What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2025-02-20 10:10:49 | (Déjà vu) CISA Vulnerability Advisories Reveal Complexity of ICS Products (lien direct) |  Overview
Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients examined 122 ICS, operational technology (OT), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities pulled from 22 recent advisories from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
The 122 vulnerabilities affect products from seven vendors across nine critical sectors, ranging from energy and healthcare to wastewater systems, transportation, manufacturing, food and agriculture, chemicals, and commercial facilities. Nine of the vulnerabilities are rated critical.
One interesting aspect of the advisories is how many of the ICS vulnerabilities come from third-party components that weren\'t made by the ICS vendor, revealing the complexity and vulnerability of these critical systems.
Four Critical Siemens Vulnerabilities
Siemens had the highest number of vulnerabilities in the CISA advisories, 100 in all, but only four were rated critical-and all of the critical vulnerabilities came from non-Siemens components.
Two of the critical vulnerabilities affect Siemens Opcenter Intelligence, a manufacturing intelligence platform used to improve manufacturing processes and stem from vulnerabilities in the Java OpenWire protocol marshaller (CVE-2023-46604, a 9.6-severity Deserialization of Untrusted Data vulnerability) and the Tableau Server Administration Agent\'s internal file transfer service (CVE-2022-22128, a 9.0-rated Path Traversal vulnerability). Opcenter Intelligence versions prior to V2501 are affected.
CISA addressed those vulnerabilities in a February 13 advisory, noting that “Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could enable an attacker to execute remote code or allow a malicious site administrator to
Overview
Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients examined 122 ICS, operational technology (OT), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities pulled from 22 recent advisories from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
The 122 vulnerabilities affect products from seven vendors across nine critical sectors, ranging from energy and healthcare to wastewater systems, transportation, manufacturing, food and agriculture, chemicals, and commercial facilities. Nine of the vulnerabilities are rated critical.
One interesting aspect of the advisories is how many of the ICS vulnerabilities come from third-party components that weren\'t made by the ICS vendor, revealing the complexity and vulnerability of these critical systems.
Four Critical Siemens Vulnerabilities
Siemens had the highest number of vulnerabilities in the CISA advisories, 100 in all, but only four were rated critical-and all of the critical vulnerabilities came from non-Siemens components.
Two of the critical vulnerabilities affect Siemens Opcenter Intelligence, a manufacturing intelligence platform used to improve manufacturing processes and stem from vulnerabilities in the Java OpenWire protocol marshaller (CVE-2023-46604, a 9.6-severity Deserialization of Untrusted Data vulnerability) and the Tableau Server Administration Agent\'s internal file transfer service (CVE-2022-22128, a 9.0-rated Path Traversal vulnerability). Opcenter Intelligence versions prior to V2501 are affected.
CISA addressed those vulnerabilities in a February 13 advisory, noting that “Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could enable an attacker to execute remote code or allow a malicious site administrator to |
Tool Vulnerability Patching Industrial Medical Commercial | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-20 07:00:00 | The Quiet Data Leak from GenAI (lien direct) | Like me, I’m sure you’re keeping an open mind about how Generative AI (GenAI) is transforming companies. It’s not only revolutionizing the way industries operate, GenAI is also training on every byte and bit of information available to build itself into the critical components of business operations. However, this change comes with an often-overlooked risk: the quiet leak of organizational data into AI models.
What most people don’t know is the heart of this data leak comes from Internet crawlers which are similar to search engines that scour the Internet for content. Crawlers collect huge amounts of data from social media, proprietary leaks, and public repositories. The collected information feeds massive datasets used to train AI models. One dataset in particular, is the Common Crawl, an open-source repository that has been collecting data since 2008 but goes back even further, into the 1990s with The Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine.
Common Crawl has and continues to collect vast portions of the public Internet every month. It’s amassing petabytes of web content regularly, providing AI models with extensive training material. If that’s not enough to worry about, companies often fail to recognize that their data may be included in these datasets without their explicit consent. How would you also like to know that the Common Crawl can’t distinguish between what data should be public, and what should be private?
I’m guessing that you’re starting to feel concerned since Common Crawl’s dataset is publicly available and immutable, meaning once data is scraped, it remains accessible indefinitely. What does indefinitely look like? Here’s a great example! Do you remember the Netscape website where we had to actually buy and download the Netscape Navigator browser? The Wayback Machine does! Just another reminder that if an organization’s website has been made publicly available, its content has likely been captured forever.
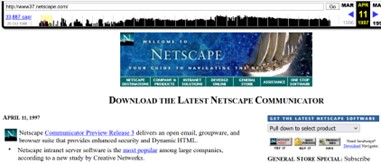 All rights to the original content remain with respective copyright holders. See fair use disclaimer below.
If you’re concerned about what to do next, start by verifying if your company’s data has been collected.
Utilize tools like the Wayback Machine at web.archive.org to review historical web snapshots.
Perform advanced searches of the Common Crawl datasets directly at index.commoncrawl.org
Employ custom scripts to scan datasets for proprietary content on your publicly facing Internet assets. You know, the stuff that should be behind an authentication wall.
Want some more fun facts? Once trained, AI models compress these gigantic amounts of data into significantly smaller instances. For example, two petabytes of training data can be distilled into as small as a five-terabyte AI model. That’s a 400:1 compression ratio! So protect these valuable critical assets like the crown jewels they are because data thieves scour through your company’s network looking for these treasured models.
Starting today, there are two types of data in this world, Stored and Trained. Stored data is unaltered retention of information like database, documents, and logs. Trained data is AI-generated knowledge inferred from patterns, relationships, and statistical modeling.
I bet you’re a bit like me and also wondering what the legal and ethical implications are for training GenAI on these massive data sets. A prime example of AI’s data exposure risk is the American Medical Association’s (AMA) Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCP
All rights to the original content remain with respective copyright holders. See fair use disclaimer below.
If you’re concerned about what to do next, start by verifying if your company’s data has been collected.
Utilize tools like the Wayback Machine at web.archive.org to review historical web snapshots.
Perform advanced searches of the Common Crawl datasets directly at index.commoncrawl.org
Employ custom scripts to scan datasets for proprietary content on your publicly facing Internet assets. You know, the stuff that should be behind an authentication wall.
Want some more fun facts? Once trained, AI models compress these gigantic amounts of data into significantly smaller instances. For example, two petabytes of training data can be distilled into as small as a five-terabyte AI model. That’s a 400:1 compression ratio! So protect these valuable critical assets like the crown jewels they are because data thieves scour through your company’s network looking for these treasured models.
Starting today, there are two types of data in this world, Stored and Trained. Stored data is unaltered retention of information like database, documents, and logs. Trained data is AI-generated knowledge inferred from patterns, relationships, and statistical modeling.
I bet you’re a bit like me and also wondering what the legal and ethical implications are for training GenAI on these massive data sets. A prime example of AI’s data exposure risk is the American Medical Association’s (AMA) Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCP |
Tool Prediction Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-19 08:52:40 | Censinet, AWS partner to improve healthcare risk management with AI-powered GRC, cybersecurity solutions (lien direct) | Censinet, provider of healthcare risk management solutions, announced a collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to launch a...
Censinet, provider of healthcare risk management solutions, announced a collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to launch a... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-18 22:15:59 | Managed healthcare defense contractor to pay $11 million over alleged cyber failings (lien direct) | The settlement with Health Net Federal Services is the latest penalty levied on a federal contractor as part of a 2021 initiative to root out cyber-related fraud.
The settlement with Health Net Federal Services is the latest penalty levied on a federal contractor as part of a 2021 initiative to root out cyber-related fraud. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-18 13:00:47 | Curb Healthcare Costs - Can Cybersecurity Platformization Help? (lien direct) | >A platformized approach to cybersecurity can help organizations navigate challenges while strengthening resilience, boosting efficiency and managing costs.
>A platformized approach to cybersecurity can help organizations navigate challenges while strengthening resilience, boosting efficiency and managing costs. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-18 12:06:07 | Story About Medical Device Security (lien direct) | Ben Rothke relates a story about me working with a medical device firm back when I was with BT. I don’t remember the story at all, or who the company was. But it sounds about right.
Ben Rothke relates a story about me working with a medical device firm back when I was with BT. I don’t remember the story at all, or who the company was. But it sounds about right. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-14 17:05:38 | Friday Squid Blogging: Squid the Care Dog (lien direct) | The Vanderbilt University Medical Center has a pediatric care dog named “Squid.”
