead.com Read the original post: CutOut.Pro AI Tool Data Breach: Hacker Leak 20 Million User Info |
Data Breach Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 21:37:13 | L'outil Ivanti Integrity Checker a besoin de la dernière mise à jour pour fonctionner, Alert Five Eyes avertit Ivanti integrity checker tool needs latest update to work, Five Eyes alert warns (lien direct) |
> La société de logiciels a repoussé le conseil conjoint, qui vient à la suite de plusieurs directives de la CISA cette année, les agences de poussette contre les exploits d'Ivanti
>The software company pushed back on the joint advisory, which comes following multiple directives from CISA this year prodding agencies to patch against Ivanti exploits. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 20:16:44 | #Hundredprees: Phobos tient #StopRansomware: Phobos Ransomware (lien direct) |
#### Description
Phobos est structuré comme un modèle ransomware en tant que service (RAAS).Depuis mai 2019, des incidents de ransomware de phobos ayant un impact sur les gouvernements de l'État, du local, des tribus et territoriaux (SLTT) ont été régulièrement signalés au MS-ISAC.Phobos Ransomware fonctionne en conjonction avec divers outils open source tels que SmokeLoader, Cobalt Strike et Bloodhound.Ces outils sont tous largement accessibles et faciles à utiliser dans divers environnements d'exploitation, ce qui en fait (et les variantes associées) un choix populaire pour de nombreux acteurs de menace.
#### URL de référence (s)
1. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-060a
#### Date de publication
26 février 2024
#### Auteurs)
Cisa
#### Description Phobos is structured as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model. Since May 2019, Phobos ransomware incidents impacting state, local, tribal, and territorial (SLTT) governments have been regularly reported to the MS-ISAC. Phobos ransomware operates in conjunction with various open source tools such as Smokeloader, Cobalt Strike, and Bloodhound. These tools are all widely accessible and easy to use in various operating environments, making it (and associated variants) a popular choice for many threat actors. #### Reference URL(s) 1. https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/cybersecurity-advisories/aa24-060a #### Publication Date February 26, 2024 #### Author(s) CISA |
Ransomware Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 19:41:02 | Android Money Transfer Xhelper App exposé comme réseau de blanchiment d'argent Android Money Transfer XHelper App Exposed as Money Laundering Network (lien direct) |
> Par deeba ahmed
ne confond pas l'application Xhelper avec le malware du malhelper, qui cible les appareils Android et est notoirement difficile à supprimer.
Ceci est un article de HackRead.com Lire le post original: Android Money Transfer Xhelper App exposé comme réseau de blanchiment d'argent
>By Deeba Ahmed Don\'t confuse the XHelper app with the notorious XHelper malware, which targets Android devices and is notoriously difficult to remove. This is a post from HackRead.com Read the original post: Android Money Transfer XHelper App Exposed as Money Laundering Network |
Malware Tool Mobile | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 10:30:00 | Blue Team Toolkit: 6 outils open source pour évaluer et améliorer les défenses des entreprises Blue Team toolkit: 6 open-source tools to assess and enhance corporate defenses (lien direct) |
Voici comment l'équipe bleue éloigne les équipes rouges et quelques outils open source qu'il peut exploiter pour identifier les caillis dans l'armure d'entreprise
Here\'s how the blue team wards off red teamers and a few open-source tools it may leverage to identify chinks in the corporate armor |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 06:00:13 | Briser la chaîne d'attaque: des mouvements décisifs Break the Attack Chain: Decisive Moves (lien direct) |
In our “Break the Attack Chain” blog series, we have looked at how threat actors compromise our defenses and move laterally within our networks to escalate privileges and prepare for their endgame. Now, we come to the final stage of the attack chain where it\'s necessary to broaden our outlook a little. While most external threat actors will follow the same playbook, they aren\'t our only adversaries. The modern reality is that data often just walks out of the door because our employees take it with them. More than 40% of employees admit to taking data when they leave. At the same time, careless employees who make security mistakes are responsible for more than half of insider-led data loss incidents. So, while it\'s important to detect and deter cybercriminals who want to exfiltrate our data, we must also watch out for our users. Whether they are malicious or careless, our users are just as capable of exposing sensitive data. In this third and final installment, we discuss how companies tend to lose data-and how we can better protect it from all manner of risks. Understanding data loss As with every stage in the attack chain, we must first understand threats before we can put protections in place. Let\'s start with the case of a cybercriminal following the typical attack chain. While this may not sound like a traditional insider attack, it\'s often aided by careless or reckless employees. Users expose data and open themselves and your business up to compromise in a multitude of ways, like using weak passwords, reusing credentials, forgoing security best practices and clicking on malicious links or attachments. Any of these risky moves give cybercriminals a way into your networks where they can embark on lateral movement and escalation. Incidents like these are so common that careless or compromised users cause over 80% of insider-led data loss. Malicious insiders make up the remainder. Insider threats could be a disgruntled employee looking to cause disruption, a user compromised by cybercriminals, or, increasingly, an employee who will soon leave your organization. In most cases, data exfiltration follows a three-stage pattern: Access. Users, whether malicious or compromised, will attempt to take as much information as possible. This could mean excessive downloading or copying from corporate drives or exporting data from web interfaces or client apps. Obfuscation. Both cybercriminals and malicious insiders will be aware of the kinds of activity likely to trigger alarms and will take steps to avoid them. Changing file names and extensions, deleting logs and browsing history, and encrypting files are typical strategies. Exfiltration. With targets acquired and tracks covered, data exfiltration is then carried out by copying files to a personal