What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2022-08-24 12:34:00 | WannaCry explained: A perfect ransomware storm (lien direct) | What is WannaCry? WannaCry is a ransomware worm that spread rapidly through across a number of computer networks in May of 2017. After infecting a Windows computer, it encrypts files on the PC's hard drive, making them impossible for users to access, then demands a ransom payment in bitcoin in order to decrypt them.A number of factors made the initial spread of WannaCry particularly noteworthy: it struck a number of important and high-profile systems, including many in Britain's National Health Service; it exploited a Windows vulnerability that was suspected to have been first discovered by the United States National Security Agency; and it was tentatively linked by Symantec and other security researchers to the Lazarus Group, a cybercrime organization that may be connected to the North Korean government.To read this article in full, please click here | Ransomware Vulnerability Medical | Wannacry Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2022-07-07 08:14:35 | North Korean State-Sponsored Threat Actors Deploying "MAUI" Ransomware (lien direct) | Today, the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) and the Department of Treasury released a joint Cybersecurity Advisory on Maui Ransomware, which is attributed to state sponsored activity by the government of North Korea. The Joint CSA provides detailed insight on the various TTPs used by the threat actors behind Maui, which has targeted the Health and Public Health Sector.How Serious of an Issue is This?High. As ransomware activity causes downtime, theft of confidential and personally identifiable information (PII) and other significant impact to operations, it is important to ensure that various security measures are in place, like being up to date with patching vulnerable machines/infrastructure. Also, ensuring employees are trained and up to date on various social engineering attempts and tactics used by threat actors will be a first line of defense against such attacks.What is Maui Ransomware?Maui ransomware is unique in a way that it requires manual execution to start the encryption routine. Maui also features a CLI (command line interface) that is used by the threat actor to target specific files to encrypt. Maui also has the ability to identify previously encrypted files due to customer headers containing the original path of the file.Who are HIDDEN COBRA/LAZARUS/APT38/BeagleBoyz?HIDDEN COBRA also known as Lazarus/APT38/BeagleBoyz has been atributed to the government of North Korea. Also, they have been linked to multiple high-profile, financially-motivated attacks in various parts of the world - some of which have caused massive infrastructure disruptions. Notable attacks include the 2014 attack on a major entertainment company and a 2016 Bangladeshi financial institution heist that almost netted nearly $1 Billion (USD) for the attackers. Had it not been for a misspelling in an instruction that caused a bank to flag and block thirty transactions, HIDDEN COBRA would have pulled off a heist unlike any other. Although HIDDEN COBRA failed in their attempt, they were still able to net around 81 million dollars in total.The most recent notable attack attributed to HIDDEN COBRA was the Wannacry Ransomware attack, which resulted in massive disruption and damage worldwide to numerous organizations, especially those in manufacturing. Various estimates of the impact were in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with some estimates claiming billions. Other verticals which this group has targeted include critical infrastructures, entertainment, finance, healthcare, and telecommunication sectors across multiple countries.Who are the BeagleBoyz?The BeagleBoyz group is a newly identified group that is a subset of activity by the threat actors known as HIDDEN COBRA/LAZARUS/APT 38 and has been observed committing financial crimes, specifically cryptocurrency related thefts. Further information about the BeagleBoyz can be found here.What Operating Systems are Affected?Windows based operating systems are affected.What is the Status of Coverage?Fortinet customers running the latest definitions are protected against Maui with the following (AV) signatures:W32/Ransom_Win32_MAUICRYPT.YACC5W32/Agent.C5C2!trW32/PossibleThreatAnything Else to Note?Victims of ransomware are cautioned against paying ransoms by such organizations as CISA, NCSC, the FBI, and HHS. Payment does not guarantee files will be recovered. It may also embolden adversaries to target additional organizations, encourage other criminal actors to engage in the distribution of ransomware, and/or fund illicit activities which could potentially be illegal according to a U.S. Department of Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) advisory. | Ransomware Threat Patching Medical | Wannacry Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2021-04-27 17:24:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: HabitsRAT Targeting Linux and Windows Servers, Lazarus Group Targetting South Korean Orgs, Multiple Zero-Days and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: APT, Android Malware, RATs, Phishing, QLocker Ransomware and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Zero-day Vulnerabilities in SonicWall Email Security Actively Exploited
(published: April 21, 2021)
US cybersecurity company SonicWall said fixes have been published to resolve three critical issues in its email security solution that are being actively exploited in the wild. The vulnerabilities are tracked as CVE-2021-20021, CVE-2021-20022, and CVE-2021-20023, impacting SonicWall ES/Hosted Email Security (HES) versions 10.0.1 and above.