Blog moderation policy.
The Vanderbilt University Medical Center has a pediatric care dog named “Squid.” Blog moderation policy. |
Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-02-14 14:00:00 | Ransomware Roundup – Lynx (lien direct) | Get insights into the Lynx ransomware, which is considered the successor to the INC ransomware. This double-extortion ransomware has threatened more than 90 organizations worldwide, including those in the healthcare and energy sectors. Learn more.
Get insights into the Lynx ransomware, which is considered the successor to the INC ransomware. This double-extortion ransomware has threatened more than 90 organizations worldwide, including those in the healthcare and energy sectors. Learn more. |
Ransomware Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-02-14 13:00:01 | Protecting Hospitals from IoT Threats with Check Point (lien direct) | >In today’s healthcare landscape, the integration of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices has revolutionized patient care. However, this technological advancement also introduces significant cyber security risks. One such threat has been highlighted by the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), which warns that Contec CMS8000 devices, widely used for patient monitoring, contain a backdoor that sends patient data to a remote IP address and could download and execute files on the device. Technical details aside, human safety is always paramount. Addressing this type of vulnerability ensures that clinicians make care decisions on accurate data, thereby ensuring patients get […]
>In today’s healthcare landscape, the integration of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices has revolutionized patient care. However, this technological advancement also introduces significant cyber security risks. One such threat has been highlighted by the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), which warns that Contec CMS8000 devices, widely used for patient monitoring, contain a backdoor that sends patient data to a remote IP address and could download and execute files on the device. Technical details aside, human safety is always paramount. Addressing this type of vulnerability ensures that clinicians make care decisions on accurate data, thereby ensuring patients get […] |
Vulnerability Threat Medical Technical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-02-13 11:15:54 | (Déjà vu) Cyble Warns of Exposed Medical Imaging, Asset Management Systems (lien direct) | > Overview
Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients warned about internet-facing medical imaging and critical infrastructure asset management systems that could be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
The report examined six ICS, operational technology (OT), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities in total, but it focused on two in particular after Cyble detected web-exposed instances of the systems.
Orthanc, Trimble Cityworks Vulnerabilities Highlighted by CISA
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued advisories alerting users to vulnerabilities in medical imaging and asset management products.
Orthanc is an open-source DICOM server used in healthcare environments for medical imaging storage and retrieval, while Trimble Cityworks is a GIS-centric asset management system used to manage all infrastructure assets for airports, utilities, municipalities, and counties.
In a February 6 ICS medical advisory, CISA said the Orthanc server prior to version 1.5.8 does not enable basic authentication by default when remote access is enabled, which could result in unauthorized access by a malicious actor. The Missing Authentication for Critical Function vulnerability, CVE-2025-0896, has been assigned a CVSS v3.1 base score of 9.8, just below the maximum score of 10.0.
Orthanc recommends that users update to the latest version or enable HTTP authentication by setting the configuration "AuthenticationEnabled": true in the configuration file.
Cyble provided a publicly accessible search query for its ODIN vulnerability search tool, which users can use to find potentially vulnerable instances.
“This flaw requires urgent attention, as Cyble researchers have identified multiple internet-facing Orthanc instances, increasing the risk of exploitation,” the Cyble report said. “The exposure of vulnerable instances could allow unauthorized access to sensitive medical data, manipulation of imaging records, or even unauthorized control over the server. Given the high stakes in healthcare cybersecurity, immediate patching to version 1.5.8 or later, along with restricting external access, is strongly recommended to mitigate potential threats.
Overview
Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients warned about internet-facing medical imaging and critical infrastructure asset management systems that could be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
The report examined six ICS, operational technology (OT), and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities in total, but it focused on two in particular after Cyble detected web-exposed instances of the systems.
Orthanc, Trimble Cityworks Vulnerabilities Highlighted by CISA
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued advisories alerting users to vulnerabilities in medical imaging and asset management products.
Orthanc is an open-source DICOM server used in healthcare environments for medical imaging storage and retrieval, while Trimble Cityworks is a GIS-centric asset management system used to manage all infrastructure assets for airports, utilities, municipalities, and counties.
In a February 6 ICS medical advisory, CISA said the Orthanc server prior to version 1.5.8 does not enable basic authentication by default when remote access is enabled, which could result in unauthorized access by a malicious actor. The Missing Authentication for Critical Function vulnerability, CVE-2025-0896, has been assigned a CVSS v3.1 base score of 9.8, just below the maximum score of 10.0.
Orthanc recommends that users update to the latest version or enable HTTP authentication by setting the configuration "AuthenticationEnabled": true in the configuration file.
Cyble provided a publicly accessible search query for its ODIN vulnerability search tool, which users can use to find potentially vulnerable instances.
“This flaw requires urgent attention, as Cyble researchers have identified multiple internet-facing Orthanc instances, increasing the risk of exploitation,” the Cyble report said. “The exposure of vulnerable instances could allow unauthorized access to sensitive medical data, manipulation of imaging records, or even unauthorized control over the server. Given the high stakes in healthcare cybersecurity, immediate patching to version 1.5.8 or later, along with restricting external access, is strongly recommended to mitigate potential threats. |
Tool Vulnerability Threat Patching Industrial Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-13 00:00:00 | Beware of Romance Scams this Valentine\\'s Day (lien direct) |
As Valentine\'s day approaches, many people are looking to connect with others online. While online dating can be a great way to meet new people, it is also important to be aware of the potential dangers. Romance scams, where fraudsters use fake profiles to financially and emotionally exploit victims are becoming more common. These scammers manipulate their victims into sending money under false pretenses. They often succeed by building trusting relationships over long periods of time.
Warning signs of Romance Scams
Scammers typically gain trust by showering their target with attention and compliments before eventually asking them for money. They may claim it\'s for travel expenses, medical emergencies (typically of a child), or a business opportunity that would help to bring the relationship closer. Common red flags can include rushing the relationship, avoiding personal questions and refusing to meet in person. They may also try to move conversation off dating platforms to a less secure platform to avoid being detected as a scam. If someone you have met online asks for financial help, it\'s a major warning sign.
How to protect yourself
Use trusted dating websites with strong security measures
Keep personal details private and be cautious when sharing information
Never send money or provide financial assistance to someone that you haven\'t met in person.
Be careful with your webcams, as scammers often try to exploit video recordings as ransom.
Trust your instincts - if something feels off, it probably is.
At CyberSkills, We\'re committed to helping people stay safe online. This Valentine\'s Day, protect both your heart and your security and stay safe!
An Garda Síochána. (2025). Beware of Romance Scams. Retrieved from https://www.garda.ie/en/crime/fraud/am-i-a-victim-of-a-romance-scam-.html
As Valentine\'s day approaches, many people are looking to connect with others online. While online dating can be a great way to meet new people, it is also important to be aware of the potential dangers. Romance scams, where fraudsters use fake profiles to financially and emotionally exploit victims are becoming more common. These scammers manipulate their victims into sending money under false pretenses. They often succeed by building trusting relationships over long periods of time. Warning signs of Romance Scams Scammers typically gain trust by showering their target with attention and compliments before eventually asking them for money. They may claim it\'s for travel expenses, medical emergencies (typically of a child), or a business opportunity that would help to bring the relationship closer. Common red flags can include rushing the relationship, avoiding personal questions and refusing to meet in person. They may also try to move conversation off dating platforms to a less secure platform to avoid being detected as a scam. If someone you have met online asks for financial help, it\'s a major warning sign. How to protect yourself Use trusted dating websites with strong security measures Keep personal details private and be cautious when sharing information Never send money or provide financial assistance to someone that you haven\'t met in person. Be careful with your webcams, as scammers often try to exploit video recordings as ransom. Trust your instincts - if something feels off, it probably is. At CyberSkills, We\'re committed to helping people stay safe online. This Valentine\'s Day, protect both your heart and your security and stay safe! An Garda Síochána. (2025). Beware of Romance Scams. Retrieved from https://www.garda.ie/en/crime/fraud/am-i-a-victim-of-a-romance-scam-.html |
Threat Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-12 15:00:00 | Is AI a Friend or Foe of Healthcare Security? (lien direct) | When it comes to keeping patient information safe, people empowerment is just as necessary as deploying new technologies.
