What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2024-02-29 19:41:02 | Android Money Transfer Xhelper App exposé comme réseau de blanchiment d'argent Android Money Transfer XHelper App Exposed as Money Laundering Network (lien direct) |
> Par deeba ahmed
ne confond pas l'application Xhelper avec le malware du malhelper, qui cible les appareils Android et est notoirement difficile à supprimer.
Ceci est un article de HackRead.com Lire le post original: Android Money Transfer Xhelper App exposé comme réseau de blanchiment d'argent
>By Deeba Ahmed Don\'t confuse the XHelper app with the notorious XHelper malware, which targets Android devices and is notoriously difficult to remove. This is a post from HackRead.com Read the original post: Android Money Transfer XHelper App Exposed as Money Laundering Network |
Malware Tool Mobile | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 10:30:00 | Blue Team Toolkit: 6 outils open source pour évaluer et améliorer les défenses des entreprises Blue Team toolkit: 6 open-source tools to assess and enhance corporate defenses (lien direct) |
Voici comment l'équipe bleue éloigne les équipes rouges et quelques outils open source qu'il peut exploiter pour identifier les caillis dans l'armure d'entreprise
Here\'s how the blue team wards off red teamers and a few open-source tools it may leverage to identify chinks in the corporate armor |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-29 06:00:13 | Briser la chaîne d'attaque: des mouvements décisifs Break the Attack Chain: Decisive Moves (lien direct) |
In our “Break the Attack Chain” blog series, we have looked at how threat actors compromise our defenses and move laterally within our networks to escalate privileges and prepare for their endgame. Now, we come to the final stage of the attack chain where it\'s necessary to broaden our outlook a little. While most external threat actors will follow the same playbook, they aren\'t our only adversaries. The modern reality is that data often just walks out of the door because our employees take it with them. More than 40% of employees admit to taking data when they leave. At the same time, careless employees who make security mistakes are responsible for more than half of insider-led data loss incidents. So, while it\'s important to detect and deter cybercriminals who want to exfiltrate our data, we must also watch out for our users. Whether they are malicious or careless, our users are just as capable of exposing sensitive data. In this third and final installment, we discuss how companies tend to lose data-and how we can better protect it from all manner of risks. Understanding data loss As with every stage in the attack chain, we must first understand threats before we can put protections in place. Let\'s start with the case of a cybercriminal following the typical attack chain. While this may not sound like a traditional insider attack, it\'s often aided by careless or reckless employees. Users expose data and open themselves and your business up to compromise in a multitude of ways, like using weak passwords, reusing credentials, forgoing security best practices and clicking on malicious links or attachments. Any of these risky moves give cybercriminals a way into your networks where they can embark on lateral movement and escalation. Incidents like these are so common that careless or compromised users cause over 80% of insider-led data loss. Malicious insiders make up the remainder. Insider threats could be a disgruntled employee looking to cause disruption, a user compromised by cybercriminals, or, increasingly, an employee who will soon leave your organization. In most cases, data exfiltration follows a three-stage pattern: Access. Users, whether malicious or compromised, will attempt to take as much information as possible. This could mean excessive downloading or copying from corporate drives or exporting data from web interfaces or client apps. Obfuscation. Both cybercriminals and malicious insiders will be aware of the kinds of activity likely to trigger alarms and will take steps to avoid them. Changing file names and extensions, deleting logs and browsing history, and encrypting files are typical strategies. Exfiltration. With targets acquired and tracks covered, data exfiltration is then carried out by copying files to a personal cloud or removable storage device and sharing files with personal or burner email accounts. Defending from the inside out As we explained in our webinar series, while the initial stage of the attack chain focuses on keeping malicious actors outside our organization, the final two stages are far more concerned with what\'s happening inside it. Therefore, any effective defense must work from the inside out. It must detect and deter suspicious activity before data can slip past internal protections and be exposed to the outside world. Of course, data can do many things-but it cannot leave an organization on its own. Whether compromised, careless or malicious, a human is integral to any data loss incident. That\'s why traditional data loss prevention (DLP) tools are not as effective as they used to be. By focusing on the content of an incident, they only address a third of the problem. Instead, a comprehensive defense against data loss must merge content classification with threat telemetry and user behavior. Proofpoint Information Protection is the only solution that uses all three across channels in a unified, cloud-native interface. With this information, security teams can identify who is accessing and moving data-when, where and why. And | Tool Threat Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-28 17:30:00 | Les problèmes du FBI ont une alerte sur les menaces russes ciblant les routeurs Ubiquiti FBI Issues Alert on Russian Threats Targeting Ubiquiti Routers (lien direct) |
Les routeurs ont été détournés pour voler des informations d'identification, du trafic proxy et des pages de phishing et des outils personnalisés
The routers were hijacked to steal credentials, proxy traffic, and host phishing pages and custom tools |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-28 06:00:52 | Briser la chaîne d'attaque: développer la position pour détecter les attaques de mouvement latérales Break the Attack Chain: Developing the Position to Detect Lateral Movement Attacks (lien direct) |
In this three-part “Break the Attack Chain” blog series, we look at how threat actors compromise our defenses and move laterally within our networks to escalate privileges and prepare for their final endgame. If one phrase could sum up the current state of the threat landscape, it is this: Threat actors don\'t break in. They log in. Rather than spend time trying to circumnavigate or brute force their way through our defenses, today\'s cybercriminals set their sights firmly on our users. Or to be more accurate, their highly prized credentials and identities. This remains true at almost every stage of the attack chain. Identities are not just an incredibly efficient way into our organizations, they also stand in the way of the most valuable and sensitive data. As a result, the cat-and-mouse game of cybersecurity is becoming increasingly like chess, with the traditional smash-and-grab approach making way for a more methodical M.O. Cybercriminals are now adept at moving laterally through our networks, compromising additional users to escalate privileges and lay the necessary groundwork for the endgame. While this more tactical gambit has the potential to do significant damage, it also gives security teams many more opportunities to spot and thwart attacks. If we understand the threat actor\'s playbook from the initial compromise to impact, we can follow suit and place protections along the length of the attack chain. Understanding the opening repertoire To continue our chess analogy, the more we understand our adversary\'s opening repertoire, the better equipped we are to counter it. When it comes to lateral movement, we can be sure that the vast majority of threat actors will follow the line of least resistance. Why attempt to break through defenses and risk detection when it is much easier to search for credentials that are stored on the compromised endpoint? This could be a search for password.txt files, stored Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) credentials, and anything of value that could be sitting in the recycle bin. If it sounds scarily simple, that\'s because it is. This approach does not require admin privileges. It is unlikely to trigger any alarms. And unfortunately, it\'s successful time and time again. Proofpoint has found through our research that one in six endpoints contain an exploitable identity risk that allows threat actors to escalate privileges and move laterally using this data. (Learn more in our Analyzing Identity Risks report.) When it comes to large-scale attacks, DCSync is also now the norm. Nation-states and many hacking groups use it. It is so ubiquitous that if it were a zero-day, security leaders would be crying out for a patch. However, as there is general acceptance that Active Directory is so difficult to secure, there is also an acceptance that vulnerabilities like this will continue to exist. In simple terms, a DCSync attack allows a threat actor to simulate the behavior of a domain controller and retrieve password data on privileged users from Active Directory. And, once again, it is incredibly easy to execute. With a simple PowerShell command, threat actors can find users with the permissions they require. Add an off-the-shelf tool like Mimikatz into the mix, and within seconds, they can access every hash and every Active Directory privilege on the network. Mastering our defense With threat actors inside our organizations, it is too late for traditional perimeter protections. Instead, we must take steps to limit attackers\' access to further privileges and encourage them to reveal their movements. This starts with an assessment of our environment. Proofpoint Identity Threat Defense offers complete transparency, allowing security teams to see where they are most vulnerable. With this information, we can shrink the potential attack surface by increasing protections around privileged users and cleaning up endpoints to make it harder for cybercriminals to access valuable identities. With Proofpoin | Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 21:38:59 | Qu'est-ce que Sora et qu'est-ce que cela signifie pour votre sécurité Internet personnelle? What is Sora and What Does It Mean for Your Personal Internet Security? (lien direct) |
>  Imaginez un outil qui peut transformer le texte en vidéos captivantes, combler l'écart entre l'imagination et la réalité en créant des vidéos ...
Imaginez un outil qui peut transformer le texte en vidéos captivantes, combler l'écart entre l'imagination et la réalité en créant des vidéos ...
>  Imagine a tool that can transform text into captivating videos, bridging the gap between imagination and reality by creating videos...