Analyst Comment: The patches for these vulnerabilities have been issued and should be applied as soon as possible to avoid potential malicious behaviour. SonicWall’s security notice can be found here https://www.sonicwall.com/support/product-notification/security-notice-sonicwall-email-security-zero-day-vulnerabilities/210416112932360/. It is important that your company has patch-maintenance policies in place. Once a vulnerability has been publicly reported,, threat actors will likely attempt to incorporate the exploitation of the vulnerability into their malicious operations. Patches should be reviewed and applied as soon as possible to prevent potential malicious activity.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote File Copy - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] File and Directory Discovery - T1083
Tags: CVE-2021-20021, CVE-2021-20023, CVE-2021-20022
Massive Qlocker Ransomware Attack Uses 7zip to Encrypt QNAP Devices
(published: April 21, 2021)
The ransomware is called Qlocker and began targeting QNAP devices on April 19th, 2021. All victims are told to pay 0.01 Bitcoins, which is approximately $557.74, to get a password for their archived files. While the files are being locked, the Resource Monitor will display numerous '7z' processes which are the 7zip command-line executable.
Analyst Comment: Attackers are using legitimate tools like 7zip to evade detections by traditional antiviruses. EDR solutions can help tracking suspicious command line arguments and process creations to potentially detect such attacks. Customers should use backup solutions to be able recover encrypted files.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials in Files - T1081
Tags: Tor, Qlocker, CVE-2020-2509, CVE-2020-36195
Novel Email-Based Campaign Targets Bloomberg Clients with RATs
(published: April 21, 2021)
A new e-mail-based campaign by an emerging threat actor aims to spread various remote access trojans (RATs) to a very specific group of targets who use Bloomberg's industry-based services. Attacks start in the form of targeted emails to c
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
Zero-day Vulnerabilities in SonicWall Email Security Actively Exploited
(published: April 21, 2021)
US cybersecurity company SonicWall said fixes have been published to resolve three critical issues in its email security solution that are being actively exploited in the wild. The vulnerabilities are tracked as CVE-2021-20021, CVE-2021-20022, and CVE-2021-20023, impacting SonicWall ES/Hosted Email Security (HES) versions 10.0.1 and above.
Analyst Comment: The patches for these vulnerabilities have been issued and should be applied as soon as possible to avoid potential malicious behaviour. SonicWall’s security notice can be found here https://www.sonicwall.com/support/product-notification/security-notice-sonicwall-email-security-zero-day-vulnerabilities/210416112932360/. It is important that your company has patch-maintenance policies in place. Once a vulnerability has been publicly reported,, threat actors will likely attempt to incorporate the exploitation of the vulnerability into their malicious operations. Patches should be reviewed and applied as soon as possible to prevent potential malicious activity.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Remote File Copy - T1105 | [MITRE ATT&CK] File and Directory Discovery - T1083
Tags: CVE-2021-20021, CVE-2021-20023, CVE-2021-20022
Massive Qlocker Ransomware Attack Uses 7zip to Encrypt QNAP Devices
(published: April 21, 2021)
The ransomware is called Qlocker and began targeting QNAP devices on April 19th, 2021. All victims are told to pay 0.01 Bitcoins, which is approximately $557.74, to get a password for their archived files. While the files are being locked, the Resource Monitor will display numerous '7z' processes which are the 7zip command-line executable.
Analyst Comment: Attackers are using legitimate tools like 7zip to evade detections by traditional antiviruses. EDR solutions can help tracking suspicious command line arguments and process creations to potentially detect such attacks. Customers should use backup solutions to be able recover encrypted files.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Credentials in Files - T1081
Tags: Tor, Qlocker, CVE-2020-2509, CVE-2020-36195
Novel Email-Based Campaign Targets Bloomberg Clients with RATs
(published: April 21, 2021)
A new e-mail-based campaign by an emerging threat actor aims to spread various remote access trojans (RATs) to a very specific group of targets who use Bloomberg's industry-based services. Attacks start in the form of targeted emails to c |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Medical | Wannacry Wannacry APT 38 APT 28 | ||
| 2019-03-12 16:27:00 | The Advanced Persistent Threat files: Lazarus Group (lien direct) |
 Lazarus Group, the threat actors likely behind the Sony breach and WannaCry outbreak, are in the news again. Here's what you need to know about this North Korean organization, and what you should do to protect against such nation-state attacks.
Categories:
Criminals
Threat analysis
Tags: APTLazarusNorth Korea
(Read more...)