When it comes to keeping patient information safe, people empowerment is just as necessary as deploying new technologies. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-11 20:00:00 | Cybercrime: A Multifaceted National Security Threat (lien direct) | Executive Summary Cybercrime makes up a majority of the malicious activity online and occupies the majority of defenders\' resources. In 2024, Mandiant Consulting responded to almost four times more intrusions conducted by financially motivated actors than state-backed intrusions. Despite this overwhelming volume, cybercrime receives much less attention from national security practitioners than the threat from state-backed groups. While the threat from state-backed hacking is rightly understood to be severe, it should not be evaluated in isolation from financially motivated intrusions. A hospital disrupted by a state-backed group using a wiper and a hospital disrupted by a financially motivated group using ransomware have the same impact on patient care. Likewise, sensitive data stolen from an organization and posted on a data leak site can be exploited by an adversary in the same way data exfiltrated in an espionage operation can be. These examples are particularly salient today, as criminals increasingly target and leak data from hospitals. Healthcare\'s share of posts on data leak sites has doubled over the past three years, even as the number of data leak sites tracked by Google Threat Intelligence Group has increased by nearly 50% year over year. The impact of these attacks mean that they must be taken seriously as a national security threat, no matter the motivation of the actors behind it. Cybercrime also facilitates state-backed hacking by allowing states to purchase cyber capabilities, or co-opt criminals to conduct state-directed operations to steal data or engage in disruption. Russia has drawn on criminal capabilities to fuel the cyber support to their war in Ukraine. GRU-linked APT44 (aka Sandworm), a unit of Russian military intelligence, has employed malware available from cybercrime communities to conduct espionage and disruptive operations in Ukraine and CIGAR (aka RomCom), a group that historically focused on cybercrime, has conducted espionage operations against the Ukrainian government since 2022. However, this is not limited to Russia. Iranian threat groups deploy ransomware to raise funds while simultaneously conducting espionage, and Chinese espionage groups often supplement their income with cybercrime. Most notably, North Korea uses state-backed groups to directly generate revenue for the regime. North Korea has heavily targeted cryptocurrencies, compromising exchanges and individual victims\' crypto wallets. Despite the overlaps in effects and collaboration with states, tackling the root causes of cybercrime requires fundamentally different solutions. Cybercrime involves collaboration between disparate groups often across borders and without respect to sovereignty. Any solution requires international cooperation by both law enforcement and intelligence agencies to track, arrest, and prosecute these criminals. Individual takedowns can have important temporary effects, but the collaborative nature of cybercrime means that the disrupted group will be quickly replaced by others offering the same service. Achieving broader success will require collaboration between countries and public and private sectors on systemic solutions such as increasing education and resilience efforts. aside_block | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Legislation Medical Cloud Technical | APT 41 APT 38 APT 29 APT 43 APT 44 | ★★★ | |
| 2025-02-11 11:23:25 | EFCC Witness Exposes Shocking Details of Cyber Terrorism and Internet Fraud Scheme (lien direct) |  Overview
In a highly anticipated trial on February 7, 2025, Rowland Turaki, a former employee of the accused, Xiao Hong Will, a Chinese national, took the stand as the first prosecution witness in the ongoing case concerning alleged cyber terrorism and internet fraud. The trial, which is being heard at the Federal High Court in Ikoyi, Lagos, is centered on Xiao Hong Will and his company, Genting International Co. Limited, both facing serious charges related to cybercrimes, identity theft, and fraud.
The witness, who was studying cybersecurity at the time, described in vivid detail how his employers instructed him to disguise himself as a woman to gain the trust of potential clients for fraudulent schemes. According to Turaki, he was employed by Genting International, a company allegedly linked to a network of cybercriminals engaged in elaborate internet fraud operations. The company is accused of using deceptive tactics, including employing Nigerian youths for identity theft and cyber-terrorism activities aimed at destabilizing Nigeria\'s constitutional structure.
The Arrest of Xiao Hong Will
Xiao Hong Will, arrested during the EFCC\'s "Eagle Flush Operation" in Lagos on December 19, 2024, is charged with a series of crimes under the Cybercrimes (Prohibition, Prevention, Etc.) Act, 2015 (As Amended, 2024). He and his company allegedly facilitated the exploitation of victims by using fraudulent identities and cryptocurrency schemes to gain financial advantage. The prosecution has charged Hong Will and Genting International with using Nigerian youths to create fake personas, potential
Overview
In a highly anticipated trial on February 7, 2025, Rowland Turaki, a former employee of the accused, Xiao Hong Will, a Chinese national, took the stand as the first prosecution witness in the ongoing case concerning alleged cyber terrorism and internet fraud. The trial, which is being heard at the Federal High Court in Ikoyi, Lagos, is centered on Xiao Hong Will and his company, Genting International Co. Limited, both facing serious charges related to cybercrimes, identity theft, and fraud.
The witness, who was studying cybersecurity at the time, described in vivid detail how his employers instructed him to disguise himself as a woman to gain the trust of potential clients for fraudulent schemes. According to Turaki, he was employed by Genting International, a company allegedly linked to a network of cybercriminals engaged in elaborate internet fraud operations. The company is accused of using deceptive tactics, including employing Nigerian youths for identity theft and cyber-terrorism activities aimed at destabilizing Nigeria\'s constitutional structure.
The Arrest of Xiao Hong Will
Xiao Hong Will, arrested during the EFCC\'s "Eagle Flush Operation" in Lagos on December 19, 2024, is charged with a series of crimes under the Cybercrimes (Prohibition, Prevention, Etc.) Act, 2015 (As Amended, 2024). He and his company allegedly facilitated the exploitation of victims by using fraudulent identities and cryptocurrency schemes to gain financial advantage. The prosecution has charged Hong Will and Genting International with using Nigerian youths to create fake personas, potential |
Threat Legislation Medical Technical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-10 13:34:05 | Cyble Warns of Patient Monitor Risk in ICS Vulnerability Report (lien direct) |  Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients included a warning about a severe vulnerability in a patient monitor that could potentially compromise patient safety.
In all, the report covered 36 ICS, operational technology (OT) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities, 31 of which affect critical manufacturing and energy systems. Ten of the 36 vulnerabilities were rated “critical” and 17 carried high-risk ratings.
Patient Monitor Vulnerability Carries a 9.8 Risk Rating
The patient monitor vulnerability, CVE-2024-12248, was one of three flaws in Contec Health CMS8000 Patient Monitors that were addressed in a January 30 advisory from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). CISA said the vulnerabilities were reported to the agency anonymously.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also issued an alert about the vulnerabilities the same day. The FDA said the flaws “may put patients at risk after being connected to the internet,” but added that the agency “is not aware of any cybersecurity incidents, injuries, or deaths related to these cybersecurity vulnerabilities at this time.”
The FDA advisory contained recommendations for patients and caregivers for mitigating the risk that included the following advice:
“If your health c
Cyble\'s weekly industrial control system (ICS) vulnerability report to clients included a warning about a severe vulnerability in a patient monitor that could potentially compromise patient safety.
In all, the report covered 36 ICS, operational technology (OT) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) vulnerabilities, 31 of which affect critical manufacturing and energy systems. Ten of the 36 vulnerabilities were rated “critical” and 17 carried high-risk ratings.
Patient Monitor Vulnerability Carries a 9.8 Risk Rating
The patient monitor vulnerability, CVE-2024-12248, was one of three flaws in Contec Health CMS8000 Patient Monitors that were addressed in a January 30 advisory from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). CISA said the vulnerabilities were reported to the agency anonymously.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also issued an alert about the vulnerabilities the same day. The FDA said the flaws “may put patients at risk after being connected to the internet,” but added that the agency “is not aware of any cybersecurity incidents, injuries, or deaths related to these cybersecurity vulnerabilities at this time.”
The FDA advisory contained recommendations for patients and caregivers for mitigating the risk that included the following advice:
“If your health c |
Tool Vulnerability Patching Industrial Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-02-07 10:55:33 | U.S. Ransomware Attacks Surge to Start 2025 (lien direct) |  Overview
According to an analysis of Cyble threat intelligence data, U.S. ransomware attacks have surged to the start of 2025, up nearly 150% from the first five weeks of 2024.
Ransomware attacks on U.S. targets have been climbing since a few organizations paid ransoms to attackers in highly publicized cases last year, making the country a more attractive target for ransomware groups.
That\'s likely the main reason for the increase. Regardless of the timeframe or changes in the most active ransomware groups, U.S. ransomware attacks have increased substantially in the last year and have been climbing steadily since the fall.