Imagine a tool that can transform text into captivating videos, bridging the gap between imagination and reality by creating videos...
|
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 19:12:51 | Khan de FTC \\ avertit l'industrie technologique que l'agence appliquera strictement la confidentialité des données de l'IA FTC\\'s Khan warns tech industry that agency will strictly enforce AI data privacy (lien direct) |
 Les outils d'intelligence artificielle seront vigoureusement réglementés par la Federal Trade Commission (FTC), en tenant compte de la vie privée des consommateurs, a déclaré mardi sa présidente Lina Khan à un audience des dirigeants de la technologie et des fondateurs de startup lors d'une conférence."Nous réalisons des remèdes facilement administrables avec des règles de ligne lumineuse sur le développement, l'utilisation et la gestion des entrées d'IA", a déclaré Khan
Les outils d'intelligence artificielle seront vigoureusement réglementés par la Federal Trade Commission (FTC), en tenant compte de la vie privée des consommateurs, a déclaré mardi sa présidente Lina Khan à un audience des dirigeants de la technologie et des fondateurs de startup lors d'une conférence."Nous réalisons des remèdes facilement administrables avec des règles de ligne lumineuse sur le développement, l'utilisation et la gestion des entrées d'IA", a déclaré Khan
 Artificial intelligence tools will be vigorously regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), with an eye on consumer privacy, its Chair Lina Khan told an audience of tech executives and startup founders at a conference Tuesday. “We\'re crafting easily administrable remedies with bright-line rules on the development, use and management of AI inputs,” Khan said
Artificial intelligence tools will be vigorously regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), with an eye on consumer privacy, its Chair Lina Khan told an audience of tech executives and startup founders at a conference Tuesday. “We\'re crafting easily administrable remedies with bright-line rules on the development, use and management of AI inputs,” Khan said |
Tool Conference | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 14:58:43 | Veracode scan pour le code vs: maintenant avec Veracode Corre Veracode Scan for VS Code: Now with Veracode Fix (lien direct) |
Veracode est heureux d'annoncer la disponibilité de la capacité de correction de Veracode dans Veracode Scan pour le code VS.Les développeurs peuvent désormais découvrir et résoudre les défauts de sécurité en utilisant des outils génératifs alimentés par Veracode \\ directement directement à partir de leur environnement de développement intégré (IDE).
Selon l'état de Veracode de la sécurité des logiciels, 45,9% des organisations ont une dette de sécurité critique.Le fait que ces données proviennent d'organisations qui testent activement leur logiciel avec une solution de haute qualité implique qu'il ne trouve pas de défauts qui sont le problème: il les répare.
L'année dernière, nous avons introduit Veracode Fix & # 8211;Un assistant AI qui peut prendre les résultats d'un scan statique Veracode et permettre aux développeurs d'appliquer des correctifs suggérés directement à leur code.Veracode Fix réduit le temps de recherche et de mise en œuvre d'un correctif pour une découverte donnée à quelques minutes, tout en gardant le développeur en contrôle.FIX a été implémenté dans le cadre de l'utilitaire CLI Veracode, qui est disponible pour Linux, Windows et MacOS.
UN…
Veracode is pleased to announce the availability of Veracode Fix capability in Veracode Scan for VS Code. Now developers can discover and remediate security flaws using Veracode\'s Generative AI-powered tools directly from their Integrated Development Environment (IDE). According to the Veracode State of Software Security, 45.9% of organizations have critical security debt. The fact that this data comes from organizations who are actively testing their software with a high-quality solution implies that it\'s not finding flaws that is the problem: it\'s fixing them. Last year we introduced Veracode Fix – an AI assistant that can take the results of a Veracode Static scan and allow developers to apply suggested fixes directly to their code. Veracode Fix cuts the time to research and implement a fix for a given finding to minutes, while still keeping the developer in control. Fix was implemented as part of the Veracode CLI utility, which is available for Linux, Windows, and MacOS. A… |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 12:03:59 | China Surveillance Company a piraté China Surveillance Company Hacked (lien direct) |
La semaine dernière, quelqu'un a publié quelque chose comme 570 fichiers, images et journaux de chat d'une entreprise chinoise appelée I-Soon.I-Soon vend des services de piratage et d'espionnage aux gouvernements nationaux et locaux chinois.
Beaucoup de Détails dans The News Articles .
Ce sont des détails sur les outils ou les techniques, plus le fonctionnement interne de l'entreprise.Et ils semblent principalement pirater régionalement.
Last week, someone posted something like 570 files, images and chat logs from a Chinese company called I-Soon. I-Soon sells hacking and espionage services to Chinese national and local government. Lots of details in the news articles. These aren’t details about the tools or techniques, more the inner workings of the company. And they seem to primarily be hacking regionally. |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 11:00:00 | L'évolution du point de terminaison - passant des critères de terminaison traditionnels aux charges de travail cloud ou conteneurisées et les solutions de sécurité pour les protéger The endpoint evolution - Evolving from traditional endpoints to cloud or containerized workloads and the security solutions to protect them (lien direct) |
As organizations grow and more endpoints are added across the enterprise, they create an increasingly broad attack surface sophisticated attackers are looking to compromise. According to the 2019 Endpoint Security Trends Report 70% of breaches originate at the endpoint¹. That is likely because endpoints typically represent the Intersection between humans and machines creating vulnerable points of entry for cybercriminals. This is why it is increasingly important to secure your endpoints.
Growth in endpoints
An endpoint is defined as any computing device that communicates back and forth with a network to which it is connected. Some end user devices serve as an interface with human users while others are servers that communicate with other endpoints on the network. Traditional endpoints began as physical devices including servers, workstations, desktops, and laptops, all connected to a corporate network. When smartphones and tablets became handheld computing devices with access to corporate email, document sharing and collaboration tools the number of endpoints at least doubled.
Then came the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) including devices like printers, webcams, smartwatches, and thermostats, all of which are connected to the network. Industries like healthcare and manufacturing are using millions of IoT sensors to collect and exchange data. This continued growth in IoT only increases the number of endpoints that need to be protected.
Another contribution to the growth in endpoints is the migration to the cloud. It is estimated that 67% of enterprise infrastructure is cloud-based². This cloud transformation is the evolution from physical devices to virtualization and containerization.
Endpoint virtualization
The cloud is a multi-tenant environment where multiple users run services on the same server hardware. Virtualization and containerization are both virtualization technologies that separate the host operating system from the programs that run in them.
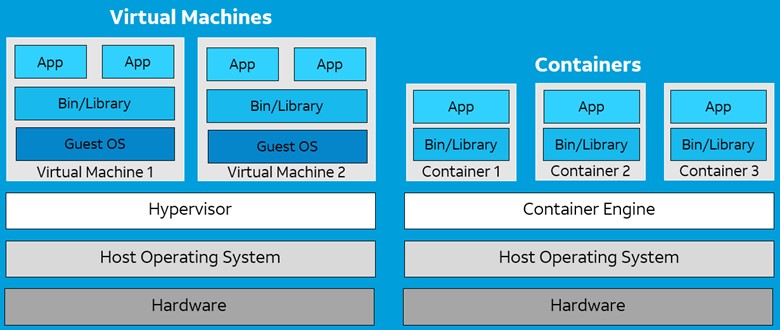 Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi
Virtualization is achieved using a hypervisor, which splits CPU, RAM, and storage resources between multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM behaves like a separate computer that gets a guest operating system and each VM is independent of each other. This allows organizations to run multiple OS instances on a single server.
Containerization, on the other hand, runs a single host OS instance and uses a container engine to help package applications into container images that can be easily deployed and re-used. By splitting each individual application function or microservice into containers they can operate independently to improve enterprise resilience and scalability. Kubernetes then manages the orchestration of multiple containers. VMs and containers present very different security challenges so let’s look at the evolution of endpoint security and the solutions that meet the needs of complex customer environments.
Securing endpoints
For decades, organizations have heavily relied on antivirus (AV) software to secure endpoints. However, traditional antivirus worked by matching known malicious signatures in a database and can no longer protect against today’s sophisticated threats. Modern endpoint security solutions are less signature-based and much more behavior-based. Endpoint protection platforms (EPP) offer cloud native architectures that provide a layered defense against fileless attacks using machine learning and behavioral AI to protect against malicious activity. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions went beyond protection by recording and storing endpoint-system level behaviors to detect malicious threats.