Lazarus Group, the threat actors likely behind the Sony breach and WannaCry outbreak, are in the news again. Here's what you need to know about this North Korean organization, and what you should do to protect against such nation-state attacks.
Categories:
Criminals
Threat analysis
Tags: APTLazarusNorth Korea
(Read more...)
|
Threat Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2018-09-06 21:43:04 | How US authorities tracked down the North Korean hacker behind WannaCry (lien direct) | US authorities put together four years worth of malware samples, domain names, email and social media accounts to track down one of the Lazarus Group hackers. | Malware Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2018-03-29 22:25:24 | WannaCry after one year (lien direct) | In the news, Boeing (an aircraft maker) has been "targeted by a WannaCry virus attack". Phrased this way, it's implausible. There are no new attacks targeting people with WannaCry. There is either no WannaCry, or it's simply a continuation of the attack from a year ago.It's possible what happened is that an anti-virus product called a new virus "WannaCry". Virus families are often related, and sometimes a distant relative gets called the same thing. I know this watching the way various anti-virus products label my own software, which isn't a virus, but which virus writers often include with their own stuff. The Lazarus group, which is believed to be responsible for WannaCry, have whole virus families like this. Thus, just because an AV product claims you are infected with WannaCry doesn't mean it's the same thing that everyone else is calling WannaCry.Famously, WannaCry was the first virus/ransomware/worm that used the NSA ETERNALBLUE exploit. Other viruses have since added the exploit, and of course, hackers use it when attacking systems. It may be that a network intrusion detection system detected ETERNALBLUE, which people then assumed was due to WannaCry. It may actually have been an nPetya infection instead (nPetya was the second major virus/worm/ransomware to use the exploit).Or it could be the real WannaCry, but it's probably not a new "attack" that "targets" Boeing. Instead, it's likely a continuation from WannaCry's first appearance. WannaCry is a worm, which means it spreads automatically after it was launched, for years, without anybody in control. Infected machines still exist, unnoticed by their owners, attacking random machines on the Internet. If you plug in an unpatched computer onto the raw Internet, without the benefit of a firewall, it'll get infected within an hour.However, the Boeing manufacturing systems that were infected were not on the Internet, so what happened? The narrative from the news stories imply some nefarious hacker activity that "targeted" Boeing, but that's unlikely.We have now have over 15 years of experience with network worms getting into strange places disconnected and even "air gapped" from the Internet. The most common reason is laptops. Somebody takes their laptop to some place like an airport WiFi network, and gets infected. They put their laptop to sleep, then wake it again when they reach their destination, and plug it into the manufacturing network. At this point, the virus spreads and infects everything. This is especially the case with maintenance/support engineers, who often have specialized software they use to control manufacturing machines, for which they have a reason to connect to the local network even if it doesn't have useful access to the Internet. A single engineer may act as a sort of Typhoid Mary, going from customer to customer, infecting each in turn whenever they open their laptop.Another cause for infection is virtual machines. A common practice is to take "snapshots" of live machines and save them to backups. Should the virtual machine crash, instead of rebooting it, it's simply restored from the backed up running image. If that backup image is infected, then bringing it out of sleep will allow the worm to start spreading.Jake Williams claims he's seen three other manufacturing networks infected with WannaCry. Why does manufacturing seem more susceptible? The reason appears to be the "killswitch" that stops WannaCry from running elsewhere. The killswitch uses a DNS lookup, stopping itself if it can resolve a certain domain. Manufacturing networks are largely disconnected from the Internet enough that such DNS lookups don't work, so the domain can't be found, so the killswitch doesn't work. Thus, manufacturing systems are no more likely to get infected, but the lack of killswitch means the virus will conti | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-10-16 22:32:36 | Taiwan Heist: Lazarus Tools and Ransomware (lien direct) | Written by Sergei Shevchenko, Hirman Muhammad bin Abu Bakar, and James WongBACKGROUNDReports emerged just over a week ago of a new cyber-enabled bank heist in Asia. Attackers targeting Far Eastern International Bank (FEIB), a commercial firm in Taiwan, moved funds from its accounts to multiple overseas beneficiaries. In a story which reminds us of the Bangladesh Bank case – the culprits had compromised the bank's system connected to the SWIFT network and used this to perform the transfers. In recent days, various malware samples have been uploaded to malware repositories which appear to originate from the intrusion. These include both known Lazarus group tools, as well as a rare ransomware variant called 'Hermes' which may have been used as a distraction or cover-up for the security team whilst the heist was occurring. The timeline below provides an overview of the key events: 01 October 2017  Malware compiled containing admin credentials for the FEIB network. 