We\'ll examine the changing ransomware landscape in the U.S. and other frequently attacked countries and consider what changes may be in store as we approach 2025.
The Effect of Ransomware Payments
In the first five weeks of 2024, Cyble documented 152 ransomware attacks on U.S. targets, in line with late 2023 trends.
In the first five weeks of 2025, that number soared to 378 attacks on U.S. targets, a 149% year-over-year increase. Compared to the end of 2024, attacks are up a still significant 29% so far in 2025, up from 282 in the last five weeks of the year.
Perhaps owing to geographical proximity, Canada has also seen a significant increase in ransomware attacks, up from 14 in the year-ago period to 28 at the end of 2024, and nearly doubling again to 46 to start 2025.
Even as North American ransomware attacks have soared, the next-most attacked regions have stayed relatively stable. France, for example, had 18 attacks to start in 2024 and has seen 19 thus far in 2025 (chart below).
Overview
According to an analysis of Cyble threat intelligence data, U.S. ransomware attacks have surged to the start of 2025, up nearly 150% from the first five weeks of 2024.
Ransomware attacks on U.S. targets have been climbing since a few organizations paid ransoms to attackers in highly publicized cases last year, making the country a more attractive target for ransomware groups.
That\'s likely the main reason for the increase. Regardless of the timeframe or changes in the most active ransomware groups, U.S. ransomware attacks have increased substantially in the last year and have been climbing steadily since the fall.
We\'ll examine the changing ransomware landscape in the U.S. and other frequently attacked countries and consider what changes may be in store as we approach 2025.
The Effect of Ransomware Payments
In the first five weeks of 2024, Cyble documented 152 ransomware attacks on U.S. targets, in line with late 2023 trends.
In the first five weeks of 2025, that number soared to 378 attacks on U.S. targets, a 149% year-over-year increase. Compared to the end of 2024, attacks are up a still significant 29% so far in 2025, up from 282 in the last five weeks of the year.
Perhaps owing to geographical proximity, Canada has also seen a significant increase in ransomware attacks, up from 14 in the year-ago period to 28 at the end of 2024, and nearly doubling again to 46 to start 2025.
Even as North American ransomware attacks have soared, the next-most attacked regions have stayed relatively stable. France, for example, had 18 attacks to start in 2024 and has seen 19 thus far in 2025 (chart below).
|
Ransomware Tool Vulnerability Threat Legislation Prediction Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-06 16:03:54 | US Health-ISAC whitepaper highlights cybersecurity responsibilities in medical device lifecycle, focuses on resilience (lien direct) | The U.S. Health-ISAC published a whitepaper addressing the tasks needed to maintain the cyber resilience of medical devices...
The U.S. Health-ISAC published a whitepaper addressing the tasks needed to maintain the cyber resilience of medical devices... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-06 14:00:00 | Using capa Rules for Android Malware Detection (lien direct) | Mobile devices have become the go-to for daily tasks like online banking, healthcare management, and personal photo storage, making them prime targets for malicious actors seeking to exploit valuable information. Bad actors often turn to publishing and distributing malware via apps as a lucrative channel for generating illegal and/or unethical profits. Android takes a multi-layered approach to combating malware to help keep users safe (more later in the post), but while we continuously strengthen our defenses against malware, threat actors are persistently updating their malware to evade detection. Malware developers used to complete their entire malicious aggression using the common Android app development toolkits in Java, which is easier to detect by reversing the Java bytecode. In recent years, malware developers are increasing the use of native code to obfuscate some of the critical malware behaviors and putting their hopes on obscuration in compiled and symbol-stripped Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) files, which can be more difficult and time-consuming to reveal their true intentions. To combat these new challenges, Android Security and Privacy Team is partnering with Mandiant FLARE to extend the open-source binary analysis tool capa to analyze native ARM ELF files targeting Android. Together, we improved existing and developed new capa rules to detect capabilities observed in Android malware, used the capa rule matches to highlight the highly suspicious code in native files, and prompted Gemini with the highlighted code behaviors for summarization to enhance our review processes for faster decisions. In this blog post, we will describe how we leverage capa behavior-detection capabilities and state-of-art Gemini summarization by: Showcasing a malware sample that used various anti-analysis tricks to evade detections Explaining how our existing and new capa rules identify and highlighted those behaviors Presenting how Gemini summarizes the highlighted code for security reviews An Illegal Gambling App Under a Music App Façade Google Play Store ensures all published apps conform to local laws and regulations. This includes gambling apps, which are prohibited or require licenses in some areas. Developing and distributing illegal gambling apps in such areas can generate significant illicit profits, which sometimes is associated with organized crimes. To bypass Google Play Store\'s security-screening procedures, some gambling apps disguise themselves with harmless façades like music or casual games. These apps only reveal their gambling portals | Malware Tool Threat Mobile Medical Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-04 07:00:00 | What Is Zero Trust? (lien direct) | Zero Trust Security Model Definition With the adoption of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the traditional network perimeter no longer exists. This has created challenges for security professionals, requiring a new approach to cybersecurity. Zero Trust has emerged as a transformative security model. Let’s take a closer look into what Zero Trust is, how it works, and the benefits it offers to modern enterprises. Zero Trust Explained Gone are the days when organizations could secure their assets with firewalls and virtual private networks (VPNs) alone. Workloads now live in the cloud, users and devices are increasingly mobile, and data flows across diverse locations and applications. This shift has widened visibility gaps and exposed vulnerabilities in legacy security approaches. Traditional security models operate on implicit trust: once a user or device gains access to the network, they’re often granted broad permissions. However, this trust can be exploited by attackers, leading to data breaches and ransomware attacks. Zero Trust flips this model on its head, assuming that no user, device, or application can be trusted by default. At its core, Zero Trust is a cybersecurity philosophy and framework designed to eliminate the assumption of trust. Instead of granting blanket access based on network location or device, Zero Trust requires: 1. Rigorous Verification: Every access request is authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated. 2. Least-Privilege Access: Users, devices, and applications are given only the permissions they need—nothing more. 3. Microsegmentation: The network is divided into granular zones to minimize potential damage in case of a breach. Zero Trust isn’t a single technology but a holistic approach that relies on solutions like identity management, secure remote access, data loss prevention, and microsegmentation to create a resilient security posture. Traditional security models grant users access to the entire network, creating opportunities for lateral movement by attackers. Zero Trust redefines access by connecting users directly to the specific applications and resources they need, bypassing the network entirely. Why It Matters: Decoupling application access from network access prevents malware from spreading and ensures users can only interact with authorized resources. o Example: Instead of relying on VPNs, Zero Trust leverages secure access solutions that enforce policies based on user identity, device posture, and real-time context. Legacy firewalls and VPNs inadvertently expose applications by making them accessible through public-facing IP addresses. Zero Trust eliminates this vulnerability by concealing applications from unauthorized users. Why It Matters: Hiding application and network resources reduces the attack surface. o Example: By obfuscating internet protocol (IP) addresses and source identities, Zero Trust prevents distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and other internet-based threats. Zero Trust uses a proxy-based approach to inspect and secure traffic between users and applications. Unlike traditional passthrough firewalls, proxies provide in-depth analysis and threat detection. Why It Matters: Proxies enable granular control and visibility, ensuring secure interactions without compromising performance. o Example: A proxy can inspect encrypted traffic for malware or unauthorized data transfers, adding an extra layer of protection. Zero Trust continuously evaluates access requests based on dynamic factors such as user identity, device health, and geolocation. Access policies are enforced throughout the session, ensuring that any changes in context trigge | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Mobile Medical Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-04 03:53:17 | What Is a Security Operations Center (SOC)? (lien direct) | Data breaches continue to cost organizations millions of dollars each year, with costs rising steadily. According to IBM\'s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach has surged to $4.88 million globally, reflecting the increasing complexity and sophistication of cyberattacks. In the United States, this figure is even higher, averaging $9.8 million per breach, and the healthcare industry remains a prime target, with an average breach cost of $10 million-the highest of any sector. What Drives These Staggering Costs? Several factors contribute to these sky-high figures...