EDR solutions use data analytics combined with threat intelligence feeds to provide incident responders with the forensic data for completing investigations and threat hunting. In addi |
Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-27 05:00:31 | Risque et ils le savent: 96% des utilisateurs de prise de risque sont conscients des dangers mais le font quand même, 2024 State of the Phish révèle Risky and They Know It: 96% of Risk-Taking Users Aware of the Dangers but Do It Anyway, 2024 State of the Phish Reveals (lien direct) |
We often-and justifiably-associate cyberattacks with technical exploits and ingenious hacks. But the truth is that many breaches occur due to the vulnerabilities of human behavior. That\'s why Proofpoint has gathered new data and expanded the scope of our 2024 State of the Phish report. Traditionally, our annual report covers the threat landscape and the impact of security education. But this time, we\'ve added data on risky user behavior and their attitudes about security. We believe that combining this information will help you to: Advance your cybersecurity strategy Implement a behavior change program Motivate your users to prioritize security This year\'s report compiles data derived from Proofpoint products and research, as well as from additional sources that include: A commissioned survey of 7,500 working adults and 1,050 IT professionals across 15 countries 183 million simulated phishing attacks sent by Proofpoint customers More than 24 million suspicious emails reported by our customers\' end users To get full access to our global findings, you can download your copy of the 2024 State of the Phish report now. Also, be sure to register now for our 2024 State of the Phish webinar on March 5, 2024. Our experts will provide more insights into the key findings and answer your questions in a live session. Meanwhile, let\'s take a sneak peek at some of the data in our new reports. Global findings Here\'s a closer look at a few of the key findings in our tenth annual State of the Phish report. Survey of working adults In our survey of working adults, about 71%, said they engaged in actions that they knew were risky. Worse, 96% were aware of the potential dangers. About 58% of these users acted in ways that exposed them to common social engineering tactics. The motivations behind these risky actions varied. Many users cited convenience, the desire to save time, and a sense of urgency as their main reasons. This suggests that while users are aware of the risks, they choose convenience. The survey also revealed that nearly all participants (94%) said they\'d pay more attention to security if controls were simplified and more user-friendly. This sentiment reveals a clear demand for security tools that are not only effective but that don\'t get in users\' way. Survey of IT and information security professionals The good news is that last year phishing attacks were down. In 2023, 71% of organizations experienced at least one successful phishing attack compared to 84% in 2022. The bad news is that the consequences of successful attacks were more severe. There was a 144% increase in reports of financial penalties. And there was a 50% increase in reports of damage to their reputation. Another major challenge was ransomware. The survey revealed that 69% of organizations were infected by ransomware (vs. 64% in 2022). However, the rate of ransom payments declined to 54% (vs. 64% in 2022). To address these issues, 46% of surveyed security pros are increasing user training to help change risky behaviors. This is their top strategy for improving cybersecurity. Threat landscape and security awareness data Business email compromise (BEC) is on the rise. And it is now spreading among non-English-speaking countries. On average, Proofpoint detected and blocked 66 million BEC attacks per month. Other threats are also increasing. Proofpoint observed over 1 million multifactor authentication (MFA) bypass attacks using EvilProxy per month. What\'s concerning is that 89% of surveyed security pros think MFA is a “silver bullet” that can protect them against account takeover. When it comes to telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD), Proofpoint saw 10 million incidents per month, on average. The peak was in August 2023, which saw 13 million incidents. When looking at industry failure rates for simulated phishing campaigns, the finance industry saw the most improvement. Last year the failure rate was only 9% (vs. 16% in 2022). “Resil | Ransomware Tool Vulnerability Threat Studies Technical | ★★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 22:20:45 | Fortress Information Security déploie l'outil de notification et d'authenticité de correctifs automatisés Fortress Information Security Deploys Automated Patch Notification and Authenticity Tool (lien direct) |
We often-and justifiably-associate cyberattacks with technical exploits and ingenious hacks. But the truth is that many breaches occur due to the vulnerabilities of human behavior. That\'s why Proofpoint has gathered new data and expanded the scope of our 2024 State of the Phish report. Traditionally, our annual report covers the threat landscape and the impact of security education. But this time, we\'ve added data on risky user behavior and their attitudes about security. We believe that combining this information will help you to: Advance your cybersecurity strategy Implement a behavior change program Motivate your users to prioritize security This year\'s report compiles data derived from Proofpoint products and research, as well as from additional sources that include: A commissioned survey of 7,500 working adults and 1,050 IT professionals across 15 countries 183 million simulated phishing attacks sent by Proofpoint customers More than 24 million suspicious emails reported by our customers\' end users To get full access to our global findings, you can download your copy of the 2024 State of the Phish report now. Also, be sure to register now for our 2024 State of the Phish webinar on March 5, 2024. Our experts will provide more insights into the key findings and answer your questions in a live session. Meanwhile, let\'s take a sneak peek at some of the data in our new reports. Global findings Here\'s a closer look at a few of the key findings in our tenth annual State of the Phish report. Survey of working adults In our survey of working adults, about 71%, said they engaged in actions that they knew were risky. Worse, 96% were aware of the potential dangers. About 58% of these users acted in ways that exposed them to common social engineering tactics. The motivations behind these risky actions varied. Many users cited convenience, the desire to save time, and a sense of urgency as their main reasons. This suggests that while users are aware of the risks, they choose convenience. The survey also revealed that nearly all participants (94%) said they\'d pay more attention to security if controls were simplified and more user-friendly. This sentiment reveals a clear demand for security tools that are not only effective but that don\'t get in users\' way. Survey of IT and information security professionals The good news is that last year phishing attacks were down. In 2023, 71% of organizations experienced at least one successful phishing attack compared to 84% in 2022. The bad news is that the consequences of successful attacks were more severe. There was a 144% increase in reports of financial penalties. And there was a 50% increase in reports of damage to their reputation. Another major challenge was ransomware. The survey revealed that 69% of organizations were infected by ransomware (vs. 64% in 2022). However, the rate of ransom payments declined to 54% (vs. 64% in 2022). To address these issues, 46% of surveyed security pros are increasing user training to help change risky behaviors. This is their top strategy for improving cybersecurity. Threat landscape and security awareness data Business email compromise (BEC) is on the rise. And it is now spreading among non-English-speaking countries. On average, Proofpoint detected and blocked 66 million BEC attacks per month. Other threats are also increasing. Proofpoint observed over 1 million multifactor authentication (MFA) bypass attacks using EvilProxy per month. What\'s concerning is that 89% of surveyed security pros think MFA is a “silver bullet” that can protect them against account takeover. When it comes to telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD), Proofpoint saw 10 million incidents per month, on average. The peak was in August 2023, which saw 13 million incidents. When looking at industry failure rates for simulated phishing campaigns, the finance industry saw the most improvement. Last year the failure rate was only 9% (vs. 16% in 2022). “Resil | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 21:39:24 | DOE annonce des investissements de 45 millions de dollars pour la recherche en cybersécurité DOE announces $45 million investment for cybersecurity research (lien direct) |
> Le financement va à 16 projets visant à développer des outils avancés pour protéger le secteur de l'énergie.
>The funding goes to 16 projects aimed at developing advanced tools to protect the energy sector. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 19:57:01 | UAC-0184 cible l'entité ukrainienne en Finlande avec Remcos Rat UAC-0184 Targets Ukrainian Entity in Finland With Remcos RAT (lien direct) |
Le logiciel malveillant IDAT Loader a été utilisé pour livrer l'outil de cyber-espionnage, en utilisant la stéganographie, une technique rarement vue dans les attaques du monde réel.
The IDAT Loader malware was used to deliver the cyber espionage tool, employing steganography, a seldom-seen technique in real-world attacks. |
Malware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 13:00:31 | Sécuriser la route à venir: aborder les erreurs de configuration du cloud persistant dans l'industrie automobile Securing the Road Ahead: Addressing Persistent Cloud Misconfigurations in the Automotive Industry (lien direct) |
> Explorez une paire d'expositions de sécurité de l'industrie automobile et comment les outils de sécurité appropriés auraient pu empêcher ces mêmes anciens problèmes \\ 'de se produire.Plus tôt ce mois-ci, BMW a été encore une autre victime de dangereux erronés dans leur stockage cloud, qui exposent des clés privées et des données sensibles.Selon un récent article de TechCrunch, un seau de stockage Azure public contenait des «fichiers de script qui comprenaient des informations d'accès, des clés secrètes pour accéder aux adresses de godet privées et des détails sur d'autres services cloud».Pour être juste, BMW n'est pas seul dans ces questions, en fait, selon le rapport de sécurité du cloud de point de contrôle de 2023, [& # 8230;]
>Explore a pair of security exposures from the automotive industry and how the proper security tools could have prevented these \'same old issues\' from happening. Earlier this month, BMW was yet another victim of dangerous misconfigurations in their cloud storage, which exposed private keys and sensitive data. According to a recent article by TechCrunch, a public Azure storage bucket held “script files that included access information, secret keys for accessing private bucket addresses, and details about other cloud services.” To be fair, BMW is not alone in these issues, in fact, according to the 2023 Check Point Cloud Security Report, […] |
Tool Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 12:00:00 | Mise à jour du voyage!Le NIST CSF 2.0 est là… avec de nombreuses ressources utiles… Travel Update! The NIST CSF 2.0 is HERE…Along with Many Helpful Resources… (lien direct) |
NIST CSF 2.0 Liens rapides |Explorez notre suite complète de ressources: CSF 2.0 Guides de démarrage rapide CSF 2.0 Profils CSF 2.0 Références informatives outil de référence de cybersécurité et de confidentialité (CPRT) CSF 2.0 Reference Tool CSF 2.0 Site Web (Home Page) NIST News Annonce de NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) Processus de développement du processus de développement de processus de développement du processus de développement de processus de développement NIST (CSF) Processus de développement du processus de développement du processus de développement de la cybersécurité (CSF) (CSF)Tous ont commencé avec le décret exécutif (EO) 13636 il y a plus de dix ans, qui a appelé à la construction d'un ensemble d'approches (un cadre) pour réduire les risques aux infrastructures critiques.Grâce à cet EO, NIST a été chargé de développer un «cadre de cybersécurité».Nous savions que faire