03 October 2017 Malware compiled containing admin credentials for the FEIB network. 03 October 2017  Transfers using MT103 messages were sent from FEIB to Cambodia, the US and Sri Lanka. Messages to cover the funds for the payments were incorrectly created and sent. 03 October 2017 Transfers using MT103 messages were sent from FEIB to Cambodia, the US and Sri Lanka. Messages to cover the funds for the payments were incorrectly created and sent. 03 October 2017  Breach discovered and ransomware uploaded to online malware repository site. 04 October 2017 Breach discovered and ransomware uploaded to online malware repository site. 04 October 2017  Individual in Sri Lanka cashes out a reported Rs30m (~$195,000). 06 October 2017 Individual in Sri Lanka cashes out a reported Rs30m (~$195,000). 06 October 2017  |
Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-06-21 11:47:47 | WannaCryptor attack \'may have come from Lazarus group\' (lien direct) | Experts in the UK and the US have reportedly claimed that the recent global WannaCryptor ransomware attack was initiated by the North Korean Lazarus Group. | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-06-14 04:00:00 | Video: North Korean hacking group has been hitting the US since 2009 (lien direct) | Hidden Cobra, a North Korean-backed hacking group, may also be responsible for WannaCry and the Sony Pictures hack. | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ★★★★ | |
| 2017-05-31 07:33:02 | Analysis of Competing Hypotheses, WCry and Lazarus (ACH part 2), (Wed, May 31st) (lien direct) | Introduction In my previous diary, I did a very brief introduction on what the ACH method is [1], so that now all readers, also those who had never seen it before, can have a common basic understanding of it. One more thing I have not mentioned yet is how the scores are calculated. There are three different algorithms: an Inconsistency Counting algorithm, a Weighted Inconsistency Counting algorithm, and a Normalized algorithm [2]. The Weighted Inconsistency Counting algorithm, the one used in todays examples, builds on the Inconsistency algorithm, but also factors in weights of credibility and relevance values. For each item of evidence, a consistency entry of I width:300px" /> Today, I will apply ACH to a recent quite known case: WCry attribution. There has been lots of analyses and speculations around it, lately several sources in the InfoSec community tied WCry strongly to Lazarus Group [3][4][5][6], while some others provided motivation for being skeptical about such attribution [7]. Therefore, it is a perfect case to show the use of ACH: several different hypotheses, facts, evidences and assumptions. Digital Shadows WCry ACH analysis About two weeks ago, Digital Shadows published a very well done post on ACH applied to WCry attribution [8]. Regarding possible attribution to Lazarus though, as stated on their post, At the time of writing, however, we assessed there to be insufficient evidence to corroborate this claim of attribution to this group, and alternative hypotheses should be considered. Therefore among the hypotheses considered is missing one specifically for Lazarus in place of a more generic nation state or state affiliate actor. The following are the four different hypotheses considered by Digital Shadows: A sophisticated financially-motivated cybercriminal actor - H1 An unsophisticated financially-motivated cybercriminal actor - H2 A nation state or state-affiliated actor conducting a disruptive operation - H3 A nation state or state-affiliated actor aiming to discredit the National Security Agency (NSA) width:600px" /> Given the final scores computed, they have assessed that though by no means definitive, a WannaCry campaign launched by an unsophisticated cybercriminal actor was the most plausible scenario based on the information that is currently available. Just one note on my side, from my calculation seems they have made a mistake, and H2 score should be -2.121 rather than -1.414. This does not change the final result, but brings H2 and H3 way closer. My WCry ACH Analysis Although the Digital Shadows analysis was a very good one, I felt something was missing, both on the hypotheses as well as on the evidences side. Particularly, in my opinion, I would add three more hypotheses. When thinking about NSA being the final target of this, other than A nation state or state-affiliated actor aiming to discredit the NSA, I think that it should be considered also a (generic/unattributed) TA aiming at unveiling/exposing the extent of possible NSA network of compromised machines (H5). This is something one would expect from a hacktivist maybe, although it seems to be way more sophisticated than what hacktivist have got us used to. One difference with the H4 could be on the lack of supporting media narrative. While if one wants to discredit NSA would be ready to have a supporting media narrative, if the goal was simply to unveil and show to everyone the potential extent of NSA infected machines, the infection as it was would have been sufficient, given also the abundant media coverage it got. Although this may still be seen as too close to H4 to be a different hypothesis, I still do see a case for it. | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-05-29 11:10:00 | Linguistic Analysis Suggests WannaCry Hackers Could be From Southern China (lien direct) | It's been almost four weeks since the outcry of WannaCry ransomware, but the hackers behind the self-spread ransomware threat have not been identified yet.