Data breaches continue to cost organizations millions of dollars each year, with costs rising steadily. According to IBM\'s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach has surged to $4.88 million globally, reflecting the increasing complexity and sophistication of cyberattacks. In the United States, this figure is even higher, averaging $9.8 million per breach, and the healthcare industry remains a prime target, with an average breach cost of $10 million-the highest of any sector. What Drives These Staggering Costs? Several factors contribute to these sky-high figures... |
Data Breach Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 21:56:28 | Your Health Information Was Compromised. Now What? (lien direct) | The healthcare industry has become increasingly reliant on technology to enhance patient care, from advanced image-guided surgery to…
The healthcare industry has become increasingly reliant on technology to enhance patient care, from advanced image-guided surgery to… |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 14:00:26 | Healthcare Cyberattacks on the Rise (lien direct) | 2024 has been a record-breaking year for cyberattacks on the healthcare sector. Hospitals and other medical facilities reported hundreds of […]
2024 has been a record-breaking year for cyberattacks on the healthcare sector. Hospitals and other medical facilities reported hundreds of […] |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 09:54:11 | (Déjà vu) 1 Million Impacted by Data Breach at Connecticut Healthcare Provider (lien direct) | >Community Health Center, Inc. says hackers stole the personal and health information of over one million individuals.
>Community Health Center, Inc. says hackers stole the personal and health information of over one million individuals. |
Data Breach Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 08:59:43 | CSA selected by American Hospital Association to boost physical security for healthcare systems (lien direct) | >Corporate Security Advisors (CSA), a management consulting firm specializing in corporate security, announced that it has been selected...
>Corporate Security Advisors (CSA), a management consulting firm specializing in corporate security, announced that it has been selected... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 03:17:11 | How the Proposed HISAA Law Could Reshape Cybersecurity Compliance (lien direct) | It\'s been a tough year for the healthcare sector. Throughout 2024, cybercriminals have unleashed a barrage of attacks on a vast number of healthcare organizations - with disconcerting levels of success. FBI research revealed that healthcare is now the US\'s most targeted industry. The attack on Change Healthcare, a United Health-owned health tech company, for example, disrupted operations at thousands of hospitals, pharmacies, and physician practices, led to the theft of up to 6TB of sensitive health data, and is thought to have affected around 100 million people. Although HIPAA regulates...
It\'s been a tough year for the healthcare sector. Throughout 2024, cybercriminals have unleashed a barrage of attacks on a vast number of healthcare organizations - with disconcerting levels of success. FBI research revealed that healthcare is now the US\'s most targeted industry. The attack on Change Healthcare, a United Health-owned health tech company, for example, disrupted operations at thousands of hospitals, pharmacies, and physician practices, led to the theft of up to 6TB of sensitive health data, and is thought to have affected around 100 million people. Although HIPAA regulates... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-02-03 02:02:06 | Medical monitoring machines spotted stealing patient data, users warned to pull the plug ASAP (lien direct) | PLUS: MGM settles breach suits; AWS doesn\'t trust you with security defaults; A new .NET backdoor; and more Infosec in brief The United States Food and Drug Administration has told medical facilities and caregivers that monitor patients using Contec equipment to disconnect the devices from the internet ASAP.…
PLUS: MGM settles breach suits; AWS doesn\'t trust you with security defaults; A new .NET backdoor; and more Infosec in brief The United States Food and Drug Administration has told medical facilities and caregivers that monitor patients using Contec equipment to disconnect the devices from the internet ASAP.… |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-31 20:00:02 | Regional healthcare systems report data breaches affecting more than 1.5 million (lien direct) | Connecticut\'s Community Health Center Inc. and California\'s NorthBay Healthcare Corporation reported intrusions that exposed the data of hundreds of thousands of patients.
Connecticut\'s Community Health Center Inc. and California\'s NorthBay Healthcare Corporation reported intrusions that exposed the data of hundreds of thousands of patients. |
Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-31 08:18:29 | US healthcare provider data breach impacts 1 million patients (lien direct) | Community Health Center (CHC), a leading Connecticut healthcare provider, is notifying over 1 million patients that their personal and health information was stolen in an October breach. [...]
Community Health Center (CHC), a leading Connecticut healthcare provider, is notifying over 1 million patients that their personal and health information was stolen in an October breach. [...] |
Data Breach Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-31 07:50:23 | Dark Web Activity January 2025: A New Hacktivist Group Emerges (lien direct) | > Overview
Cyble dark web researchers investigated more than 250 dark web claims by threat actors in January 2025, with more than a quarter of those targeting U.S.-based organizations.
Of threat actors (TAs) on the dark web targeting U.S. organizations during the month, 15 were ransomware groups claiming successful attacks or selling data from those attacks.
Ransomware group claims accounted for about 40% of the Cyble investigations. Most of the investigations examined threat actors claiming to be selling data stolen from organizations, or selling access to those organizations\' networks.
Several investigations focused on cyberattacks orchestrated by hacktivist groups – including a new Russian threat group identified here for the first time.
\'Sector 16\' Teams Up With Russian Hacktivists Z-Pentest
New on the scene is a group calling itself “Sector 16,” which teamed with Z-Pentest – a threat group profiled by Cyble last month – in an attack on a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system managing oil pumps and storage tanks in Texas. The groups shared a video showcasing the system interface, revealing real-time data on tank levels, pump pressures, casing pressures, and alarm management features.
Both groups put their logos on the video, suggesting a close alliance between the two (image below).
Overview
Cyble dark web researchers investigated more than 250 dark web claims by threat actors in January 2025, with more than a quarter of those targeting U.S.-based organizations.
Of threat actors (TAs) on the dark web targeting U.S. organizations during the month, 15 were ransomware groups claiming successful attacks or selling data from those attacks.
Ransomware group claims accounted for about 40% of the Cyble investigations. Most of the investigations examined threat actors claiming to be selling data stolen from organizations, or selling access to those organizations\' networks.
Several investigations focused on cyberattacks orchestrated by hacktivist groups – including a new Russian threat group identified here for the first time.
\'Sector 16\' Teams Up With Russian Hacktivists Z-Pentest
New on the scene is a group calling itself “Sector 16,” which teamed with Z-Pentest – a threat group profiled by Cyble last month – in an attack on a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system managing oil pumps and storage tanks in Texas. The groups shared a video showcasing the system interface, revealing real-time data on tank levels, pump pressures, casing pressures, and alarm management features.
Both groups put their logos on the video, suggesting a close alliance between the two (image below).
 Sector 16 also claimed responsibility for unauthorized access to the control systems of a U.S. oil and gas production facility, releasing a video purportedly demonstrating their access to the facility\'s operational data and systems. The video reveals control interfaces associated with the monitoring and management of critical infrastructure. Displayed systems include shutdown management, production monitoring, tank level readings, gas lift operations, and Lease Automatic Custody Transfer (LACT) data, all critical components in the facility\'s operations. Additionally, they were also able to access valve control interfaces, pressure monitoring, and flow measurement data, highlighting the potential extent of access.
Russian hacktivist groups have posted several videos of their members tampering with critical infrastructure control panels in recent months, perhaps more to establish credibility or threaten than to inflict actual damage, although in one case, Z-Pentest claimed to disrupt a U.S. o
Sector 16 also claimed responsibility for unauthorized access to the control systems of a U.S. oil and gas production facility, releasing a video purportedly demonstrating their access to the facility\'s operational data and systems. The video reveals control interfaces associated with the monitoring and management of critical infrastructure. Displayed systems include shutdown management, production monitoring, tank level readings, gas lift operations, and Lease Automatic Custody Transfer (LACT) data, all critical components in the facility\'s operations. Additionally, they were also able to access valve control interfaces, pressure monitoring, and flow measurement data, highlighting the potential extent of access.