NIST CSF 2.0 QUICK LINKS | Explore our Full Suite of Resources: CSF 2.0 Quick Start Guides CSF 2.0 Profiles CSF 2.0 Informative References Cybersecurity & Privacy Reference Tool (CPRT) CSF 2.0 Reference Tool CSF 2.0 Website ( Homepage ) Official NIST News Announcement The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) development process all started with Executive Order (EO)13636 over a decade ago, which called for building a set of approaches ( a framework ) for reducing risks to critical infrastructure. Through this EO, NIST was tasked with developing a "Cybersecurity Framework." We knew that, to do |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 11:00:00 | Construire une cyber-résilience contre l'ingénierie sociale alimentée par l'IA Building Cyber resilience against AI-powered social engineering (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Exploring advanced AI tactics in social engineering and effective strategies for cyber defense Long-standing as a significant threat in the business world, social engineering attacks constitute a major portion of global cyberattacks. An average business regularly faces a substantial number of such attacks every year. These attacks manifest in various forms, from intricate phishing emails to complex interactions designed to deceive employees, often leading to grave outcomes. This alarming reality is further underscored by the following statistics: · Social engineering is implicated in 98% of all cyberattacks · Approximately 90% of malicious data breaches occur due to social engineering · The typical organization faces over 700 social engineering attacks each year · The average cost incurred from a social engineering attack is about $130,000 | Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 05:03:36 | Les tenants et aboutissants de la confidentialité des données, partie 2: confidentialité par conception en protection de l'information The Ins and Outs of Data Privacy, Part 2: Privacy by Design in Information Protection (lien direct) |
This is the second blog in a two-part series about data privacy. In our previous post, we discussed how data privacy has become increasingly important. And we covered why data loss protection (DLP) and insider threat management (ITM) tools are critical to ensuring data privacy. The shift to “work from anywhere” and the increase in cloud adoption have caused a rise in data loss and insider threats. To defend data from careless, malicious and compromised insiders-and the harm that they cause-security teams must implement data security tools like data loss prevention (DLP) and insider threat management (ITM) platforms. These tools monitor and control how employees interact with data. At the same time, companies are collecting more and more data about employees themselves, like protected health information (PHI). The abundance of all this data-which is being collected and processed in the cloud-creates a critical challenge for security teams. They must protect employee privacy without impeding productivity. In this post, we\'ll explore the topic of privacy by design, which aims to strike a balance between these two challenges. We\'ll cover why it\'s so important. And we\'ll discuss how Proofpoint Information Protection can help you build a modern DLP program and comply with data privacy laws. Why privacy by design matters for DLP and ITM Privacy by design is a framework that embeds privacy into the design of IT systems, infrastructure and business processes. Privacy is not an afterthought. It is considered right from the start-in the initial design phase. What\'s more, it\'s a core component that integrates visibility, transparency and user-centricity into its design. In short, privacy by design ensures that everything is built with the user in mind. Privacy by design is important to DLP and ITM because it helps to: Protect employee rights. Personal data is sacred. Employees expect their personal data to be safe and their rights protected. When a company takes a proactive, transparent approach to data privacy, it helps maintain trust with employees. Comply with privacy laws. Data privacy laws protect people by requiring businesses to keep their data safe and avoid sharing it unethically with third parties. These laws often require companies to tell users exactly how their data is used and collected, and to notify them in the event of a data breach. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines and penalties, which can damage a firm\'s finances and brand image. Prevent bias in investigations. When user data is kept secure and private, it ensures insider threat investigations maintain their integrity and objectivity. If a user is identified, it could influence a security analyst\'s response to an incident. User privacy helps take emotion and subjectivity out of the picture. Ensure data privacy with Proofpoint DLP and ITM Proofpoint Information Protection includes administration and access controls. These controls can help your business keep data private and meet compliance requirements. Data residency and storage Proofpoint uses regional data centers in the U.S., Europe, Australia and Japan to meet data privacy and data residency requirements. You can control exactly where your data is stored at all of these data centers. For example, you can group your endpoints and map each group to a regional data center. This ensures that data on all those endpoints are stored in that regional center. So, a U.S. realm can manage U.S. endpoint data, which is sent to the U.S. data center. Attribute-based access controls Attribute-based access controls give you a flexible and easy way to manage access to data. You can use these controls to ensure that security analysts have visibility into data on a need-to-know basis only. For instance, you can write granular policies and assign access so that a U.S.-based security analyst can only see U.S. data. They cannot see data in Europe or the Asia-Pacific region. And when an analyst needs to access a specific user\'s data for an | Data Breach Tool Threat Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-26 02:45:39 | Plonger dans le nouveau guide de cybersécurité SMB de NCSC \\ Delving into NCSC\\'s New SMB Cybersecurity Guide (lien direct) |
Bien que les attaques contre les petites et moyennes entreprises (PME) aient rarement fait la une des journaux, elles restent une menace sérieuse.Contrairement à leurs homologues d'entreprise, de nombreuses PME n'ont pas les outils, les compétences et les services d'atténuation dont ils ont besoin pour lutter contre les menaces modernes.Comprenant que les prévenus ont été prévenus, le National Cyber Security Center (NCSC) a récemment fait ses débuts sur un guide destiné aux petites entreprises qui manquent de personnel informatique ou de soutien dédié appelé «utilisant des services en ligne en toute sécurité».Son objectif est d'aider les petits joueurs à renforcer leurs défenses de cybersécurité et à atténuer l'impact potentiel des attaques contre les entreprises ...
Although attacks on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) rarely hit the headlines, they remain a serious threat. Unlike their corporate counterparts, many SMBs lack the tools, skills, and mitigation services they need to combat modern threats. Understanding that forewarned is forearmed, the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recently debuted a guide aimed at smaller companies that lack dedicated IT or support staff called “ Using Online Services Safely ”. Its purpose is to help smaller players bolster their cybersecurity defenses and mitigate the potential impact of attacks on companies... |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 17:01:00 | Microsoft publie Pyrit - un outil d'équipe rouge pour AI génératif Microsoft Releases PyRIT - A Red Teaming Tool for Generative AI (lien direct) |
Microsoft a publié un cadre d'automatisation d'accès ouvert appelé & nbsp; pyrit & nbsp; (abréviation de l'outil d'identification du risque de Python) pour identifier de manière proactive les risques dans les systèmes génératifs de l'intelligence artificielle (IA).
L'outil d'équipe rouge est conçu pour «permettre à chaque organisation à travers le monde d'innover avec responsabilité avec les dernières avancées de l'intelligence artificielle», Ram Shankar Siva Kumar, AI Red Team
Microsoft has released an open access automation framework called PyRIT (short for Python Risk Identification Tool) to proactively identify risks in generative artificial intelligence (AI) systems. The red teaming tool is designed to "enable every organization across the globe to innovate responsibly with the latest artificial intelligence advances," Ram Shankar Siva Kumar, AI red team |
Tool Tool | ★★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 16:59:00 | Comment utiliser la matrice de capacités SoC d'automatisation de Tines \\ How to Use Tines\\'s SOC Automation Capability Matrix (lien direct) |
Créé par John Tuckner et l'équipe de Workflow and Automation Platform & NBSP; Tines, The & NBSP; Soc Automation Capability Matrix (SOC ACM) & NBSP; est un ensemble de techniques conçues pour aider les équipes d'opérations de sécurité à comprendre leurs capacités d'automatisation et à répondre plus efficacement aux incidents. & NBSP;
Un outil personnalisable, fournisseur-agnostique, avec des listes d'opportunités d'automatisation, elle a été partagée
Created by John Tuckner and the team at workflow and automation platform Tines, the SOC Automation Capability Matrix (SOC ACM) is a set of techniques designed to help security operations teams understand their automation capabilities and respond more effectively to incidents. A customizable, vendor-agnostic tool featuring lists of automation opportunities, it\'s been shared |
Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 16:14:27 | Sites Web de piratage AIS AIs Hacking Websites (lien direct) |
nouveau recherche :
les agents LLM peuvent pirater de manière autonome les sites Web
Résumé: Ces dernières années, les modèles de grandes langues (LLM) sont devenus de plus en plus capables et peuvent désormais interagir avec les outils (c'est-à-dire les fonctions d'appel), lire des documents et s'appeler récursivement.En conséquence, ces LLM peuvent désormais fonctionner de manière autonome en tant qu'agents.Avec l'augmentation des capacités de ces agents, les travaux récents ont spéculé sur la façon dont les agents LLM affecteraient la cybersécurité.Cependant, on ne sait pas grand-chose sur les capacités offensives des agents LLM.
Dans ce travail, nous montrons que les agents LLM peuvent pirater de manière autonome des sites Web, effectuant des tâches aussi complexes que l'extraction de schéma de base de données aveugle et les injections SQL sans rétroaction humaine.Surtout, l'agent n'a pas besoin de connaître au préalable la vulnérabilité.Cette capacité est de manière unique par des modèles frontières qui sont très capables d'utiliser des outils et de tirer parti du contexte étendu.À savoir, nous montrons que le GPT-4 est capable de ces hacks, mais les modèles open-source existants ne le sont pas.Enfin, nous montrons que GPT-4 est capable de trouver de manière autonome des vulnérabilités dans les sites Web à l'état sauvage.Nos résultats soulèvent des questions sur le déploiement généralisé de LLMS ...
New research: LLM Agents can Autonomously Hack Websites Abstract: In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have become increasingly capable and can now interact with tools (i.e., call functions), read documents, and recursively call themselves. As a result, these LLMs can now function autonomously as agents. With the rise in capabilities of these agents, recent work has speculated on how LLM agents would affect cybersecurity. However, not much is known about the offensive capabilities of LLM agents. In this work, we show that LLM agents can autonomously hack websites, performing tasks as complex as blind database schema extraction and SQL injections without human feedback. Importantly, the agent does not need to know the vulnerability beforehand. This capability is uniquely enabled by frontier models that are highly capable of tool use and leveraging extended context. Namely, we show that GPT-4 is capable of such hacks, but existing open-source models are not. Finally, we show that GPT-4 is capable of autonomously finding vulnerabilities in websites in the wild. Our findings raise questions about the widespread deployment of LLMs... |
Hack Tool Vulnerability | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 12:53:03 | Groupes de cybercrimins exploitant activement \\ 'Catastrophic \\' Screenconnect Bogue Cybercriminal groups actively exploiting \\'catastrophic\\' ScreenConnect bug (lien direct) |
 Une vulnérabilité de sécurité dans un outil d'accès à distance disponible dans le commerce est exploitée par des criminels de ransomware quelques jours seulement après la première fois.La vulnérabilité spécifique, affectant certaines versions du produit ScreenConnect de ConnectWise \\, a reçu le maximum score CVSS de 10 , indiquantqu'il représente une menace critique pour les organisations qui n'ont pas corrigé leur logiciel.