cloud or removable storage device and sharing files with personal or burner email accounts. Defending from the inside out As we explained in our webinar series, while the initial stage of the attack chain focuses on keeping malicious actors outside our organization, the final two stages are far more concerned with what\'s happening inside it. Therefore, any effective defense must work from the inside out. It must detect and deter suspicious activity before data can slip past internal protections and be exposed to the outside world. Of course, data can do many things-but it cannot leave an organization on its own. Whether compromised, careless or malicious, a human is integral to any data loss incident. That\'s why traditional data loss prevention (DLP) tools are not as effective as they used to be. By focusing on the content of an incident, they only address a third of the problem. Instead, a comprehensive defense against data loss must merge content classification with threat telemetry and user behavior. Proofpoint Information Protection is the only solution that uses all three across channels in a unified, cloud-native interface. With this information, security teams can identify who is accessing and moving data-when, where and why. And | Tool Threat Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-28 17:30:00 | Les problèmes du FBI ont une alerte sur les menaces russes ciblant les routeurs Ubiquiti FBI Issues Alert on Russian Threats Targeting Ubiquiti Routers (lien direct) |
Les routeurs ont été détournés pour voler des informations d'identification, du trafic proxy et des pages de phishing et des outils personnalisés
The routers were hijacked to steal credentials, proxy traffic, and host phishing pages and custom tools |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-28 06:00:52 | Briser la chaîne d'attaque: développer la position pour détecter les attaques de mouvement latérales Break the Attack Chain: Developing the Position to Detect Lateral Movement Attacks (lien direct) |
In this three-part “Break the Attack Chain” blog series, we look at how threat actors compromise our defenses and move laterally within our networks to escalate privileges and prepare for their final endgame. If one phrase could sum up the current state of the threat landscape, it is this: Threat actors don\'t break in. They log in. Rather than spend time trying to circumnavigate or brute force their way through our defenses, today\'s cybercriminals set their sights firmly on our users. Or to be more accurate, their highly prized credentials and identities. This remains true at almost every stage of the attack chain. Identities are not just an incredibly efficient way into our organizations, they also stand in the way of the most valuable and sensitive data. As a result, the cat-and-mouse game of cybersecurity is becoming increasingly like chess, with the traditional smash-and-grab approach making way for a more methodical M.O. Cybercriminals are now adept at moving laterally through our networks, compromising additional users to escalate privileges and lay the necessary groundwork for the endgame. While this more tactical gambit has the potential to do significant damage, it also gives security teams many more opportunities to spot and thwart attacks. If we understand the threat actor\'s playbook from the initial compromise to impact, we can follow suit and place protections along the length of the attack chain. Understanding the opening repertoire To continue our chess analogy, the more we understand our adversary\'s opening repertoire, the better equipped we are to counter it. When it comes to lateral movement, we can be sure that the vast majority of threat actors will follow the line of least resistance. Why attempt to break through defenses and risk detection when it is much easier to search for credentials that are stored on the compromised endpoint? This could be a search for password.txt files, stored Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) credentials, and anything of value that could be sitting in the recycle bin. If it sounds scarily simple, that\'s because it is. This approach does not require admin privileges. It is unlikely to trigger any alarms. And unfortunately, it\'s successful time and time again. Proofpoint has found through our research that one in six endpoints contain an exploitable identity risk that allows threat actors to escalate privileges and move laterally using this data. (Learn more in our Analyzing Identity Risks report.) When it comes to large-scale attacks, DCSync is also now the norm. Nation-states and many hacking groups use it. It is so ubiquitous that if it were a zero-day, security leaders would be crying out for a patch. However, as there is general acceptance that Active Directory is so difficult to secure, there is also an acceptance that vulnerabilities like this will continue to exist. In simple terms, a DCSync attack allows a threat actor to simulate the behavior of a domain controller and retrieve password data on privileged users from Active Directory. And, once again, it is incredibly easy to execute. With a simple PowerShell command, threat actors can find users with the permissions they require. Add an off-the-shelf tool like Mimikatz into the mix, and within seconds, they can access every hash and every Active Directory privilege on the network. Mastering our defense With threat actors inside our organizations, it is too late for traditional perimeter protections. Instead, we must take steps to limit attackers\' access to further privileges and encourage them to reveal their movements. This starts with an assessment of our environment. Proofpoint Identity Threat Defense offers complete transparency, allowing security teams to see where they are most vulnerable. With this information, we can shrink the potential attack surface by increasing protections around privileged users and cleaning up endpoints to make it harder for cybercriminals to access valuable identities. With Proofpoin | Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 21:38:59 | Qu'est-ce que Sora et qu'est-ce que cela signifie pour votre sécurité Internet personnelle? What is Sora and What Does It Mean for Your Personal Internet Security? (lien direct) |
>  Imaginez un outil qui peut transformer le texte en vidéos captivantes, combler l'écart entre l'imagination et la réalité en créant des vidéos ...
Imaginez un outil qui peut transformer le texte en vidéos captivantes, combler l'écart entre l'imagination et la réalité en créant des vidéos ...
>  Imagine a tool that can transform text into captivating videos, bridging the gap between imagination and reality by creating videos...