Russian hacktivist groups have posted several videos of their members tampering with critical infrastructure control panels in recent months, perhaps more to establish credibility or threaten than to inflict actual damage, although in one case, Z-Pentest claimed to disrupt a U.S. o |
Ransomware Tool Threat Legislation Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-31 07:00:00 | Living with AI: The Future We Once Imagined (lien direct) | Living with AI: The Future We Once Imagined Smartphones, smart homes, and virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri have seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. Yet, many of us rarely stop to think about the technology behind them. We enjoy the convenience these devices offer, but behind the scenes, artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the way we live, work, and interact with the world. At first glance, AI-related terms like machine learning, neural networks, and natural language processing might seem complex and almost like learning a new language. However, as AI becomes more common, understanding these concepts is becoming essential. But what exactly is AI, and how is it making an impact? Breaking Down AI Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence—such as problem-solving, pattern recognition, learning from experience, and making decisions. AI works by processing information similarly to the human brain. Machine Learning (ML): A branch of AI where computers learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed for every task. Deep Learning: A more advanced form of machine learning that mimics the human brain’s structure to recognize patterns and make predictions. Natural Language Processing (NLP): The technology that enables computers to understand and respond to human language—powering tools like chatbots and virtual assistants. Think about WALL-E from Disney or R2-D2 from Star Wars. WALL-E demonstrates how AI-powered robots can assist humans while developing unique personalities. R2-D2, on the other hand, serves as a problem-solver, working alongside people to navigate challenges. These fictional characters reflect AI’s potential—enhancing our lives in both practical and creative ways. AI in Action: How It’s Changing Society AI is no longer just a futuristic concept, it’s actively improving various aspects of life today: Revolutionizing Healthcare AI assists doctors by improving surgical precision and analyzing medical tests faster. Robots enable remote healthcare, allowing patients to receive treatment from home. AI-powered medical imaging helps detect diseases earlier, leading to better outcomes. Supporting Senior Citizens AI-powered assistants help older adults by reminding them to take medication, assisting with household tasks, and even providing companionship. Enhancing Education AI is personalizing learning, allowing students to study at their own pace. Teachers use AI-powered tools to grade assignments and provide instant feedback. Looking Ahead AI is becoming as essential to daily life as email or the internet. Just as WALL-E and R2-D2 helped the characters around them, AI is designed to assist humans—not replace them. By understanding these technologies, we can better prepare for a future where AI plays an even greater role in shaping our world. Key AI Concepts to Know Artificial Intelligence (AI): Computers performing human-like tasks. Machine Learning (ML): AI systems that improve through experience. Deep Learning: A type of ML using brain-inspired models. Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI’s ability to understand and process human language. Robotics: Machines equipped with AI to perform various tasks. AI isn’t just for scientists or tech experts, it’s for everyone. From healthcare and education to entertainment and everyday convenience, AI is woven into modern life. By learning the basics, we can better understand its growing influence and how it continues to shape our future. | Tool Studies Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-30 22:51:23 | Healthcare Sector Charts 2 More Ransomware Attacks (lien direct) | No ransomware groups have yet to claim responsibility for either attack, and both institutions have yet to reveal what may have been stolen.
No ransomware groups have yet to claim responsibility for either attack, and both institutions have yet to reveal what may have been stolen. |
Ransomware Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-30 12:00:00 | Frederick Health Hit by Ransomware Attack (lien direct) | >Maryland healthcare provider Frederick Health has taken some of its systems offline in response to a ransomware attack.
>Maryland healthcare provider Frederick Health has taken some of its systems offline in response to a ransomware attack. |
Ransomware Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-30 08:54:57 | HTTP Client Tools Exploitation for Account Takeover Attacks (lien direct) | Key takeaways According to Proofpoint findings, 78% of Microsoft 365 tenants were targeted at least once by an account takeover attempt utilizing a distinct HTTP client. Most HTTP-based cloud attacks utilize brute force methods, resulting in low success rates. Proofpoint researchers found that a recent campaign using the unique HTTP client Axios had an especially high success rate, compromising 43% of targeted user accounts. Proofpoint researchers identified a brute force campaign, distinguished by its high velocity and distributed access attempts, utilizing the Node Fetch client. Overview HTTP client tools are software applications or libraries used to send HTTP requests and receive HTTP responses from web servers. These tools allow users to craft requests with various HTTP methods (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), customize headers, include payloads, and inspect server responses. Proofpoint has observed a rising trend of attackers repurposing legitimate HTTP client tools, such as those emulating XMLHttpRequest and Node.js HTTP requests, to compromise Microsoft 365 environments. Originally sourced from public repositories like GitHub, these tools are increasingly used in attacks like Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) and brute force techniques, leading to numerous account takeover (ATO) incidents. This blog explores the historical and current use of HTTP clients in ATO attack chains, shedding light on the evolving tactics of threat actors. Historical trends In February 2018, Proofpoint researchers identified a widespread malicious campaign targeting thousands of organizations worldwide, leveraging an uncommon OkHttp client version (\'okhttp/3.2.0\') to target Microsoft 365 environments. Using dedicated hosting services in Canada and the U.S., the attacker consistently launched unauthorized access attempts for nearly four years, focusing on high-value targets such as C-level executives and privileged users. According to Proofpoint research, much of the targeted users\' data seems to have come from breaches like the 2016 LinkedIn credentials leak, enabling attackers to launch sizeable attacks against thousands of organizations. In addition, further analysis revealed that these OkHttp-based activities were just the initial stage of a sophisticated attack chain. It turned out that threat actors employed user enumeration methods to identify valid email addresses before executing other threat vectors, such as spear phishing and password spraying. This technique generated high volumes of login attempts, mostly aimed at nonexistent accounts. By 2021, the campaign peaked with tens of thousands of attacks monthly but significantly declined by late 2021, signaling a shift in attackers\' tactics. Current trends Since 2018, HTTP clients remain widely used in ATO attacks. According to Proofpoint threat researchers, early 2024 saw OkHttp variants dominate, but by March 2024, a broader range of HTTP clients gained traction. Moreover, in terms of scale, the second half of 2024 saw 78% of organizations experience at least one ATO attempt involving an HTTP client, a 7% increase from the prior six months. During this time, newly observed HTTP clients, like \'python-request,\' were being integrated into brute force attack chains, significantly increasing threat volume and diversity. In May 2024, these attacks peaked, leveraging millions of hijacked residential IPs to target cloud accounts. ATO attacks leveraging HTTP clients by volume of affected user-accounts (JAN – DEC 2024). In fact, most HTTP-based ATO attacks are brute force attempts with low success rates. However, Proofpoint investigated more effective threats, such as a recent campaign using the Axios HTTP client, which combines precision targeting with Adversary-in-the-Middle (AitM) techniques. This approach achieved a monthly average success rate of 38% when trying to compromise user accounts, by effectively overcoming modern security measu | Spam Malware Tool Threat Prediction Medical Cloud Technical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-30 08:19:22 | Australia\\'s CI-ISAC secures $6.4 million government grant; set to bolster cyber resilience in healthcare (lien direct) | The CI-ISAC Australia has been awarded a $6.4 million grant from the Australian government to establish a dedicated...
The CI-ISAC Australia has been awarded a $6.4 million grant from the Australian government to establish a dedicated... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 16:00:00 | How Interlock Ransomware Infects Healthcare Organizations (lien direct) | Ransomware attacks have reached an unprecedented scale in the healthcare sector, exposing vulnerabilities that put millions at risk. Recently, UnitedHealth revealed that 190 million Americans had their personal and healthcare data stolen during the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, a figure that nearly doubles the previously disclosed total.
This breach shows just how deeply ransomware
Ransomware attacks have reached an unprecedented scale in the healthcare sector, exposing vulnerabilities that put millions at risk. Recently, UnitedHealth revealed that 190 million Americans had their personal and healthcare data stolen during the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, a figure that nearly doubles the previously disclosed total. This breach shows just how deeply ransomware |
Ransomware Vulnerability Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 15:11:50 | Maryland healthcare network forced to shut down IT systems after ransomware attack (lien direct) | Frederick Health Medical Group, which operates a hospital and other healthcare facilities northwest of Baltimore and Washington, D.C., took systems offline in response to a ransomware attack.
Frederick Health Medical Group, which operates a hospital and other healthcare facilities northwest of Baltimore and Washington, D.C., took systems offline in response to a ransomware attack. |
Ransomware Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 14:00:30 | IoMT Security Is Critical as Patients Take Control of Own Healthcare (lien direct) | >IoMT devices were not created with cybersecurity at the forefront, a robust security strategy can alleviate attack concerns for organizations and patients.
>IoMT devices were not created with cybersecurity at the forefront, a robust security strategy can alleviate attack concerns for organizations and patients. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 10:38:59 | Australia\\'s Health Sector Receives $6.4 Million Cybersecurity Boost with New Threat Information-Sharing Network (lien direct) | > The Australian Government has awarded a $6.4 million grant to CI-ISAC Australia, enabling the establishment of a new Health Cyber Sharing Network (HCSN). This initiative is designed to facilitate the rapid exchange of critical cyber threat information within Australia\'s healthcare industry, which has become a target for cyberattacks.
The recent surge in cyberattacks on Australian healthcare organizations, including hospitals and health insurance providers, has highlighted the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. In response, the Australian Government has made healthcare the priority sector for its formal funding efforts.