Une vulnérabilité de sécurité dans un outil d'accès à distance disponible dans le commerce est exploitée par des criminels de ransomware quelques jours seulement après la première fois.La vulnérabilité spécifique, affectant certaines versions du produit ScreenConnect de ConnectWise \\, a reçu le maximum score CVSS de 10 , indiquantqu'il représente une menace critique pour les organisations qui n'ont pas corrigé leur logiciel.
 A security vulnerability in a commercially available remote access tool is being exploited by ransomware criminals just days after first being disclosed. The specific vulnerability, affecting some versions of ConnectWise\'s ScreenConnect product, has been given the maximum CVSS score of 10, indicating that it poses a critical threat to organizations that haven\'t patched their software.
A security vulnerability in a commercially available remote access tool is being exploited by ransomware criminals just days after first being disclosed. The specific vulnerability, affecting some versions of ConnectWise\'s ScreenConnect product, has been given the maximum CVSS score of 10, indicating that it poses a critical threat to organizations that haven\'t patched their software. |
Ransomware Tool Vulnerability Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 11:00:00 | Détection des connexions anormales O365 et des techniques d'évasion Detecting anomalous O365 logins and evasion techniques (lien direct) |
The content of this post is solely the responsibility of the author. AT&T does not adopt or endorse any of the views, positions, or information provided by the author in this article. Summary Businesses across multiple industries, regardless of size, are at risk of being targeted with Microsoft 365 phishing campaigns. These campaigns trick users into visiting fake Microsoft login page where threat actors capture the user’s credentials. Even accounts with MFA can be victim to these types of attacks. There are several ways in which MFA is being bypassed with these types of campaigns. MFA Fatigue is one of the ways threat actors are bypassing MFA and this method attempts to exploit human error by repeatedly logging in with the stolen credentials causing an overwhelming number of MFA prompts in attempts to get the user to approve the login. Another MFA bypass technique is SIM Swapping. A SIM card is a small chip that your mobile carrier uses to hold identification information to tie your phone to you and your mobile carrier. Threat actors have found a weakness in this because there are scenarios where a customer may need a new SIM card (for example, they lost their phone). Carriers can transfer your identification information from your old SIM card to new one. SIM Swapping is when a threat actor abuses this feature and impersonates you to convince your mobile carrier to switch your phone number to a SIM card that is in the threat actor’s possession. This then allows the threat actor to receive MFA codes sent to your number via phone call or SMS. | Tool Threat Mobile Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 10:46:53 | Fortress déploie une notification de correctifs automatisé, l'outil d'authenticité pour sécuriser les actifs critiques des États-nations hostiles Fortress deploys automated patch notification, authenticity tool to secure critical assets from hostile nation-states (lien direct) |
L'Agence de sécurité de la cybersécurité et des infrastructures (CISA), la National Security Agency (NSA) et le Federal Bureau of Investigation ...
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the National Security Agency (NSA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation... |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-23 08:00:00 | Wallace – L\'analyseur CSS qui vous juge et vous conseille (lien direct) | Rédiger du CSS peut sembler aisé, mais l'outil en ligne Wallace révèle les erreurs commises. Il analyse les feuilles de style, offre des statistiques et des conseils pour améliorer la qualité du code. En suivant ses recommandations, on peut optimiser son CSS, le rendre plus performant et facile à maintenir. | Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-22 16:14:00 | Les cybercriminels ont armé l'outil SSH-Ssh-Sake open source pour les attaques de réseau Cybercriminals Weaponizing Open-Source SSH-Snake Tool for Network Attacks (lien direct) |
Un outil de cartographie de réseau récemment open open appelé & nbsp; ssh-snake & nbsp; a été réutilisé par des acteurs de la menace pour mener des activités malveillantes.
"SSH-Snake est un ver auto-modifiant qui exploite les informations d'identification SSH découvertes sur un système compromis pour commencer à se propager dans tout le réseau", a déclaré le chercheur de Sysdig, Miguel Hern & Aacute; Ndez & Nbsp.
"Le ver recherche automatiquement les informations d'identification connues
A recently open-sourced network mapping tool called SSH-Snake has been repurposed by threat actors to conduct malicious activities. "SSH-Snake is a self-modifying worm that leverages SSH credentials discovered on a compromised system to start spreading itself throughout the network," Sysdig researcher Miguel Hernández said. "The worm automatically searches through known credential |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-22 16:13:00 | Backdoor du logiciel du gouvernement russe pour déployer des logiciels malveillants de rat Konni Russian Government Software Backdoored to Deploy Konni RAT Malware (lien direct) |
Un programme d'installation d'un outil probablement utilisé par le département consulaire russe du ministère des Affaires étrangères (MID) a été détrommé pour livrer un cheval de Troie à distance appelé & nbsp; konni rat & nbsp; (aka & nbsp; updog).
Les résultats proviennent de la société allemande de cybersécurité DCSO, qui a lié l'activité à l'origine des acteurs de la République de Corée du peuple démocrate (DPRC) -nexus ciblant la Russie.
Le
An installer for a tool likely used by the Russian Consular Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MID) has been backdoored to deliver a remote access trojan called Konni RAT (aka UpDog). The findings come from German cybersecurity company DCSO, which linked the activity as originating from the Democratic People\'s Republic of Korea (DPRK)-nexus actors targeting Russia. The |
Malware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 20:59:32 | Bogue critique RMM Connectwise Posée pour l'exploitation Avalanche Critical ConnectWise RMM Bug Poised for Exploitation Avalanche (lien direct) |
Deux jours après la divulgation, la plupart des cas de l'outil de bureau à distance restent non corrigées, tandis que les cyberattaquants ont commencé l'exploitation dans la volonté - et les chercheurs préviennent que cela pourrait devenir laid et rapide.
Two days after disclosure, most instances of the remote desktop tool remain unpatched, while cyberattackers have started in-the-wild exploitation - and researchers warn it could get ugly, fast. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 15:58:44 | Rapport 2024 Incident Response - Unit 42/Palo Alto Networks (lien direct) | Rapport 2024 Incident Response - Unit 42/Palo Alto Networks Dans le paysage des menaces de cybersécurité en constante évolution, il est plus que jamais crucial de garder une longueur d'avance sur les acteurs malveillants. Pour cela, il faut comprendre leurs comportements, connaître leurs techniques et outils. - Investigations | Tool Threat Studies | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 14:03:25 | Les nouveaux logiciels malveillants SSH-Sake volent les clés SSH pour se propager sur le réseau New SSH-Snake malware steals SSH keys to spread across the network (lien direct) |
Un acteur de menace utilise un outil de cartographie de réseau open source nommé SSH-Snake pour rechercher des clés privées non détectées et se déplacer latéralement sur l'infrastructure de victime.[...]
A threat actor is using an open-source network mapping tool named SSH-Snake to look for private keys undetected and move laterally on the victim infrastructure. [...] |
Malware Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 11:00:00 | Le SoC moderne de Next Gen propulsé par l'IA The modern next gen SOC powered by AI (lien direct) |
AI is among the most disruptive technologies of our time. While AI/ML has been around for decades, it has become a hot topic with continued innovations in generative AI (GenAI) from start-up OpenAI to tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Meta. When large language models (LLMs) combined with big data and behavior analytics, AI/ML can supercharge productivity and scale operations across every sector from healthcare to manufacturing, transportation, retail, finance, government & defense, telecommunications, media, entertainment, and more. Within the cybersecurity industry, SentinelOne, Palo Alto Networks, Cisco, Fortinet and others are pioneering AI in Cybersecurity. In a research report of the global markets by Allied Market Research, AI in Cybersecurity is estimated to surge to $154.8 billion in 2032 from $19.2 billion in 2022, rising at a CAGR of 23.6%. Challenges of the traditional SOC SIEM One of the challenges with the traditional Security Operations Center (SOC) is SOC analysts are overwhelmed by the sheer number of alerts that come from Security Information Event Management (SIEM). Security teams are bombarded with low fidelity alerts and spend considerable time separating them from high fidelity alerts. The alerts come from almost any sources across the enterprise and is further compounded with too many point solutions and with multi-vendor environment. The numerous tools and lack of integration across multiple vendor product solutions often require a great deal of manual investigation and analysis. The pressure that comes with having to keep up with vendor training and correlate data and logs into meaningful insights becomes burdensome. While multi-vendor, multi-source, and multi-layered security solutions provides a lot of data, without ML and security analytics, it also creates a lot of noise and a disparate view of the threat landscape with insufficient context. SOAR Traditional Security Orchestration and Automation Response (SOAR) platforms used by mature security operations teams to develop run playbooks that automate action responses from a library of APIs for an ecosystem of security solution is complex and expensive to implement, manage, and maintain. Often SOCs are playing catch up on coding and funding development cost for run playbooks making it challenging to maintain and scale the operations to respond to new attacks quickly and efficiently. XDR Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solves a lot of these challenges with siloed security solutions by providing a unified view with more visibility and better context from a single holistic data lake across the entire ecosystem. XDR provides prevention as well as detection and response with integration and automation capabilities across endpoint, cloud, and network. Its automation capabilities can incorporate basic common SOAR like functions to API connected security tools. It collects enriched data from multiple sources and applies big data and ML based analysis to enable response of policy enforcement using security controls throughout the infrastructure. AI in the modern next gen SOC The use of AI and ML are increasingly essential to cyber operations to proactively identify anomalies and defend against cyber threats in a hyperconnected digital world. Canalys research estimates suggest that more than 7 | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Prediction Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-21 02:43:59 | Tendances de la cybersécurité en 2024: 5 domaines clés à suivre Cybersecurity Trends in 2024: 5 Key Areas to Follow (lien direct) |
Comme nous sommes bien en 2024 maintenant, chez Fortra, nous voulons continuer notre engagement à vous autonomiser tous les connaissances et les outils nécessaires pour vous protéger, votre organisation et même votre famille.Cette année, nous rechercherons de plus en plus l'élément humain et vous fournirons des méthodes pour pratiquer des techniques répétables du monde réel pour corriger les habitudes positives et les comportements de sécurité pour vous garder aussi en sécurité que possible.Le pendule de la société comme toute industrie, la cybersécurité est influencée par la dernière traction gravitationnelle de la société.Bien qu'il existe de nombreux développements positifs, les cybercriminels sont souvent ...