Imagine a tool that can transform text into captivating videos, bridging the gap between imagination and reality by creating videos...
|
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 19:12:51 | Khan de FTC \\ avertit l'industrie technologique que l'agence appliquera strictement la confidentialité des données de l'IA FTC\\'s Khan warns tech industry that agency will strictly enforce AI data privacy (lien direct) |
 Les outils d'intelligence artificielle seront vigoureusement réglementés par la Federal Trade Commission (FTC), en tenant compte de la vie privée des consommateurs, a déclaré mardi sa présidente Lina Khan à un audience des dirigeants de la technologie et des fondateurs de startup lors d'une conférence."Nous réalisons des remèdes facilement administrables avec des règles de ligne lumineuse sur le développement, l'utilisation et la gestion des entrées d'IA", a déclaré Khan
Les outils d'intelligence artificielle seront vigoureusement réglementés par la Federal Trade Commission (FTC), en tenant compte de la vie privée des consommateurs, a déclaré mardi sa présidente Lina Khan à un audience des dirigeants de la technologie et des fondateurs de startup lors d'une conférence."Nous réalisons des remèdes facilement administrables avec des règles de ligne lumineuse sur le développement, l'utilisation et la gestion des entrées d'IA", a déclaré Khan
 Artificial intelligence tools will be vigorously regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), with an eye on consumer privacy, its Chair Lina Khan told an audience of tech executives and startup founders at a conference Tuesday. “We\'re crafting easily administrable remedies with bright-line rules on the development, use and management of AI inputs,” Khan said
Artificial intelligence tools will be vigorously regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), with an eye on consumer privacy, its Chair Lina Khan told an audience of tech executives and startup founders at a conference Tuesday. “We\'re crafting easily administrable remedies with bright-line rules on the development, use and management of AI inputs,” Khan said |
Tool Conference | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 14:58:43 | Veracode scan pour le code vs: maintenant avec Veracode Corre Veracode Scan for VS Code: Now with Veracode Fix (lien direct) |
Veracode est heureux d'annoncer la disponibilité de la capacité de correction de Veracode dans Veracode Scan pour le code VS.Les développeurs peuvent désormais découvrir et résoudre les défauts de sécurité en utilisant des outils génératifs alimentés par Veracode \\ directement directement à partir de leur environnement de développement intégré (IDE).
Selon l'état de Veracode de la sécurité des logiciels, 45,9% des organisations ont une dette de sécurité critique.Le fait que ces données proviennent d'organisations qui testent activement leur logiciel avec une solution de haute qualité implique qu'il ne trouve pas de défauts qui sont le problème: il les répare.
L'année dernière, nous avons introduit Veracode Fix & # 8211;Un assistant AI qui peut prendre les résultats d'un scan statique Veracode et permettre aux développeurs d'appliquer des correctifs suggérés directement à leur code.Veracode Fix réduit le temps de recherche et de mise en œuvre d'un correctif pour une découverte donnée à quelques minutes, tout en gardant le développeur en contrôle.FIX a été implémenté dans le cadre de l'utilitaire CLI Veracode, qui est disponible pour Linux, Windows et MacOS.
UN…
Veracode is pleased to announce the availability of Veracode Fix capability in Veracode Scan for VS Code. Now developers can discover and remediate security flaws using Veracode\'s Generative AI-powered tools directly from their Integrated Development Environment (IDE). According to the Veracode State of Software Security, 45.9% of organizations have critical security debt. The fact that this data comes from organizations who are actively testing their software with a high-quality solution implies that it\'s not finding flaws that is the problem: it\'s fixing them. Last year we introduced Veracode Fix – an AI assistant that can take the results of a Veracode Static scan and allow developers to apply suggested fixes directly to their code. Veracode Fix cuts the time to research and implement a fix for a given finding to minutes, while still keeping the developer in control. Fix was implemented as part of the Veracode CLI utility, which is available for Linux, Windows, and MacOS. A… |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 12:03:59 | China Surveillance Company a piraté China Surveillance Company Hacked (lien direct) |
La semaine dernière, quelqu'un a publié quelque chose comme 570 fichiers, images et journaux de chat d'une entreprise chinoise appelée I-Soon.I-Soon vend des services de piratage et d'espionnage aux gouvernements nationaux et locaux chinois.
Beaucoup de Détails dans The News Articles .
Ce sont des détails sur les outils ou les techniques, plus le fonctionnement interne de l'entreprise.Et ils semblent principalement pirater régionalement.
Last week, someone posted something like 570 files, images and chat logs from a Chinese company called I-Soon. I-Soon sells hacking and espionage services to Chinese national and local government. Lots of details in the news articles. These aren’t details about the tools or techniques, more the inner workings of the company. And they seem to primarily be hacking regionally. |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 11:00:00 | L'évolution du point de terminaison - passant des critères de terminaison traditionnels aux charges de travail cloud ou conteneurisées et les solutions de sécurité pour les protéger The endpoint evolution - Evolving from traditional endpoints to cloud or containerized workloads and the security solutions to protect them (lien direct) |
As organizations grow and more endpoints are added across the enterprise, they create an increasingly broad attack surface sophisticated attackers are looking to compromise. According to the 2019 Endpoint Security Trends Report 70% of breaches originate at the endpoint¹. That is likely because endpoints typically represent the Intersection between humans and machines creating vulnerable points of entry for cybercriminals. This is why it is increasingly important to secure your endpoints.
Growth in endpoints
An endpoint is defined as any computing device that communicates back and forth with a network to which it is connected. Some end user devices serve as an interface with human users while others are servers that communicate with other endpoints on the network. Traditional endpoints began as physical devices including servers, workstations, desktops, and laptops, all connected to a corporate network. When smartphones and tablets became handheld computing devices with access to corporate email, document sharing and collaboration tools the number of endpoints at least doubled.
Then came the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) including devices like printers, webcams, smartwatches, and thermostats, all of which are connected to the network. Industries like healthcare and manufacturing are using millions of IoT sensors to collect and exchange data. This continued growth in IoT only increases the number of endpoints that need to be protected.
Another contribution to the growth in endpoints is the migration to the cloud. It is estimated that 67% of enterprise infrastructure is cloud-based². This cloud transformation is the evolution from physical devices to virtualization and containerization.