This grant is part of a broader strategy to address the vulnerabilities in the nation\'s health sector and ensure it is better equipped to handle the cyber threats faced by the industry.
A Growing Threat: The Cost of Cybersecurity Breaches
The healthcare industry globally has been facing increasing cybersecurity challenges, and Australia is no exception. According to reports from 2023, the global healthcare sector continues to experience the most expensive data breaches across industries for the 13th consecutive year. The average cost of a healthcare data breach was a staggering AUD$10.93 million, nearly double that of the financial industry, which recorded an average cost of $5.9 million.
Australia\'s health sector, which encompasses a diverse range of organizations, from public and private hospitals to medical clinics and insurance providers, is increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. This sector includes approximately 750 government hospitals, 650 private hospitals, and over 6,500 general practitioner clinics, along with numerous third-party suppliers and vendors.
The creation of the HCSN aims to address these risks by providing a secure, collaborative platform for information sharing. The network will enable health sector organizations to work together more effectively, breaking down silos and improving the speed and quality of cybersecurity threat information exchange.
The Role of CI-ISAC and the Health Cyber-Sharing Network
CI-ISAC Australia, the recipient of the $6.4 million Australian Government grant, will spearhead the creation and management of the Health Cyber Sharing Network. The HCSN will focus on fostering collaboration between Australian healthcare organizations, ensuring they can share relevant
The Australian Government has awarded a $6.4 million grant to CI-ISAC Australia, enabling the establishment of a new Health Cyber Sharing Network (HCSN). This initiative is designed to facilitate the rapid exchange of critical cyber threat information within Australia\'s healthcare industry, which has become a target for cyberattacks.
The recent surge in cyberattacks on Australian healthcare organizations, including hospitals and health insurance providers, has highlighted the pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. In response, the Australian Government has made healthcare the priority sector for its formal funding efforts.
This grant is part of a broader strategy to address the vulnerabilities in the nation\'s health sector and ensure it is better equipped to handle the cyber threats faced by the industry.
A Growing Threat: The Cost of Cybersecurity Breaches
The healthcare industry globally has been facing increasing cybersecurity challenges, and Australia is no exception. According to reports from 2023, the global healthcare sector continues to experience the most expensive data breaches across industries for the 13th consecutive year. The average cost of a healthcare data breach was a staggering AUD$10.93 million, nearly double that of the financial industry, which recorded an average cost of $5.9 million.
Australia\'s health sector, which encompasses a diverse range of organizations, from public and private hospitals to medical clinics and insurance providers, is increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats. This sector includes approximately 750 government hospitals, 650 private hospitals, and over 6,500 general practitioner clinics, along with numerous third-party suppliers and vendors.
The creation of the HCSN aims to address these risks by providing a secure, collaborative platform for information sharing. The network will enable health sector organizations to work together more effectively, breaking down silos and improving the speed and quality of cybersecurity threat information exchange.
The Role of CI-ISAC and the Health Cyber-Sharing Network
CI-ISAC Australia, the recipient of the $6.4 million Australian Government grant, will spearhead the creation and management of the Health Cyber Sharing Network. The HCSN will focus on fostering collaboration between Australian healthcare organizations, ensuring they can share relevant |
Data Breach Vulnerability Threat Medical Cloud | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 08:15:23 | CISA flags hardware vulnerabilities in ICS and medical devices; affects B&R, Schneider Electric, Rockwell, BD Systems (lien direct) | The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released six industrial control systems (ICS) advisories and updated an...
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released six industrial control systems (ICS) advisories and updated an... |
Vulnerability Industrial Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-29 06:42:08 | A Guide for Insider Risk Teams: 10 Tips for Monitoring User Activity While Protecting Privacy (lien direct) | As security teams, we often face a tough dilemma: how can we monitor users for risky activity without compromising their privacy? It\'s a delicate balance. There\'s a fine line between ensuring security while also respecting the confidentiality of sensitive employee data. However, achieving this balance isn\'t only possible, it\'s essential. It must be part of any insider risk program for it to be both trustworthy and effective. In honor of Data Privacy Week, in this blog post I\'ll walk you through 10 best practices to help you build a robust insider risk program that meets both your data privacy and security needs. 1: Involve privacy and legal stakeholders early From the very beginning, you should invite the right people to the table. During the program\'s design phase, reach out to privacy councils or worker councils to get them involved. This will ensure that important privacy aspects are addressed right from the start. These councils can offer invaluable insights into the ethical and legal considerations that must be taken into account. Once involved, keep these stakeholders close throughout the journey. Regular updates about the program\'s goals, scope and processes will help foster trust between security teams and privacy advocates. In fact, demonstrating that privacy has been top of mind all along, the insider risk team will equally be the face of privacy advocacy. Example If you\'re rolling out an insider risk management program, involve your privacy officer in the planning stages. This will ensure that your program is compliant with GDPR and other data protection regulations. When privacy concerns are addressed proactively, personally identifiable information (PII) won\'t be used in ways that could lead to violations. 2: Define program scope and reporting thresholds One of the most critical components of any insider risk program is clear boundaries. Define what constitutes risky activity, which is typically aligned to existing conduct, compliance or security policies. It is also important to clearly define what behaviors result in a certain risk level as well as at which point risky behaviors require a deeper inquiry or investigation. Not only does this help reduce the likelihood of overreach, but it also ensures that monitoring stays proportionate to the risk. Keep in mind that although organizational policies are defined and shared broadly, thresholds and detection capabilities should only be shared with those with a need-to know. Example Let\'s say your program detects users downloading large amounts of sensitive data. Set a threshold that only triggers an alert when someone downloads more than their typical number of files. Other thresholds might be when they are considered a flight risk or when they are circumventing a security control. This keeps the scope narrow, and it provides a much lower possibility that an analyst will review innocuous behavior. There\'s never a complete guarantee that this won\'t happen in the world of risk mitigation. However, that is why implementing the next eight best practices is so critical. 3: Be transparent, but guide the message thoughtfully In many organizations, the insider risk program is often shrouded in mystery. Unfortunately, this can breed rumors and distrust. Avoid this issue by communicating transparently and proactively where you can. Doing so sends a clear message that the program aligns with your organization\'s goals and its core values. It\'s also crucial to share stores about your program\'s positive impact. And make sure to remind everyone about privacy mechanisms that are in place as well as the overall purpose of your program. Transparency helps demystify the process and reassures employees that their privacy is being respected. While transparency is important, so is discretion. The details about triggered alerts and investigation details should not be shared beyond designated groups. This will ensure that your program isn\'t undermined and prevent people from circumventing controls. Example When your program starts t | Tool Threat Studies Medical Technical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-28 11:37:09 | BT urges UK critical national infrastructure sector to ditch outdated copper network by 2025 for better digital resilience (lien direct) | BT is calling on the U.K.\'s critical national infrastructure (CNI) providers – including sectors such as healthcare, water,...
BT is calling on the U.K.\'s critical national infrastructure (CNI) providers – including sectors such as healthcare, water,... |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-28 09:37:55 | phpMyAdmin 5.2.2 Addresses Critical XSS and Library Vulnerabilities (lien direct) | > Overview
phpMyAdmin, a popular web-based tool for managing MySQL and MariaDB databases, has recently released version 5.2.2, addressing multiple vulnerabilities that posed a medium severity risk. This widely-used tool is a basis for database administrators, offering strong features and ease of use. However, the vulnerabilities discovered could potentially expose users to risks such as unauthorized actions, session hijacking, and data theft.
The update resolves two cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-24530 and CVE-2025-24529) and a potential issue in the glibc/iconv library (CVE-2024-2961). These vulnerabilities underline the importance of staying up to date with security patches to safeguard sensitive data and ensure secure database management.
According to the advisory:
Reported By: The vulnerability was reported by a security researcher identified as "bluebird."
Severity: Moderate.
Solution: Users are encouraged to upgrade to version 5.2.2 or apply the patch.
Vulnerability Details
Three significant vulnerabilities were identified in phpMyAdmin versions prior to 5.2.2:
1. CVE-2025-24530: XSS in “Check Tables”
Description: This XSS vulnerability allows an attacker to exploit the "Check Tables" feature by crafting a malicious table name. This could result in injecting malicious scripts into the application.
Impact: Successful exploitation could lead to session hijacking, data theft, and unauthorized actions.
CWE ID: CWE-661 (Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation).