However, two weeks ago researchers at Google, Kaspersky Lab, Intezer and Symantec linked WannaCry to 'Lazarus Group,' a state-sponsored hacking group believed to work for the North Korean government.
Now, new research from dark web
|
Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-05-19 13:00:19 | Threatpost News Wrap, May 19, 2017 (lien direct) | Mike Mimoso and Chris Brook discuss WannaCry, Microsoft's response, the killswitches, a potential link with Lazarus Group, and what the future holds for the ShadowBrokers. | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-05-17 06:50:12 | 3 Security Firms Say WannaCry Ransomware Shares Code with North Korean Malware (lien direct) | While initially, we thought this would be a silly and unsubstantiated discovery, the number of security firms claiming they've identified and confirmed connections between the WannaCry ransomware and malware used by the Lazarus Group has now gone up to three. [...] | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-05-17 03:33:55 | WanaCrypt0r Ransomworm (lien direct) | Written by Sergei Shevchenko and Adrian NishBACKGROUNDSince the release of the ETERNALBLUE exploit by 'The Shadow Brokers' last month security researchers have been watching for a mass attack on global networks. This came on Friday 12th May when it was bundled with ransomware called WanaCrypt0r and let loose. Initial reports of attacks were highlighted by Telefonica in Spain but the malware quickly spread to networks in the UK where the National Health Service (NHS) was impacted, followed by many other networks across the world.The infographic below illustrates the key components of the WanaCrypt0r ransomware. This is described in further detail in subsequent sections of this report along with initial clues on attribution.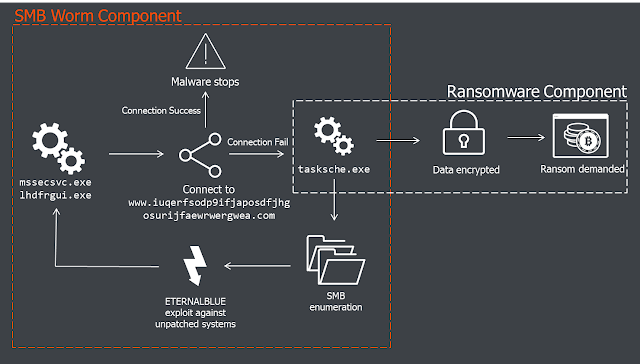 ANALYSIS: Initial VectorThe initial infection vector is still unknown. Reports by some of phishing emails have been dismissed by other researchers as relevant only to a different (unrelated) ransomware campaign, called Jaff.There is also a working theory that initial compromise may have come from SMB shares exposed to the public internet. Results from Shodan show over 1.5 million devices with port 445 open – the attacker could have infected those shares directly.The Dropper/WormThe infection starts from a 3.6Mb executable file named mssecsvc.exe or lhdfrgui.exe. Depending on how it's executed, it can function as a dropper or as a worm.When run, the executable first checks if it can connect to the following URL:http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea[.]com The connection is checked with the WinINet functions, shown below: 01 qmemcpy(&szUrl, 02 "http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea[.]com", 03 57u); 04 h1 = InternetOpenA(0,&nbs ANALYSIS: Initial VectorThe initial infection vector is still unknown. Reports by some of phishing emails have been dismissed by other researchers as relevant only to a different (unrelated) ransomware campaign, called Jaff.There is also a working theory that initial compromise may have come from SMB shares exposed to the public internet. Results from Shodan show over 1.5 million devices with port 445 open – the attacker could have infected those shares directly.The Dropper/WormThe infection starts from a 3.6Mb executable file named mssecsvc.exe or lhdfrgui.exe. Depending on how it's executed, it can function as a dropper or as a worm.When run, the executable first checks if it can connect to the following URL:http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea[.]com The connection is checked with the WinINet functions, shown below: 01 qmemcpy(&szUrl, 02 "http://www.iuqerfsodp9ifjaposdfjhgosurijfaewrwergwea[.]com", 03 57u); 04 h1 = InternetOpenA(0,&nbs |
Guideline Medical | Wannacry APT 38 | ||
| 2017-05-16 10:39:48 | WannaCry ransomware cyber-attack \'may have N Korea link\' (lien direct) | You may not have heard of the Lazarus Group, but you may be aware of its work. The devastating hack on Sony Pictures in 2014, and another on a Bangladeshi bank in 2016, have both been attributed to the highly sophisticated group. It is widely believed that the Lazarus Group worked out of China, but on behalf ... | Medical | Wannacry APT 38 |
1
We have: 15 articles.
We have: 15 articles.
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