Endpoint virtualization
The cloud is a multi-tenant environment where multiple users run services on the same server hardware. Virtualization and containerization are both virtualization technologies that separate the host operating system from the programs that run in them.
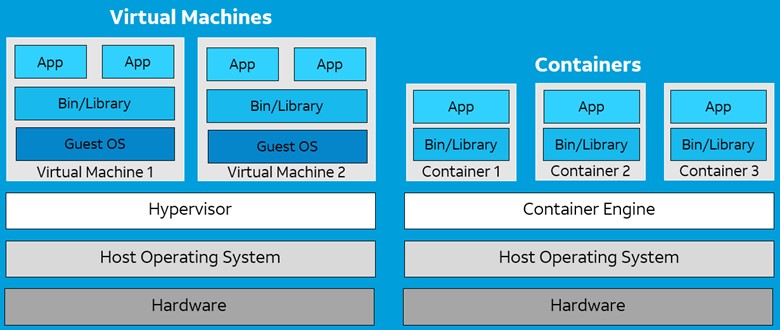 Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi
Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi |
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 05:00:31 | Risque et ils le savent: 96% des utilisateurs de prise de risque sont conscients des dangers mais le font quand même, 2024 State of the Phish révèle Risky and They Know It: 96% of Risk-Taking Users Aware of the Dangers but Do It Anyway, 2024 State of the Phish Reveals (lien direct) |
We often-and justifiably-associate cyberattacks with technical exploits and ingenious hacks. But the truth is that many breaches occur due to the vulnerabilities of human behavior. That\'s why Proofpoint has gathered new data and expanded the scope of our 2024 State of the Phish report. Traditionally, our annual report covers the threat landscape and the impact of security education. But this time, we\'ve added data on risky user behavior and their attitudes about security. We believe that combining this information will help you to: Advance your cybersecurity strategy Implement a behavior change program Motivate your users to prioritize security This year\'s report compiles data derived from Proofpoint products and research, as well as from additional sources that include: A commissioned survey of 7,500 working adults and 1,050 IT professionals across 15 countries 183 million simulated phishing attacks sent by Proofpoint customers More than 24 million suspicious emails reported by our customers\' end users To get full access to our global findings, you can download your copy of the 2024 State of the Phish report now. Also, be sure to register now for our 2024 State of the Phish webinar on March 5, 2024. Our experts will provide more insights into the key findings and answer your questions in a live session. Meanwhile, let\'s take a sneak peek at some of the data in our new reports. Global findings Here\'s a closer look at a few of the key findings in our tenth annual State of the Phish report. Survey of working adults In our survey of working adults, about 71%, said they engaged in actions that they knew were risky. Worse, 96% were aware of the potential dangers. About 58% of these users acted in ways that exposed them to common social engineering tactics. The motivations behind these risky actions varied. Many users cited convenience, the desire to save time, and a sense of urgency as their main reasons. This suggests that while users are aware of the risks, they choose convenience. The survey also revealed that nearly all participants (94%) said they\'d pay more attention to security if controls were simplified and more user-friendly. This sentiment reveals a clear demand for security tools that are not only effective but that don\'t get in users\' way. Survey of IT and information security professionals The good news is that last year phishing attacks were down. In 2023, 71% of organizations experienced at least one successful phishing attack compared to 84% in 2022. The bad news is that the consequences of successful attacks were more severe. There was a 144% increase in reports of financial penalties. And there was a 50% increase in reports of damage to their reputation. Another major challenge was ransomware. The survey revealed that 69% of organizations were infected by ransomware (vs. 64% in 2022). However, the rate of ransom payments declined to 54% (vs. 64% in 2022). To address these issues, 46% of surveyed security pros are increasing user training to help change risky behaviors. This is their top strategy for improving cybersecurity. Threat landscape and security awareness data Business email compromise (BEC) is on the rise. And it is now spreading among non-English-speaking countries. On average, Proofpoint detected and blocked 66 million BEC attacks per month. Other threats are also increasing. Proofpoint observed over 1 million multifactor authentication (MFA) bypass attacks using EvilProxy per month. What\'s concerning is that 89% of surveyed security pros think MFA is a “silver bullet” that can protect them against account takeover. When it comes to telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD), Proofpoint saw 10 million incidents per month, on average. The peak was in August 2023, which saw 13 million incidents. When looking at industry failure rates for simulated phishing campaigns, the finance industry saw the most improvement. Last year the failure rate was only 9% (vs. 16% in 2022). “Resil | Ransomware Tool Vulnerability Threat Studies Technical | ★★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 22:20:45 | Fortress Information Security déploie l'outil de notification et d'authenticité de correctifs automatisés Fortress Information Security Deploys Automated Patch Notification and Authenticity Tool (lien direct) |
We often-and justifiably-associate cyberattacks with technical exploits and ingenious hacks. But the truth is that many breaches occur due to the vulnerabilities of human behavior. That\'s why Proofpoint has gathered new data and expanded the scope of our 2024 State of the Phish report. Traditionally, our annual report covers the threat landscape and the impact of security education. But this time, we\'ve added data on risky user behavior and their attitudes about security. We believe that combining this information will help you to: Advance your cybersecurity strategy Implement a behavior change program Motivate your users to prioritize security This year\'s report compiles data derived from Proofpoint products and research, as well as from additional sources that include: A commissioned survey of 7,500 working adults and 1,050 IT professionals across 15 countries 183 million simulated phishing attacks sent by Proofpoint customers More than 24 million suspicious emails reported by our customers\' end users To get full access to our global findings, you can download your copy of the 2024 State of the Phish report now. Also, be sure to register now for our 2024 State of the Phish webinar on March 5, 2024. Our experts will provide more insights into the key findings and answer your questions in a live session. Meanwhile, let\'s take a sneak peek at some of the data in our new reports. Global findings Here\'s a closer look at a few of the key findings in our tenth annual State of the Phish report. Survey of working adults In our survey of working