As we are well into 2024 now, we at Fortra want to continue our commitment to empowering you all with the knowledge and tools needed to protect you, your organization, and even your family. This year, we will be looking more and more at the human element, and provide you with methods to practice repeatable, real-world techniques to ingrain positive habits and security behaviors to keep you as safe as possible. Society\'s Pendulum Like any industry, cybersecurity is influenced by the latest gravitational pull of society. While there are many positive developments, cybercriminals are often... |
Tool Studies | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 21:35:38 | Alpha Ransomware émerge des cendres Netwalker Alpha Ransomware Emerges from NetWalker Ashes (lien direct) |
#### Description
Alpha, un nouveau ransomware qui est apparu pour la première fois en février 2023 a intensifié ses activités ces dernières semaines et ressemble fortement aux ransomwares de Netwalker désormais disparus qui ont disparu en janvier 2021. L'analyse d'Alpha révèle des parallèles importants avec Netwalker, y compris l'utilisation d'une puissance similaire baséechargeur et code de code.Alors qu'Alpha est initialement resté peu profond après son apparition en février 2023, les attaques récentes indiquent une augmentation des opérations, y compris le déploiement d'un site de fuite de données et l'utilisation d'outils de vie comme TaskKill et Psexec.Les similitudes entre Alpha et Netwalker suggèrent un renouveau potentiel de l'ancienne opération de ransomware par les développeurs originaux ou l'acquisition et la modification de la charge utile Netwalker par les nouveaux attaquants.
#### URL de référence (s)
1. https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/thereat-intelligence/alpha-netwalker-ransomware
2. https://gbhackers.com/alpha-ransomware-livingof-fthe-land/
#### Date de publication
16 février 2024
#### Auteurs)
Équipe de chasseurs de menace symantec
#### Description Alpha, a new ransomware that first appeared in February 2023 has intensified its activities in recent weeks and strongly resembles the now defunct NetWalker ransomware that vanished in January 2021. Analysis of Alpha reveals significant parallels with NetWalker, including the use of a similar PowerShell-based loader and code overlap. While Alpha initially remained low-profile after its appearance in February 2023, recent attacks indicate a surge in operations, including the deployment of a data leak site and the utilization of living-off-the-land tools like Taskkill and PsExec. The similarities between Alpha and NetWalker suggest a potential revival of the old ransomware operation by original developers or the acquisition and modification of the NetWalker payload by new attackers. #### Reference URL(s) 1. https://symantec-enterprise-blogs.security.com/blogs/threat-intelligence/alpha-netwalker-ransomware 2. https://gbhackers.com/alpha-ransomware-living-off-the-land/ #### Publication Date February 16, 2024 #### Author(s) Symantec Threat Hunter Team |
Ransomware Tool Threat | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 17:09:00 | FEDS Saisissez les sites Web de ransomwares de lockbit, proposent des outils de décryptage, des affiliés troll Feds Seize LockBit Ransomware Websites, Offer Decryption Tools, Troll Affiliates (lien direct) |
Les autorités américaines et britanniques ont saisi les sites Web DarkNet gérés par Lockbit, un groupe de ransomware prolifiques et destructeurs qui a réclamé plus de 2 000 victimes dans le monde et extorqué plus de 120 millions de dollars en paiements.Au lieu de répertorier les données volées aux victimes de ransomwares qui n'ont pas payé, le site Web de la honte des victimes de Lockbit \\ propose désormais des outils de récupération gratuits, ainsi que des nouvelles sur les arrestations et les accusations criminelles impliquant des affiliés de Lockbit.
U.S. and U.K. authorities have seized the darknet websites run by LockBit, a prolific and destructive ransomware group that has claimed more than 2,000 victims worldwide and extorted over $120 million in payments. Instead of listing data stolen from ransomware victims who didn\'t pay, LockBit\'s victim shaming website now offers free recovery tools, as well as news about arrests and criminal charges involving LockBit affiliates. |
Ransomware Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 13:05:41 | Takedown de Lockbit de NCA \\: le code source, les arrestations et l'outil de récupération révélé NCA\\'s LockBit Takedown: Source Code, Arrests and Recovery Tool Revealed (lien direct) |
par waqas
À ce jour, le gang de ransomware de verrouillage a ciblé plus de 2 000 victimes et a reçu plus de 120 millions de dollars en paiements de rançon.
Ceci est un article de HackRead.com Lire la publication originale: Takedown de Lockbit NCA & # 8217;
By Waqas To date, the LockBit ransomware gang targeted over 2,000 victims and received more than $120 million in ransom payments. This is a post from HackRead.com Read the original post: NCA’s LockBit Takedown: Source Code, Arrests and Recovery Tool Revealed |
Ransomware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 12:02:00 | Microsoft espère les utilisateurs de ses outils d'IA Microsoft Is Spying on Users of Its AI Tools (lien direct) |
Microsoft a annoncé qu'il Catché hackers chinois, russe et iranien en utilisant ses outils AI & # 8212; vraisemblablement les outils de codage & # 8212; pour améliorer leurs capacités de piratage.
de leur Rapport :
En collaboration avec OpenAI, nous partageons des renseignements sur les menaces montrant des adversaires affiliés à l'État détectés & # 8212; suivi comme Forest Blizzard, Emerald Sleet, Crimson Sandstorm, Typhoon du charbon de bois et le typhon de saumon & # 8212; Utilisation de LLMS pour augmenter les cyberopérations.
La seule façon dont Microsoft ou Openai sauraient que cela serait d'espionner les sessions de chatbot.Je suis sûr que les conditions d'utilisation & # 8212; si je prenais la peine de les lire & # 8212; leur donne cette permission.Et bien sûr, il n'est pas surprenant que Microsoft et Openai (et, vraisemblablement, tout le monde) espèrent notre utilisation de l'IA, mais cela le confirme ...
Microsoft announced that it caught Chinese, Russian, and Iranian hackers using its AI tools—presumably coding tools—to improve their hacking abilities. From their report: In collaboration with OpenAI, we are sharing threat intelligence showing detected state affiliated adversaries—tracked as Forest Blizzard, Emerald Sleet, Crimson Sandstorm, Charcoal Typhoon, and Salmon Typhoon—using LLMs to augment cyberoperations. The only way Microsoft or OpenAI would know this would be to spy on chatbot sessions. I’m sure the terms of service—if I bothered to read them—gives them that permission. And of course it’s no surprise that Microsoft and OpenAI (and, presumably, everyone else) are spying on our usage of AI, but this confirms it... |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 11:00:00 | Un guide fondamental pour la sécurité des points finaux A fundamental guide to endpoint security (lien direct) |
 Anyone that utilizes technology in their daily lives understands that it is ever-changing, and the sentiment is especially true within the cybersecurity industry. Adversaries continue to evolve with new tactics to bypass defenses, so it is necessary that the methods of detecting and preventing these threats do so at an even more rapid pace.
However, keeping up with all the changes can be quite difficult, even for the most seasoned cybersecurity professional. The way in which we work has changed not just in where but also in how. Today employees conduct business from multiple devices, with some being company-issued and others being privately owned. Sensitive data is being stored across many locations including on these devices, within corporate data centers, and in the cloud. This means that organizations likely need more than one technology to defend their endpoints against security breach or data loss. With cybersecurity vendors marketing a wide range of branded product names for their offers, it may be challenging to determine which are ideal for your particular environment. This article aims to help demystify the various endpoint security technologies you may come across during your research, highlight the primary differences, and explain how they can complement each other. This is not intended to be an exhaustive list and it should be noted that there are some technologies that may fall into more than one category, for example, endpoint and cloud security.
Four key endpoint security technologies
To begin, let’s define exactly what an endpoint is. At the most fundamental level, an endpoint is any device that connects and exchanges data on a network. That could include traditional desktop and laptop computers, tablets, smartphones, printers, and servers. Endpoints also encompass network appliances like routers, switches, or firewalls, and a wide range of IoT devices such as wearables, security cameras, sensors, and connected medical or manufacturing equipment. But we must also think beyond the physical devices and consider virtual machines that host applications and data in public or private clouds.
Although this may seem trivial, it is important to note because they all represent entry points into the network that can be exploited and opportunities for sensitive data loss. As such, they must all be accounted for when building an endpoint security strategy. The following are some of the more common endpoint security technologies you are likely to encounter:
Unified endpoint management (UEM) or mobile device management (MDM): There is a widely accepted concept within the cybersecurity industry that you cannot effectively protect what you can’t see. Therefore, the first step in building a comprehensive endpoint security policy is to inventory all the devices accessing your network, and this can be accomplished with UEM or MDM technologies. The primary difference between the two is that MDM is for iOS and Android operating systems (OS), while UEM includes those OS plus Windows and Mac operating systems--even productivity devices and wearables in some cases. Once the devices are discovered and profiled, administrators will be able to apply consistent security policies across them, regardless of where the endpoint is located.