Fix: This issue was resolved through commit a45efd0eb9415240480adeefc587158c766bc4a0.
2. CVE-2025-24529: XSS in “Insert”
Description: This vulnerability involves the "Insert" functionality, which could be manipulated to execute malicious scripts.
Impact: Exploitation could compromise user accounts and sensitive data by injecting malicious code into user
Overview
phpMyAdmin, a popular web-based tool for managing MySQL and MariaDB databases, has recently released version 5.2.2, addressing multiple vulnerabilities that posed a medium severity risk. This widely-used tool is a basis for database administrators, offering strong features and ease of use. However, the vulnerabilities discovered could potentially expose users to risks such as unauthorized actions, session hijacking, and data theft.
The update resolves two cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-24530 and CVE-2025-24529) and a potential issue in the glibc/iconv library (CVE-2024-2961). These vulnerabilities underline the importance of staying up to date with security patches to safeguard sensitive data and ensure secure database management.
According to the advisory:
Reported By: The vulnerability was reported by a security researcher identified as "bluebird."
Severity: Moderate.
Solution: Users are encouraged to upgrade to version 5.2.2 or apply the patch.
Vulnerability Details
Three significant vulnerabilities were identified in phpMyAdmin versions prior to 5.2.2:
1. CVE-2025-24530: XSS in “Check Tables”
Description: This XSS vulnerability allows an attacker to exploit the "Check Tables" feature by crafting a malicious table name. This could result in injecting malicious scripts into the application.
Impact: Successful exploitation could lead to session hijacking, data theft, and unauthorized actions.
CWE ID: CWE-661 (Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation).
Fix: This issue was resolved through commit a45efd0eb9415240480adeefc587158c766bc4a0.
2. CVE-2025-24529: XSS in “Insert”
Description: This vulnerability involves the "Insert" functionality, which could be manipulated to execute malicious scripts.
Impact: Exploitation could compromise user accounts and sensitive data by injecting malicious code into user |
Tool Vulnerability Threat Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-27 22:15:23 | Change Healthcare Breach Impact Doubles to 190M People (lien direct) | One of the largest data breaches in history was apparently twice as impactful as previously thought, with PII belonging to hundreds of millions of people sitting in the hands of cybercriminals.
One of the largest data breaches in history was apparently twice as impactful as previously thought, with PII belonging to hundreds of millions of people sitting in the hands of cybercriminals. |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-27 18:09:00 | [27 January] (lien direct) | Welcome to your weekly cybersecurity scoop! Ever thought about how the same AI meant to protect our hospitals could also compromise them? This week, we\'re breaking down the sophisticated world of AI-driven threats, key updates in regulations, and some urgent vulnerabilities in healthcare tech that need our attention.
As we unpack these complex topics, we\'ll equip you with sharp insights to
Welcome to your weekly cybersecurity scoop! Ever thought about how the same AI meant to protect our hospitals could also compromise them? This week, we\'re breaking down the sophisticated world of AI-driven threats, key updates in regulations, and some urgent vulnerabilities in healthcare tech that need our attention. As we unpack these complex topics, we\'ll equip you with sharp insights to |
Tool Vulnerability Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-27 11:26:55 | Change Healthcare Data Breach Impact Grows to 190 Million Individuals (lien direct) | >The impact of the Change Healthcare ransomware-caused data breach has increased from 100 million to 190 million individuals.
>The impact of the Change Healthcare ransomware-caused data breach has increased from 100 million to 190 million individuals. |
Data Breach Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-27 10:15:00 | Change Healthcare Breach Almost Doubles in Size to 190 Million Victims (lien direct) | Change Healthcare has claimed 190 million customers were affected by a mega-breach last year
Change Healthcare has claimed 190 million customers were affected by a mega-breach last year |
Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-27 01:19:44 | Cybersecurity Stop of the Month: E-Signature Phishing Nearly Sparks Disaster for an Electric Company (lien direct) | The Cybersecurity Stop of the Month blog series explores the ever-evolving tactics of today\'s cybercriminals and how Proofpoint helps organizations better fortify their email defenses to protect people against today\'s emerging threats. Phishing remains the No. 1 tactic that cybercriminals use to target your people and steal valuable data and funds. According to Verizon, phishing is the top method that attackers use to gain unauthorized access, and it continues to evolve in both frequency and sophistication. This trend is not just alarming-it\'s costly. IBM estimates the average data breach that originates with phishing causes a staggering $4.88 million in damages. In this post, we\'ll analyze a new and complex e-signature phishing threat. In it, attackers combine several novel tactics to get around native Microsoft email security. Background In an e-signature phishing attack, bad actors will spoof a trusted brand and send malicious content through legitimate digital channels. Often, they use advanced methods like adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) to bypass multifactor authentication (MFA) in an effort to further extend their access. And when bad actors use combined tactics, such as Adversary-in-the-Middle plus geofencing, they can be extremely successful in evading detection. Let\'s look at e-signature phishing attacks in more depth: Impersonating trusted brands Threat actors leverage brands and services of trusted electronic signature services, such as DocuSign or Adobe Sign. They use them to trick recipients into directly downloading malicious documents or visiting fake websites where they enter their login credentials. Of the billions of phishing emails that Proofpoint sees each year, our 2024 State of the Phish report shows that 3.5M malicious messages abused DocuSign branding. Bypassing MFA Attackers that use e-signature phishing lures frequently seek more than just credentials. They also aim to intercept MFA codes or steal session cookies. Adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) tactics use proxy sites to capture login details and MFA codes in real-time. This grants attackers access to the victim\'s account and any active session cookies which can, in turn, unlock other websites. Steps in the adversary-in-the-middle threat technique. Geofencing access Threat actors use geofencing techniques to limit from where their targets can access their phishing sites or malicious content. By restricting access to specific geographic locations, such as the target\'s region or country, they reduce the likelihood of detection by IT teams and automated security scanning tools based in other regions. Deploying just one of these tactics can be enough to convince your people to take action. But what happens when a savvy scammer uses all three? The scenario Our recent example shows how combining the methods above enabled a threat actor to successfully target a global electric company. The threat actor\'s intended victim supplies power to one of the world\'s largest cities and employs more than 15K people. In this attack, the offending message was delivered to the mailbox of a C-suite executive. It bypassed Microsoft security tools as well as additional detection meant to stop such multi-stage campaigns. Thankfully, Proofpoint caught this threat and helped secure the company from a possible cyberattack or data breach. The named threat actor launching this threat was first observed by Proofpoint in 2021. They are known for using delivery mechanisms like multistep redirection chains, advanced filtering and highly customized lures. Frequent targets include the manufacturing, technology and energy industries. While they often spoof brands like Microsoft OneDrive and LinkedIn, in this e-signature-based phishing attack they chose popular digital transaction management platform, DocuSign. The threat: How did the attack happen? Here\'s how the attack unfolded: 1. Setting a lure. The attack started with an email that spoofed DocuSign\'s brand to appear as a legitimate follow up notice. It offered the recipient | Data Breach Malware Tool Threat Prediction Medical Cloud | ★★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-26 11:29:17 | UnitedHealth now says 190 million impacted by 2024 data breach (lien direct) | UnitedHealth has revealed that 190 million Americans had their personal and healthcare data stolen in the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, nearly doubling the previously disclosed figure. [...]
UnitedHealth has revealed that 190 million Americans had their personal and healthcare data stolen in the Change Healthcare ransomware attack, nearly doubling the previously disclosed figure. [...] |
Ransomware Data Breach Medical | ★★★ | ||
| 2025-01-25 17:05:12 | UnitedHealth Group\\'s Massive Data Breach Impacts 190 Million Americans (lien direct) | UnitedHealth Group has confirmed that a ransomware attack targeted its subsidiary, Change Healthcare, in February 2024, impacting 190…
UnitedHealth Group has confirmed that a ransomware attack targeted its subsidiary, Change Healthcare, in February 2024, impacting 190… |
Ransomware Data Breach Medical | ★★ | ||
| 2025-01-25 12:52:12 | UnitedHealth updates number of data breach victims to 190 million (lien direct) | The 2024 ransomware attack on Change Healthcare exposed the data of about 190 million people, according to an update from parent company UnitedHealth Group.
The 2024 ransomware attack on Change Healthcare exposed the data of about 190 million people, according to an update from parent company UnitedHealth Group. |
Ransomware Data Breach Medical | ★★ |
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