adults, about 71%, said they engaged in actions that they knew were risky. Worse, 96% were aware of the potential dangers. About 58% of these users acted in ways that exposed them to common social engineering tactics. The motivations behind these risky actions varied. Many users cited convenience, the desire to save time, and a sense of urgency as their main reasons. This suggests that while users are aware of the risks, they choose convenience. The survey also revealed that nearly all participants (94%) said they\'d pay more attention to security if controls were simplified and more user-friendly. This sentiment reveals a clear demand for security tools that are not only effective but that don\'t get in users\' way. Survey of IT and information security professionals The good news is that last year phishing attacks were down. In 2023, 71% of organizations experienced at least one successful phishing attack compared to 84% in 2022. The bad news is that the consequences of successful attacks were more severe. There was a 144% increase in reports of financial penalties. And there was a 50% increase in reports of damage to their reputation. Another major challenge was ransomware. The survey revealed that 69% of organizations were infected by ransomware (vs. 64% in 2022). However, the rate of ransom payments declined to 54% (vs. 64% in 2022). To address these issues, 46% of surveyed security pros are increasing user training to help change risky behaviors. This is their top strategy for improving cybersecurity. Threat landscape and security awareness data Business email compromise (BEC) is on the rise. And it is now spreading among non-English-speaking countries. On average, Proofpoint detected and blocked 66 million BEC attacks per month. Other threats are also increasing. Proofpoint observed over 1 million multifactor authentication (MFA) bypass attacks using EvilProxy per month. What\'s concerning is that 89% of surveyed security pros think MFA is a “silver bullet” that can protect them against account takeover. When it comes to telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD), Proofpoint saw 10 million incidents per month, on average. The peak was in August 2023, which saw 13 million incidents. When looking at industry failure rates for simulated phishing campaigns, the finance industry saw the most improvement. Last year the failure rate was only 9% (vs. 16% in 2022). “Resil | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 21:39:24 | DOE annonce des investissements de 45 millions de dollars pour la recherche en cybersécurité DOE announces $45 million investment for cybersecurity research (lien direct) |
> Le financement va à 16 projets visant à développer des outils avancés pour protéger le secteur de l'énergie.
>The funding goes to 16 projects aimed at developing advanced tools to protect the energy sector. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 19:57:01 | UAC-0184 cible l'entité ukrainienne en Finlande avec Remcos Rat UAC-0184 Targets Ukrainian Entity in Finland With Remcos RAT (lien direct) |
Le logiciel malveillant IDAT Loader a été utilisé pour livrer l'outil de cyber-espionnage, en utilisant la stéganographie, une technique rarement vue dans les attaques du monde réel.
The IDAT Loader malware was used to deliver the cyber espionage tool, employing steganography, a seldom-seen technique in real-world attacks. |
Malware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 13:00:31 | Sécuriser la route à venir: aborder les erreurs de configuration du cloud persistant dans l'industrie automobile Securing the Road Ahead: Addressing Persistent Cloud Misconfigurations in the Automotive Industry (lien direct) |
> Explorez une paire d'expositions de sécurité de l'industrie automobile et comment les outils de sécurité appropriés auraient pu empêcher ces mêmes anciens problèmes \\ 'de se produire.Plus tôt ce mois-ci, BMW a été encore une autre victime de dangereux erronés dans leur stockage cloud, qui exposent des clés privées et des données sensibles.Selon un récent article de TechCrunch, un seau de stockage Azure public contenait des «fichiers de script qui comprenaient des informations d'accès, des clés secrètes pour accéder aux adresses de godet privées et des détails sur d'autres services cloud».Pour être juste, BMW n'est pas seul dans ces questions, en fait, selon le rapport de sécurité du cloud de point de contrôle de 2023, [& # 8230;]
>Explore a pair of security exposures from the automotive industry and how the proper security tools could have prevented these \'same old issues\' from happening. Earlier this month, BMW was yet another victim of dangerous misconfigurations in their cloud storage, which exposed private keys and sensitive data. According to a recent article by TechCrunch, a public Azure storage bucket held “script files that included access information, secret keys for accessing private bucket addresses, and details about other cloud services.” To be fair, BMW is not alone in these issues, in fact, according to the 2023 Check Point Cloud Security Report, […] |
Tool Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 12:00:00 | Mise à jour du voyage!Le NIST CSF 2.0 est là… avec de nombreuses ressources utiles… Travel Update! The NIST CSF 2.0 is HERE…Along with Many Helpful Resources… (lien direct) |
NIST CSF 2.0 Liens rapides |Explorez notre suite complète de ressources: CSF 2.0 Guides de démarrage rapide CSF 2.0 Profils CSF 2.0 Références informatives outil de référence de cybersécurité et de confidentialité (CPRT) CSF 2.0 Reference Tool CSF 2.0 Site Web (Home Page) NIST News Annonce de NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) Processus de développement du processus de développement de processus de développement du processus de développement de processus de développement NIST (CSF) Processus de développement du processus de développement du processus de développement de la cybersécurité (CSF) (CSF)Tous ont commencé avec le décret exécutif (EO) 13636 il y a plus de dix ans, qui a appelé à la construction d'un ensemble d'approches (un cadre) pour réduire les risques aux infrastructures critiques.Grâce à cet EO, NIST a été chargé de développer un «cadre de cybersécurité».Nous savions que faire