A key feature of both UEM and MDM is that they allow an organization to set standards regarding the security posture of devices accessing the network. For example, rules can be created that a device cannot be jailbroken and must be running on the latest O
Anyone that utilizes technology in their daily lives understands that it is ever-changing, and the sentiment is especially true within the cybersecurity industry. Adversaries continue to evolve with new tactics to bypass defenses, so it is necessary that the methods of detecting and preventing these threats do so at an even more rapid pace.
However, keeping up with all the changes can be quite difficult, even for the most seasoned cybersecurity professional. The way in which we work has changed not just in where but also in how. Today employees conduct business from multiple devices, with some being company-issued and others being privately owned. Sensitive data is being stored across many locations including on these devices, within corporate data centers, and in the cloud. This means that organizations likely need more than one technology to defend their endpoints against security breach or data loss. With cybersecurity vendors marketing a wide range of branded product names for their offers, it may be challenging to determine which are ideal for your particular environment. This article aims to help demystify the various endpoint security technologies you may come across during your research, highlight the primary differences, and explain how they can complement each other. This is not intended to be an exhaustive list and it should be noted that there are some technologies that may fall into more than one category, for example, endpoint and cloud security.
Four key endpoint security technologies
To begin, let’s define exactly what an endpoint is. At the most fundamental level, an endpoint is any device that connects and exchanges data on a network. That could include traditional desktop and laptop computers, tablets, smartphones, printers, and servers. Endpoints also encompass network appliances like routers, switches, or firewalls, and a wide range of IoT devices such as wearables, security cameras, sensors, and connected medical or manufacturing equipment. But we must also think beyond the physical devices and consider virtual machines that host applications and data in public or private clouds.
Although this may seem trivial, it is important to note because they all represent entry points into the network that can be exploited and opportunities for sensitive data loss. As such, they must all be accounted for when building an endpoint security strategy. The following are some of the more common endpoint security technologies you are likely to encounter:
Unified endpoint management (UEM) or mobile device management (MDM): There is a widely accepted concept within the cybersecurity industry that you cannot effectively protect what you can’t see. Therefore, the first step in building a comprehensive endpoint security policy is to inventory all the devices accessing your network, and this can be accomplished with UEM or MDM technologies. The primary difference between the two is that MDM is for iOS and Android operating systems (OS), while UEM includes those OS plus Windows and Mac operating systems--even productivity devices and wearables in some cases. Once the devices are discovered and profiled, administrators will be able to apply consistent security policies across them, regardless of where the endpoint is located.
A key feature of both UEM and MDM is that they allow an organization to set standards regarding the security posture of devices accessing the network. For example, rules can be created that a device cannot be jailbroken and must be running on the latest O |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Medical Cloud | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 08:45:00 | Guardians of the Digital Realm: Comment vous protéger de l'ingénierie sociale Guardians of the Digital Realm: How to Protect Yourself from Social Engineering (lien direct) |
Social engineering has been around for as long as coveted information has existed. In the digital realm, threat actors use this psychological manipulation tactic to drive people to break normal security procedures. It is a con game that relies on human error rather than digital hacking. These are some common forms of social engineering in digital communications: Impersonation. In these attacks, bad actors pose as trusted entities. Pretexting. Bad actors use fake stories to bait their targets into revealing sensitive information. Baiting. Attackers use promises of rewards or benefits to lure in their targets. In social engineering attacks, bad actors exploit psychological principles like trust, the fear of missing out, authority and the desire to be helpful. When you and your users learn to recognize these triggers, you can build a strong defense. In this blog post, we\'ll cover three more steps you can take to protect yourself and your business. 1. Build a human firewall If you want your employees to be able to recognize social engineering attacks, you need to educate them. Training should cover various types of social engineering tactics. Some top examples include: Phishing Telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD) Pretexting Baiting Quid pro quo Tailgating It\'s a good idea to keep your employees informed of the latest attack trends. That is why continuous education has more of an impact than one-off training sessions. Regular updates can help you keep your workforce up to speed. You may want to support your training efforts with a comprehensive security awareness platform. It can provide content that\'s designed to increase user participation and help lessons stick, like gamification and microlearning. Quizzes, interactive modules and mock phishing scenarios can all help your users learn how to become better defenders, too. Actionable tips: Test your team with simulated phishing emails at least once a month Conduct security awareness training sessions at least once per quarter Build a yearlong campaign that also provides employees with other training information, like digital newsletters or packets that they can take home 2. Slow down and ask questions You might assume your security team has put technology in place to defend against social engineering. However, there is no silver bullet to stop these attacks. That\'s why you need to approach digital communications with a critical eye, especially when they include requests for sensitive information or prompts to take urgent actions. You want to complete your work quickly and be responsive to your leadership team, of course. But threat actors count on these types of triggers. Instead, do your best to: Slow down This is a crucial move in the fight against social engineering. It enables you to evaluate the situation with a critical eye and recognize potential red flags. When you slow down, you transform automatic, reflexive responses into thoughtful, deliberate actions. Practice skepticism When you stop to question whether an interaction is legitimate, you can spot inconsistencies. You can ask questions like: “Is this request from a person or entity I can trust?”, “Can I verify their identity?” and “Is this request truly urgent?” You might consult with colleagues or managers or refer to company policies. Or you might even do a quick internet search to validate claims. Actionable tips: Examine emails for unusual language or requests Double-check that email addresses and domain names are authentic Verify requests that come through alternative communication channels 3. Use a multilayered defense If you want to have an edge in combatting social engineering, you need to adopt a multilayered security approach. In other words, you need to combine the human element of user vigilance with advanced tools. A core part of this strategy is to deploy an advanced email security solution that can stop an initial attack. Ideally, it should use a combination of behaviora | Tool Threat Prediction | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-20 08:12:28 | Manage Engine dévoile des analyses de triade à exploits alimentés par ML ManageEngine Unveils ML-powered Exploit Triad Analytics (lien direct) |
GestionneraGine dévoile ML Exploited Exploit Triad Analytics dans sa solution SIEM pour raccourcir le cycle de vie de violation
Les entreprises peuvent affiner leur détection et leur atténuation de violation avec des analyses contextuelles, granulaires et intelligentes
● Associez les acteurs malveillants en tirant parti des données contextuelles de AD et UEBA pour déconstruire la triade d'exploit: utilisateurs, entités et processus
● Neutraliser les menaces avec un ensemble de corrélation contenant des règles pour détecter les outils d'attaquants répandus et vivre des menaces terrestres (LOTL)
-
revues de produits
ManageEngine Unveils ML-powered Exploit Triad Analytics in Its SIEM Solution to Shorten the Breach Life Cycle Enterprises Can Refine Their Breach Detection and Mitigation With Contextual, Granular, Smart Analytics ● Outsmart malicious actors by leveraging contextual data from AD and UEBA to deconstruct the exploit triad: users, entities and processes ● Neutralize threats with a correlation package containing rules for detecting prevalent attacker tools and living off the land (LOTL) threats - Product Reviews |
Tool Threat | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-19 08:00:00 | JXL et AVIF – Les nouveaux champions des formats d\'image (lien direct) | En 2024, les formats d'image AVIF et JXL sont plus efficaces que JPEG, PNG et WebP. AVIF, issu du codec vidéo AV1, est idéal pour les images web et animées, et supporté par de nombreux navigateurs. JXL permet une compression photo haute résolution avec ou sans perte. Les deux formats open source de 2019 supportent la transparence. Des outils comme cavif-rs, FFMPEG et libjxl facilitent la conversion des images existantes, permettant d'importantes économies de taille avec une qualité préservée, et fonctionnent sur les navigateurs modernes. | Tool | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-17 12:56:00 | Google Open Sources Magika: outil d'identification des fichiers alimentée par AI Google Open Sources Magika: AI-Powered File Identification Tool (lien direct) |
Google a annoncé qu'il \\ est Open-Sourcing & NBSP; Magika, un outil alimenté par l'intelligence artificielle (IA) pour identifier les types de fichiers, pour aider les défenseurs à détecter avec précision les types de fichiers binaires et textuels.
"Magika surpasse les méthodes d'identification des fichiers conventionnels offrant une augmentation globale de 30% de précision et une précision jusqu'à 95% plus élevée sur un contenu traditionnellement difficile à identifier, mais potentiellement problématique
Google has announced that it\'s open-sourcing Magika, an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered tool to identify file types, to help defenders accurately detect binary and textual file types. "Magika outperforms conventional file identification methods providing an overall 30% accuracy boost and up to 95% higher precision on traditionally hard to identify, but potentially problematic content |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-17 11:26:28 | Magika, le détecteur de fichiers ultra-rapide de Google (lien direct) | Google a récemment lancé Magika, un système d'identification de types de fichiers basé sur l'IA, visant à améliorer la détection des fichiers binaires et textuels. Magika utilise un modèle de deep learning optimisé pour une identification rapide des fichiers. Il est accessible en tant que bibliothèque Python et outil en ligne de commande. Magika surpasse les outils existants et sera intégré à VirusTotal pour renforcer la cybersécurité. | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-17 02:10:11 | Google Open Sources Magika Ai d'identification des fichiers pour les chasseurs de logiciels malveillants et autres Google open sources file-identifying Magika AI for malware hunters and others (lien direct) |
cool, mais il est 2024 & # 8211;Besoin de plus de battage médiatique, d'essouffement à la main et de démos enracinées flashy pour être appropriée ML Google a ouvert Magika d'origine, un identifiant de fichier à apprentissage machine interne, dans le cadre de son initiative de cyber-défense AI, qui, quivise à lui donner des défenseurs du réseau et d'autres outils automatisés.…
Cool, but it\'s 2024 – needs more hype, hand wringing, and flashy staged demos to be proper ML Google has open sourced Magika, an in-house machine-learning-powered file identifier, as part of its AI Cyber Defense Initiative, which aims to give IT network defenders and others better automated tools.… |
Malware Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-17 00:05:10 | CORNE CISO: convergence CIO, 10 mesures de sécurité critiques, & amp;Ivanti Fallout CISO Corner: CIO Convergence, 10 Critical Security Metrics, & Ivanti Fallout (lien direct) |
Toujours dans ce numéro: investissement au Moyen-Orient, nouvelles règles de notification de violation de la FCC et comment les lecteurs de lecture sombres utilisent les outils Genai dans leur appareil de cybersécurité.