NIST CSF 2.0 QUICK LINKS | Explore our Full Suite of Resources: CSF 2.0 Quick Start Guides CSF 2.0 Profiles CSF 2.0 Informative References Cybersecurity & Privacy Reference Tool (CPRT) CSF 2.0 Reference Tool CSF 2.0 Website ( Homepage ) Official NIST News Announcement The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) development process all started with Executive Order (EO)13636 over a decade ago, which called for building a set of approaches ( a framework ) for reducing risks to critical infrastructure. Through this EO, NIST was tasked with developing a "Cybersecurity Framework." We knew that, to do |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 11:00:00 | Construire une cyber-résilience contre l'ingénierie sociale alimentée par l'IA Building Cyber resilience against AI-powered social engineering (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Exploring advanced AI tactics in social engineering and effective strategies for cyber defense Long-standing as a significant threat in the business world, social engineering attacks constitute a major portion of global cyberattacks. An average business regularly faces a substantial number of such attacks every year. These attacks manifest in various forms, from intricate phishing emails to complex interactions designed to deceive employees, often leading to grave outcomes. This alarming reality is further underscored by the following statistics: · Social engineering is implicated in 98% of all cyberattacks · Approximately 90% of malicious data breaches occur due to social engineering · The typical organization faces over 700 social engineering attacks each year · The average cost incurred from a social engineering attack is about $130,000 | Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 05:03:36 | Les tenants et aboutissants de la confidentialité des données, partie 2: confidentialité par conception en protection de l'information The Ins and Outs of Data Privacy, Part 2: Privacy by Design in Information Protection (lien direct) |
This is the second blog in a two-part series about data privacy. In our previous post, we discussed how data privacy has become increasingly important. And we covered why data loss protection (DLP) and insider threat management (ITM) tools are critical to ensuring data privacy. The shift to “work from anywhere” and the increase in cloud adoption have caused a rise in data loss and insider threats. To defend data from careless, malicious and compromised insiders-and the harm that they cause-security teams must implement data security tools like data loss prevention (DLP) and insider threat management (ITM) platforms. These tools monitor and control how employees interact with data. At the same time, companies are collecting more and more data about employees themselves, like protected health information (PHI). The abundance of all this data-which is being collected and processed in the cloud-creates a critical challenge for security teams. They must protect employee privacy without impeding productivity. In this post, we\'ll explore the topic of privacy by design, which aims to strike a balance between these two challenges. We\'ll cover why it\'s so important. And we\'ll discuss how Proofpoint Information Protection can help you build a modern DLP program and comply with data privacy laws. Why privacy by design matters for DLP and ITM Privacy by design is a framework that embeds privacy into the design of IT systems, infrastructure and business processes. Privacy is not an afterthought. It is considered right from the start-in the initial design phase. What\'s more, it\'s a core component that integrates visibility, transparency and user-centricity into its design. In short, privacy by design ensures that everything is built with the user in mind. Privacy by design is important to DLP and ITM because it helps to: Protect employee rights. Personal data is sacred. Employees expect their personal data to be safe and their rights protected. When a company takes a proactive, transparent approach to data privacy, it helps maintain trust with employees. Comply with privacy laws. Data privacy laws protect people by requiring businesses to keep their data safe and avoid sharing it unethically with third parties. These laws often require companies to tell users exactly how their data is used and collected, and to notify them in the event of a data breach. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines and penalties, which can damage a firm\'s finances and brand image. Prevent bias in investigations. When user data is kept secure and private, it ensures insider threat investigations maintain their integrity and objectivity. If a user is identified, it could influence a security analyst\'s response to an incident. User privacy helps take emotion and subjectivity out of the picture. Ensure data privacy with Proofpoint DLP and ITM Proofpoint Information Protection includes administration and access controls. These controls can help your business keep data private and meet compliance requirements. Data residency and storage Proofpoint uses regional data centers in the U.S., Europe, Australia and Japan to meet data privacy and data residency requirements. You can control exactly where your data is stored at all of these data centers. For example, you can group your endpoints and map each group to a regional data center. This ensures that data on all those endpoints are stored in that regional center. So, a U.S. realm can manage U.S. endpoint data, which is sent to the U.S. data center. Attribute-based access controls Attribute-based access controls give you a flexible and easy way to manage access to data. You can use these controls to ensure that security analysts have visibility into data on a need-to-know basis only. For instance, you can write granular policies and assign access so that a U.S.-based security analyst can only see U.S. data. They cannot see data in Europe or the Asia-Pacific region. And when an analyst needs to access a specific user\'s data for an | Data Breach Tool Threat Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 02:45:39 | Plonger dans le nouveau guide de cybersécurité SMB de NCSC \\ Delving into NCSC\\'s New SMB Cybersecurity Guide (lien direct) |
Bien que les attaques contre les petites et moyennes entreprises (PME) aient rarement fait la une des journaux, elles restent une menace sérieuse.Contrairement à leurs homologues d'entreprise, de nombreuses PME n'ont pas les outils, les compétences et les services d'atténuation dont ils ont besoin pour lutter contre les menaces modernes.Comprenant que les prévenus ont été prévenus, le National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) a récemment fait ses débuts sur un guide destiné aux petites entreprises qui manquent de personnel informatique ou de soutien dédié appelé «utilisant des services en ligne en toute sécurité».Son objectif est d'aider les petits joueurs à renforcer leurs défenses de cybersécurité et à atténuer l'impact potentiel des attaques contre les entreprises ...
Although attacks on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) rarely hit the headlines, they remain a serious threat. Unlike their corporate counterparts, many SMBs lack the tools, skills, and mitigation services they need to combat modern threats. Understanding that forewarned is forearmed, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recently debuted a guide aimed at smaller companies that lack dedicated IT or support staff called “ Using Online Services Safely ”. Its purpose is to help smaller players bolster their cybersecurity defenses and mitigate the potential impact of attacks on companies... |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 17:01:00 | Microsoft publie Pyrit - un outil d'équipe rouge pour AI génératif Microsoft Releases PyRIT - A Red Teaming Tool for Generative AI (lien direct) |
Microsoft a publié un cadre d'automatisation d'accès ouvert appelé & nbsp; pyrit & nbsp; (abréviation de l'outil d'identification du risque de Python) pour identifier de manière proactive les risques dans les systèmes génératifs de l'intelligence artificielle (IA).
L'outil d'équipe rouge est conçu pour «permettre à chaque organisation à travers le monde d'innover avec responsabilité avec les dernières avancées de l'intelligence artificielle», Ram Shankar Siva Kumar, AI Red Team
Microsoft has released an open access automation framework called PyRIT (short for Python Risk Identification Tool) to proactively identify risks in generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The red teaming tool is designed to "enable every organization across the globe to innovate responsibly with the latest artificial intelligence advances," Ram Shankar Siva Kumar, AI red team |
Tool Tool | ★★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 16:59:00 | Comment utiliser la matrice de capacités SoC d'automatisation de Tines \\ How to Use Tines\\'s SOC Automation Capability Matrix (lien direct) |
Créé par John Tuckner et l'équipe de Workflow and Automation Platform & NBSP; Tines, The & NBSP; Soc Automation Capability Matrix (SOC ACM) & NBSP; est un ensemble de techniques conçues pour aider les équipes d'opérations de sécurité à comprendre leurs capacités d'automatisation et à répondre plus efficacement aux incidents. & NBSP;
Un outil personnalisable, fournisseur-agnostique, avec des listes d'opportunités d'automatisation, elle a été partagée
Created by John Tuckner and the team at workflow and automation platform Tines, the SOC Automation Capability Matrix (SOC ACM) is a set of techniques designed to help security operations teams understand their automation capabilities and respond more effectively to incidents. A customizable, vendor-agnostic tool featuring lists of automation opportunities, it\'s been shared |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 16:14:27 | Sites Web de piratage AIS AIs Hacking Websites (lien direct) |
nouveau recherche :
les agents LLM peuvent pirater de manière autonome les sites Web
Résumé: Ces dernières années, les modèles de grandes langues (LLM) sont devenus de plus en plus capables et peuvent désormais interagir avec les outils (c'est-à-dire les fonctions d'appel), lire des documents et s'appeler récursivement.En conséquence, ces LLM peuvent désormais fonctionner de manière autonome en tant qu'agents.Avec l'augmentation des capacités de ces agents, les travaux récents ont spéculé sur la façon dont les agents LLM affecteraient la cybersécurité.Cependant, on ne sait pas grand-chose sur les capacités offensives des agents LLM.
Dans ce travail, nous montrons que les agents LLM peuvent pirater de manière autonome des sites Web, effectuant des tâches aussi complexes que l'extraction de schéma de base de données aveugle et les injections SQL sans rétroaction humaine.Surtout, l'agent n'a pas besoin de connaître au préalable la vulnérabilité.Cette capacité est de manière unique par des modèles frontières qui sont très capables d'utiliser des outils et de tirer parti du contexte étendu.À savoir, nous montrons que le GPT-4 est capable de ces hacks, mais les modèles open-source existants ne le sont pas.Enfin, nous montrons que GPT-4 est capable de trouver de manière autonome des vulnérabilités dans les sites Web à l'état sauvage.Nos résultats soulèvent des questions sur le déploiement généralisé de LLMS ...
New research: LLM Agents can Autonomously Hack Websites Abstract: In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly capable and can now interact with tools (i.e., call functions), read documents, and recursively call themselves. As a result, these LLMs can now function autonomously as agents. With the rise in capabilities of these agents, recent work has speculated on how LLM agents would affect cybersecurity. However, not much is known about the offensive capabilities of LLM agents. In this work, we show that LLM agents can autonomously hack websites, performing tasks as complex as blind database schema extraction and SQL injections without human feedback. Importantly, the agent does not need to know the vulnerability beforehand. This capability is uniquely enabled by frontier models that are highly capable of tool use and leveraging extended context. Namely, we show that GPT-4 is capable of such hacks, but existing open-source models are not. Finally, we show that GPT-4 is capable of autonomously finding vulnerabilities in websites in the wild. Our findings raise questions about the widespread deployment of LLMs... |
Hack Tool Vulnerability | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 12:53:03 | Groupes de cybercrimins exploitant activement \\ 'Catastrophic \\' Screenconnect Bogue Cybercriminal groups actively exploiting \\'catastrophic\\' ScreenConnect bug (lien direct) |
 Une vulnérabilité de sécurité dans un outil d'accès à distance disponible dans le commerce est exploitée par des criminels de ransomware quelques jours seulement après la première fois.La vulnérabilité spécifique, affectant certaines versions du produit ScreenConnect de ConnectWise \\, a reçu le maximum score CVSS de 10 , indiquantqu'il représente une menace critique pour les organisations qui n'ont pas corrigé leur logiciel.
Une vulnérabilité de sécurité dans un outil d'accès à distance disponible dans le commerce est exploitée par des criminels de ransomware quelques jours seulement après la première fois.La vulnérabilité spécifique, affectant certaines versions du produit ScreenConnect de ConnectWise \\, a reçu le maximum score CVSS de 10 , indiquantqu'il représente une menace critique pour les organisations qui n'ont pas corrigé leur logiciel.