Also in this issue: Mideast investment, new FCC breach notification rules, and how Dark Reading readers use GenAI tools in their cybersecurity apparatus. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-16 20:41:12 | SNS Sender | Active Campaigns Unleash Messaging Spam Through the Cloud (lien direct) | #### Description
Les chercheurs de Sentinelone ont découvert un nouveau script Python appelé SNS Sender qui utilise AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS) pour envoyer des messages SMS en vrac dans le but de spammer des liens de phishing, également connus sous le nom de swishing.
Il s'agit du premier script observé à l'aide d'AWS SNS, et on pense que l'acteur derrière cet outil utilise des services cloud pour envoyer des messages de phishing SMS en vrac.L'auteur du script est connu par l'alias Arduino_Das et est prolifique dans la scène du kit Phish.
Le script nécessite une liste de liens de phishing nommés links.txt dans son répertoire de travail.SNS Sender prend également plusieurs arguments entrés en entrée: un fichier texte contenant une liste de clés d'accès AWS, de secrets et de région délimitées par un côlon;un fichier texte contenant une liste de numéros de téléphone à cibler;un ID de l'expéditeur, similaire à un nom d'affichage pour un message;et le contenu du message.Le script remplace toutes les occurrences de la chaîne dans la variable de contenu du message par une URL du fichier links.txt, qui arme le message en tant que SMS de phishing.L'acteur derrière cet outil a été lié à de nombreux kits de phishing utilisés pour cibler les victimes \\ 'Informations personnellement identifiables (PII) et les détails de la carte de paiement sous le couvert d'un message de laUnited States Postal Service (USPS) concernant une livraison de colis manquée.
#### URL de référence (s)
1. https://www.sentinelone.com/labs/sns-sender-active-campaignes-se détendre
#### Date de publication
15 février 2024
#### Auteurs)
Alex Delamotte
#### Description SentinelOne researchers have discovered a new Python script called SNS Sender that uses AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS) to send bulk SMS messages for the purpose of spamming phishing links, also known as Smishing. This is the first script observed using AWS SNS, and it is believed that the actor behind this tool is using cloud services to send bulk SMS phishing messages. The script author is known by the alias ARDUINO_DAS and is prolific in the phish kit scene. The script requires a list of phishing links named links.txt in its working directory. SNS Sender also takes several arguments that are entered as input: a text file containing a list of AWS access keys, secrets, and region delimited by a colon; a text file containing a list of phone numbers to target; a sender ID, similar to a display name for a message; and the message content. The script replaces any occurrences of the string in the message content variable with a URL from the links.txt file, which weaponizes the message as a phishing SMS. The actor behind this tool has been linked to many phishing kits used to target victims\' personally identifiable information (PII) and payment card details under the guise of a message from the United States Postal Service (USPS) regarding a missed package delivery. #### Reference URL(s) 1. https://www.sentinelone.com/labs/sns-sender-active-campaigns-unleash-messaging-spam-through-the-cloud/ #### Publication Date February 15, 2024 #### Author(s) Alex Delamotte |
Spam Tool Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2024-02-16 20:34:13 | Plate-forme de messagerie Telegram Sprouts Cyber Crime «Market lieux» des outils, des idées et des données Messaging Platform Telegram Sprouts Cyber Crime “Marketplaces” of Tools, Insights and Data (lien direct) |
 Les cybercriminels profitent du télégramme de la plate-forme de messagerie en créant des canaux et des groupes où l'apprentissage et le commerce peuvent tous avoir lieu librement.
Les cybercriminels profitent du télégramme de la plate-forme de messagerie en créant des canaux et des groupes où l'apprentissage et le commerce peuvent tous avoir lieu librement.
 Cybercriminals are taking advantage of the messaging platform Telegram by creating channels and groups where learning and commerce all can take place freely.
Cybercriminals are taking advantage of the messaging platform Telegram by creating channels and groups where learning and commerce all can take place freely. |
Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-16 13:16:07 | Google annonce l\'IA Cyber Defense Initiative pour renforcer la cybersécurité (lien direct) | Google annonce l'IA Cyber Defense Initiative pour renforcer la cybersécurité ● L'IA Cyber Defense Initiative vise à aider les défenseurs du numérique à prendre le dessus sur les attaquants, renforçant ainsi la sécurité mondiale. ● L'initiative comprend des investissements, un soutien aux startups, aux petites entreprises, aux établissements universitaires et aux chercheurs ; et permettre de nouveaux outils de sécurité d'IA open source. - Business | Tool | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-16 09:45:39 | Les signes Goldilock «Made in America» traitent des outils patriotes pour la fabrication américaine d'OT Cyber Kill-Switch Goldilock signs “Made in America” deal with Patriot Tools for US manufacture of OT cyber kill-switch (lien direct) |
Les panneaux Goldilock «Made in America» traitent des outils patriotes pour la fabrication américaine d'OT Cyber Kill-Switch
Cyber-kill-switch britannique, développé et utilisé par le ministère britannique de la Défense et déployé par le cybercommand ukrainien, sera désormais fabriqué en Amérique, en utilisant des composants américains
-
nouvelles commerciales
Goldilock signs “Made in America” deal with Patriot Tools for US manufacture of OT cyber kill-switch British multi-patented cyber kill-switch, developed and used by UK Ministry of Defence and deployed by Ukrainian CyberCommand will now be Made in America, using US components - Business News |
Tool Industrial | ★★ | ||
| 2024-02-16 06:00:45 | Les tenants et aboutissants de la confidentialité des données, partie 1: la complexité importante et croissante d'assurer la confidentialité des données The Ins and Outs of Data Privacy, Part 1: The Importance-and Growing Complexity-of Ensuring Data Privacy (lien direct) |
This blog is the first in a series where we explore data privacy. In these two blogs, we\'ll cover why data privacy is increasingly important as well as some tips for keeping data safe. We\'ll also discuss how data loss protection (DLP) and insider threat management tools (ITM) are critical to ensuring data privacy. Data Privacy Week in January 2024 highlighted the increasing importance and challenges of data privacy. Trends like digital transformation, remote work and the proliferation of cloud applications have made the task of protecting sensitive data harder than ever. As the volume and perceived value of data grows, so does the risk of data loss and theft, including by insiders. Despite these challenges, businesses can\'t afford missteps when it comes to keeping sensitive data safe. Companies everywhere are under pressure to meet strict data privacy laws that promote data security and data privacy. Noncompliance can be costly. Hefty fines and market loss are common. Research from our 2023 Voice of the CISO report underscores the risk. One-third of the CISOs who told us that their company suffered a material loss of sensitive data within the past 12 months also reported their business was hit with regulatory sanctions as a result. In this blog post, we take a closer look at data privacy and how it relates to data security. We also discuss how laws around data privacy are evolving. And we cover how data loss prevention (DLP) and insider threat management (ITM) tools can help you stay on top of your data compliance challenges. What is data privacy? Data privacy is about protecting sensitive data that belongs to individuals or entities. This includes personally identifiable information (PII), which can be used to identify an individual or a corporate customer. Examples of PII include names, addresses, Social Security or tax ID numbers, credit card data and dates of birth. A business that stores or manages this type of information must follow data privacy laws. These laws ensure that data is kept confidential and secure and that it is only used for authorized purposes. They are intended to help a business: Protect personal information Safeguard critical business data Preserve users\' autonomy Maintain trust with customers and employees Data privacy is also about trust. The misuse or theft of sensitive data can lead to email fraud, insurance fraud, identity theft and more. So, customers need to trust that the companies they share their private data with will guard it carefully. An evolving regulatory landscape Data privacy laws are designed to compel businesses to keep sensitive data safe. Data compliance mandates often require businesses to tell users exactly how their data is used and collected. They may also require companies to notify users when a data breach happens. As noted earlier, not following these laws can result in stiff penalties. Multiple data privacy laws around the globe govern regulations based on their type, the user\'s location and other criteria. Some examples include the: GDPR in the European Union CCPA in the U.S. HIPAA in the U.S. LGPD in Brazil Several state governments in the United States are stepping up efforts to enact data privacy laws. California, Colorado, Connecticut, Utah and Virginia enacted comprehensive consumer privacy laws before 2023. Those laws became enforceable last year. In 2023, these states enacted privacy laws: Delaware Florida Indiana Iowa Montana Oregon Tennessee Texas As data privacy laws emerge or evolve, the definition of sensitive data may change. For example, GDPR expanded the definition of PII to include data elements like email and IP addresses. That is why it is so important for companies to stay attuned to this ever-changing landscape. The rise of generative AI sites has also sparked new concerns about data privacy. New laws are likely to be developed soon. The Biden Administration\'s new executive order will also have an impact on data use in the year ahead. Why | Data Breach Malware Tool Threat Cloud | ★★ |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