 A security vulnerability in a commercially available remote access tool is being exploited by ransomware criminals just days after first being disclosed. The specific vulnerability, affecting some versions of ConnectWise\'s ScreenConnect product, has been given the maximum CVSS score of 10, indicating that it poses a critical threat to organizations that haven\'t patched their software.
A security vulnerability in a commercially available remote access tool is being exploited by ransomware criminals just days after first being disclosed. The specific vulnerability, affecting some versions of ConnectWise\'s ScreenConnect product, has been given the maximum CVSS score of 10, indicating that it poses a critical threat to organizations that haven\'t patched their software. |
Ransomware Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 11:00:00 | Détection des connexions anormales O365 et des techniques d'évasion Detecting anomalous O365 logins and evasion techniques (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Summary Businesses across multiple industries, regardless of size, are at risk of being targeted with Microsoft 365 phishing campaigns. These campaigns trick users into visiting fake Microsoft login page where threat actors capture the user’s credentials. Even accounts with MFA can be victim to these types of attacks. There are several ways in which MFA is being bypassed with these types of campaigns. MFA Fatigue is one of the ways threat actors are bypassing MFA and this method attempts to exploit human error by repeatedly logging in with the stolen credentials causing an overwhelming number of MFA prompts in attempts to get the user to approve the login. Another MFA bypass technique is SIM Swapping. A SIM card is a small chip that your mobile carrier uses to hold identification information to tie your phone to you and your mobile carrier. Threat actors have found a weakness in this because there are scenarios where a customer may need a new SIM card (for example, they lost their phone). Carriers can transfer your identification information from your old SIM card to new one. SIM Swapping is when a threat actor abuses this feature and impersonates you to convince your mobile carrier to switch your phone number to a SIM card that is in the threat actor’s possession. This then allows the threat actor to receive MFA codes sent to your number via phone call or SMS. | Tool Threat Mobile Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 10:46:53 | Fortress déploie une notification de correctifs automatisé, l'outil d'authenticité pour sécuriser les actifs critiques des États-nations hostiles Fortress deploys automated patch notification, authenticity tool to secure critical assets from hostile nation-states (lien direct) |
L'Agence de sécurité de la cybersécurité et des infrastructures (CISA), la National Security Agency (NSA) et le Federal Bureau of Investigation ...
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation... |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 08:00:00 | Wallace – L\'analyseur CSS qui vous juge et vous conseille (lien direct) | Rédiger du CSS peut sembler aisé, mais l'outil en ligne Wallace révèle les erreurs commises. Il analyse les feuilles de style, offre des statistiques et des conseils pour améliorer la qualité du code. En suivant ses recommandations, on peut optimiser son CSS, le rendre plus performant et facile à maintenir. | Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-22 16:14:00 | Les cybercriminels ont armé l'outil SSH-Ssh-Sake open source pour les attaques de réseau Cybercriminals Weaponizing Open-Source SSH-Snake Tool for Network Attacks (lien direct) |
Un outil de cartographie de réseau récemment open open appelé & nbsp; ssh-snake & nbsp; a été réutilisé par des acteurs de la menace pour mener des activités malveillantes.
"SSH-Snake est un ver auto-modifiant qui exploite les informations d'identification SSH découvertes sur un système compromis pour commencer à se propager dans tout le réseau", a déclaré le chercheur de Sysdig, Miguel Hern & Aacute; Ndez & Nbsp.
"Le ver recherche automatiquement les informations d'identification connues
A recently open-sourced network mapping tool called SSH-Snake has been repurposed by threat actors to conduct malicious activities. "SSH-Snake is a self-modifying worm that leverages SSH credentials discovered on a compromised system to start spreading itself throughout the network," Sysdig researcher Miguel Hernández said. "The worm automatically searches through known credential |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-22 16:13:00 | Backdoor du logiciel du gouvernement russe pour déployer des logiciels malveillants de rat Konni Russian Government Software Backdoored to Deploy Konni RAT Malware (lien direct) |
Un programme d'installation d'un outil probablement utilisé par le département consulaire russe du ministère des Affaires étrangères (MID) a été détrommé pour livrer un cheval de Troie à distance appelé & nbsp; konni rat & nbsp; (aka & nbsp; updog).
Les résultats proviennent de la société allemande de cybersécurité DCSO, qui a lié l'activité à l'origine des acteurs de la République de Corée du peuple démocrate (DPRC) -nexus ciblant la Russie.
Le
An installer for a tool likely used by the Russian Consular Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MID) has been backdoored to deliver a remote access trojan called Konni RAT (aka UpDog). The findings come from German cybersecurity company DCSO, which linked the activity as originating from the Democratic People\'s Republic of Korea (DPRK)-nexus actors targeting Russia. The |
Malware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 20:59:32 | Bogue critique RMM Connectwise Posée pour l'exploitation Avalanche Critical ConnectWise RMM Bug Poised for Exploitation Avalanche (lien direct) |
Deux jours après la divulgation, la plupart des cas de l'outil de bureau à distance restent non corrigées, tandis que les cyberattaquants ont commencé l'exploitation dans la volonté - et les chercheurs préviennent que cela pourrait devenir laid et rapide.
Two days after disclosure, most instances of the remote desktop tool remain unpatched, while cyberattackers have started in-the-wild exploitation - and researchers warn it could get ugly, fast. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 15:58:44 | Rapport 2024 Incident Response - Unit 42/Palo Alto Networks (lien direct) | Rapport 2024 Incident Response - Unit 42/Palo Alto Networks Dans le paysage des menaces de cybersécurité en constante évolution, il est plus que jamais crucial de garder une longueur d'avance sur les acteurs malveillants. Pour cela, il faut comprendre leurs comportements, connaître leurs techniques et outils. - Investigations | Tool Threat Studies | ★★★ |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
